Abstract
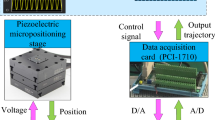
In this paper, a novel rate-dependent Prandtl-Ishlinskii (P-I) model is proposed to characterize the rate-dependent hysteresis nonlinearity of piezoelectric actuators. The new model is based on a modified rate-dependent play operator, in which a dynamic envelope function is introduced to replace the input function of the classical play operator. Moreover, a dynamic density function is utilized in the proposed P-I model. The parameters of the proposed model are identified by a modified particle swarm optimization algorithm. Finally, experiments are conducted on a piezo-actuated nanopositioning stage to validate the proposed P-I model under the sinusoidal inputs. The experimental results show that the developed rate-dependent P-I model precisely characterize the rate-dependent hysteresis loops up to 1000 Hz.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salapaka S, Salapaka M. Scanning probe microscopy. IEEE Control Systems, 2008, 28(2): 65–83
Leang K, Devasia S. Design of hysteresis-compensating iterative learning control for piezo-positioners: Application to atomic force microscopes. Mechatronics, 2006, 16(3–4): 141–158
Qin Y, Shirinzadeh B, Tian Y, et al. Design issues in a decoupled XY stage: Static and dynamics modeling, hysteresis compensation, and tracking control. Sensors and Actuators. A, Physical, 2013, 194: 95–105
Gawthrop P, Bhikkaji B, Moheimani S. Physical-model-based control of a piezoelectric tube for nano-scale positioning applications. Mechatronics, 2010, 20(1): 74–84
Yang M, Gu G, Zhu L. High-bandwidth tracking control of piezo-actuated nanopositioning stages using closed-loop input shaper. Mechatronics, 2014, 24(6): 724–733
Iamail M, Ikhouane F, Rodellar J. The hysteresis Bouc-Wen model, a survey. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2009, 16(2): 161–188
Xu Q, Li Y. Dahl model-based hysteresis compensation and precise positioning control of an XY parallel micromanipulator with piezoelectric actuation. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2010, 132(4): 041011
Hu H, Ben Mrad R. On the classical Preisach model for hysteresis in piezoceramic actuators. Mechatronics, 2003, 13(2): 85–94
Kuhnen K. Modeling, identification and compensation of complex hysteretic nonlinearities: A modified Prandtl-Ishlinskii approach. European Journal of Control, 2003, 9(4): 407–418
Gu G, Yang M, Zhu L. Real-time inverse hysteresis compensation of piezoelectric actuators with a modified Prandtl-Ishlinskii model. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2012, 83(6): 065106
Gu G, Zhu L, Su C. Modeling and compensation of asymmetric hysteresis nonlinearity for piezoceramic actuators with a modified Prandtl-Ishlinskii model. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(3): 1583–1595
Liu S, Su C. A note on the properties of a generalized Prandtl-Ishlinskii model. Smart Materials and Structures, 2011, 20(8): 087003
Ang W, Khosla P, Riviere C. Feedforward controller with inverse rate-dependent model for piezoelectric actuators in trajectory-tracking applications. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2007, 12(2): 134–142
Tan U X, Latt W T, Widjaja F, et al. Tracking control of hysteretic piezoelectric actuator using adaptive rate-dependent controller. Sensors and Actuators. A, Physical, 2009, 150(1): 116–123
Janaideh M, Su C, Rakheja S. Development of the rate-dependent Prandtl-Ishlinskii model for smart actuators. Smart Materials and Structures, 2008, 17(3): 035026
Janaideh M, Krejc P. Inverse rate-dependent Prandtl-Ishlinskii model for feedforward compensation of hysteresis in a piezo-micropositioning actuator. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2013, 18(5): 1498–1507
Zhang G, Zhang C, Gu J. Modeling and control of rate-dependent hysteresis in piezoelectric actuators. In: Proceedings of the 32nd Chinese Control Conference (CCC). IEEE, 2013, 1929–1934
Janocha H, Kuhnen K. Real-time compensation of hysteresis and creep in piezoelectric actuators. Sensors and Actuators, 2000, 79(2): 83–89
Yang M, Gu G, Zhu L. Parameter identification of the generalized Prandtl-Ishlinskii model for piezoelectric actuators using modified particle swarm optimization. Sensors and Actuators. A, Physical, 2013, 189: 254–265
Li C, Gu G, Yang M, et al. Design, analysis and testing of a parallel-kinematic high-bandwidth XY nanopositioning stage. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2013, 84(12): 125111
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Li, C., Gu, G. et al. A rate-dependent Prandtl-Ishlinskii model for piezoelectric actuators using the dynamic envelope function based play operator. Front. Mech. Eng. 10, 37–42 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-015-0326-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-015-0326-1