Abstract
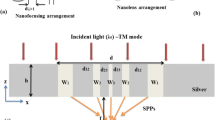
Conventionally, plasmonic lenses introduce a phase delay distribution across their surfaces by modulating the dimensions of nanostructures within a metal film. However, there is very limited modulation of the phase delay due to the small dependence of the mode propagation constant on the structure dimensions. In this paper, a novel design of plasmonic zone plate lenses (PZPL) with both slit width and refractive index modulation is proposed to enable integrating more slits in a fixed lens aperture with the extended phase delay range and, therefore, greatly enhance the performance of the devices. More than three-time enhancement of the light intensity at the focus is achieved compared to the structure with only slit width modulation. Like a conventional immersion system, a PZPL embedded in a dielectric is found to have a further improved focusing performance, where light is focused down to a 0.44λ spot using a PZPL with an aperture of 12λ and a focal length of 6λ. Dispersive light-focusing behaviour is also analysed and the modulation of the focal length by colour has a potential application in stacked image sensors and multi-dimensional optical data storage.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee B, Kim S, Kim H, Lim Y (2010) Prog Quant Electron 34:47–87
Fu Y, Zhou X (2010) Plasmonics 5:287–310
Sun Z (2006) Appl Phys Lett 89:261119
Xu T, Wang C, Du C, Luo X (2008) Opt Express 16:4753–4759
Verslegers L, Catrysse PB, Yu Z, Fan S (2009) Appl Phys Lett 95:071112
Sun Z, Kim HK (2004) Appl Phys Lett 85:642–644
Shi H, Wang C, Du C, Luo X, Dong X, Gao H (2005) Opt Express 13:6815–6820
Verslegers L, Catrysse PB, Yu Z, White JS, Barnard ES, Brongersma ML, Fan S (2009) Nano Lett 9:235–238
Fu Y, Liu Y, Zhou X, Xu Z, Fang F (2010) Opt Express 18:3438–3443
Fu Y, Zhou X, Zhu S (2010) Plasmonics 5:111–116
Lin L, Goh XM, McGuinness LP, Roberts A (2010) Nano Lett 10:1936–1940
Chen Q, Cumming DRS (2010) Opt Express 18:14788–14793
Chen Q (2010) Plasmonics 5 doi:10.1007/s11468-010-9171-6
Grbic A, Jiang L, Merlin R (2008) Science 320:511–513
Eleftheriades GV, Wong AMH (2008) IEEE Microw Wirel Compon Lett 18:236–238
Gordon R (2009) Phys Rev Lett 102:207402-1–207402-4
Gordon R, Brolo AG (2005) Opt Express 13:1933–1938
Lumerical FDTD Solutions, http://www.lumerical.com/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q. A Novel Plasmonic Zone Plate Lens Based on Nano-Slits with Refractive Index Modulation. Plasmonics 6, 381–385 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-011-9214-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-011-9214-7