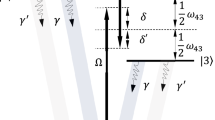
Abstract
In the coherently trapped populations of a four-level atom, we demonstrated the quantum beats with different mechanism, which originate from the interference between transition channels with different dipole moments. The beat frequency is determined by the intrinsic atomic parameters, i.e., the spacing of upper levels and ratio of dipole moments. The resonant plasmonic nanoantenna, as a candidate for the creation of anisotropic vacuum, was proposed to achieve the nanoscale realization of the quantum beats, spontaneous emission cancellation, and Rabi oscillation in two-photon correlations through the enhanced near-field and modified decay rates.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu S, Scully MO (1996) Spectral line elimination and spontaneous emission cancellation via quantum interference. Phys Rev Lett 76:388–341
Lee H, Polynkin P, Scully MO, Zhu SY (1997) Quenching of spontaneous emission via quantum interference. Phys Rev A 55:4454–4465
Paspalakis E, Knight PL (1998) Phase control of spontaneous emission. Phys Rev Lett 81:293–296
Paspalakis E, Kylstra NJ, Knight PL (1999) Transparency induced via decay interference. Phys Rev Lett 82:2079–2082
Zhou P, Swain S (1999) Phase-dependent spectra in a driven two-level atom. Phys Rev Lett 82:2500–2503
Agarwal GS (2000) Anisotropic vacuum-induced interference in decay channels. Phys Rev Lett 84:5500–5503
Zhu SY, Chen H, Huang H (1997) Quantum interference effects in spontaneous emission from an atom embedded in a photonic band gap structure. Phys Rev Lett 79:205–208
Quang T, Woldeyohannes M, John S, Agarwal GS (1997) Coherent control of spontaneous emission near a photonic band edge: a single-atom optical memory device. Phys Rev Lett 79:5238–5241
Yang Y, Xu J, Chen H, Zhu SY (2008) Quantum interference enhancement with left-handed materials. Phys Rev Lett 100:043601
Yannopapas V, Paspalakis E, Vitanov NV (2009) Plasmon-induced enhancement of quantum interference near metallic nanostructures. Phys Rev Lett 103:063602
Brongersma ML, Shalaev VM (2010) Applied physics. The case for plasmonics. Science 328:440–441
Chang DE, Sorensen AS, Hemmer PR, Lukin MD (2006) Quantum optics with surface plasmons. Phys Rev Lett 97:053002
Ozel T et al (2008) Selective enhancement of surface-state emission and simultaneous quenching of interband transition in white-luminophor CdS nanocrystals using localized plasmon coupling. New J Phys 10:083035
Gu Y, Huang L, Martin OJF, Gong QH (2010) Resonance fluorescence of single molecules assisted by a plasmonic structure. Phys Rev B 81:193103
Marty R, Arbouet A, Paillard V, Girard C, ColasdesFrancs G (2010) Photon antibunching in the optical near field. Phys Rev B 82:081403(R)
Hendrickson SM, Lai MM, Pittman TB, Franson JD (2010) Observation of two-photon absorption at low power levels using tapered optical fibers in rubidium vapor. Phys Rev Lett 105:173602
Lakowicz JR (2006) Plasmonics in biology and plasmon-controlled fluorescence. Plasmonics 1:5–33
Lange W, Mlynek J (1978) Quantum beats in transmission by time-resolved polarization spectroscopy. Phys Rev Lett 40:1373–1376
Mühlschlegel P et al (2005) Resonant optical antennas. Science 308:1607–1609
Scully MO, Zubairy MS (1997) Quantum optics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Novotny L, Hecht B (2006) Principles of nano-optics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Barnett SM et al (1996) Decay of excited atoms in absorbing dielectrics. J Phys B 29:3763–3781
Li G, Li F, Zhu SY (2001) Quantum interference between decay channels of a three-level atom in a multilayer dielectric medium. Phys Rev A 64:013819
Gu Y et al (2008) Resonance capacity of surface plasmon on subwavelength metallic structures. EPL 83:27004
Martin OJF, Girard C, Dereux A (1995) Generalized field propagator for electromagnetic scattering and light confinement. Phys Rev Lett 74:526–529
Dulkeith E et al (2002) Fluorescence quenching of dye molecules near gold nanoparticles: radiative and nonradiative effects. Phys Rev Lett 89:203002
Ye J, Vernooy DM, Kimble HJ (1999) Trapping of single atoms in cavity QED. Phys Rev Lett 83:4987–4990
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants No. 10874004 and 10821062 and the National Key Basic Research Program under Grant No. 2007CB307001. We would like to thank Professors Xiaoyong Hu, Gaoxiang Li, and Jie Zhang for their helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, Y., Wang, L., Ren, P. et al. Intrinsic Quantum Beats of Atomic Populations and Their Nanoscale Realization Through Resonant Plasmonic Antenna. Plasmonics 7, 33–38 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-011-9272-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-011-9272-x