Abstract
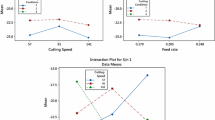
This paper describes the development of multi response optimization technique using utility method to predict and select the optimal setting of machining parameters in wire electro-discharge machining (WEDM) process. The experimental studies in WEDM process were conducted under varying experimental conditions of process parameters, such as pulse on time(T on), pulse off time(T off), peak current (IP), wire feed (WF), wire tension (WT) and servo voltage (SV) using pure titanium as work material. Experiments were planned using Taguchi’s L27 orthogonal array. Multi response optimization was performed for both cutting speed (CS) and surface roughness (SR) using utility concept to find out the optimal process parameter setting. The level of significance of the machining parameters for their effect on the CS and SR was determined by using analysis of variance (ANOVA). Finally, confirmation experiment was performed to validate the effectiveness of the proposed optimal condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kahles J F, Field M, Eylon D, Froes F H. Grindability of titanium alloys. Journal of Materials, 1985, 37: 27–35
Myers J R, Bomberger H B, Froes F J. Corrosion behavior and use of titanium and its alloys. J ournal of Materials, 1984, 36(10): 50–60
Ezugwu E O, Bonney J, Yamane Y. An overview of machinability of aeroengine alloys. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 134(2): 233–253
Hong H, Riga A T, Gahoon J M, Scott C G. Machinability of steel and titanium alloys under lubrication. Wear, 1993, 162–164: 34–39
Konig W. Effect of drill geometry of uncoated tool when drilling titanium. In: proceedings of 47th Meeting of AGARD Structural and Materials Panel, Florence, 1979, 1–10
Dearnley P A, Grearson A N. Evaluation of principal wear mechanisms of cemented carbides and ceramics used for machining titanium alloy IMI 318. Materials Science and Technology, 1986, 2(1): 47–58
Hartung P D, Kramer B M, von Turkovich B F. Tool wear in machining Titanium. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 1982, 31(1): 75–80
Tosun N, Cogun C, Tosun G. A study on kerf and material removal rate in wire electrical discharge machining based on Taguchi method. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2004, 152(3): 316–322
Mahapatra S S, Patnaik A. Parametric optimization of wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process using Taguchi method. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 2006, 28(4): 422–429
Liao Y S, Huang J T, Su H C. A study on the machining-parameters optimization of wire electrical discharge machining. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1997, 71(3): 487–493
Han F Z, Jiang J, Yu D W. Influence of machining parameters on surface roughness in finish cut of WEDM. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2007, 34(5–6): 538–546
Kanlayasiri K, Boonmung S. Effects of wire-EDM machining variables on surface roughness of newly developed DC 53 die steel: Design of experiments and regression model. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 192–193: 459–464
Ramakrishnan R, Karunamoorthy L. Modeling and multi-response optimization of Inconel 718 on machining of CNC WEDM process. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008, 207(1–3): 343–349
Gökler M İ, Ozanözgü AM. Experimental investigation of effects of cutting parameters on surface roughness in the WEDM process. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2000, 40(13): 1831–1848
Tosun N, Cogun C. An investigation on wire wear in WEDM. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 134(3): 273–278
Prohaszka J, Mamalis A G, Vaxevanidis N M. The effect of electrode material on machinability in wire electro-discharge machining. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1997, 69(1–3): 233–237
Balasubramanian G, Ganapathy S. Grey relational analysis to determine optimum process parameters for wire electro discharge machining (WEDM). International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 2011, 3(1): 95–101
Lin J L, Lin C L. The use of the orthogonal array with grey relational analysis to optimize the electrical discharge machining process with multiple performance characteristics. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2002, 42(2): 237–244
Jangra K, Jain A, Grover S. Optimization of multiple-machining characteristics in wire electrical discharge machining of punching die using grey relational analysis. Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research, 2010, 69(8): 606–612
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chalisgaonkar, R., Kumar, J. Optimization of WEDM process of pure titanium with multiple performance characteristics using Taguchi’s DOE approach and utility concept. Front. Mech. Eng. 8, 201–214 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-013-0256-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-013-0256-8