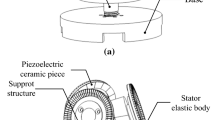
Abstract
Based on the principle of alternative operation of two bending vibration modes in an annular stator, this paper presents a standing-wave stepping ultrasonic motor characterized by no accumulative errors driven by an open-loop control circuitry. The driving forces are generated from the motions of projections on the stator in two modes. The positioning of the motor is achieved by the cooperation between the stator projections and rotor teeth, and the number of the rotors determines the stepping angle of the motor. Two-phase sinusoidal signals corresponding to the two modal frequencies drive the motor bi-direction stepping rotation via a switch unit. The prototype runs steadily without miss-step on trial. The single-step angle displacement of the motor is 2.5°.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao C S. Ultrasonic motor techniques in the 21st century. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2000, 20(1): 7–12 (in Chinese)
Uchino K. Piezoelectric ultrasonic motors: overview. Smart Mater Struct, 1998, (7): 273–285
Zhang Tiemin, Zhao Chunsheng. Comments on servo control over ultrasonic motors. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2001, 21(3): 203–208 (in Chinese)
Snitka V. Stepping ultrasonic motors for precision positioning. In: Proceedings of IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium. Baltimore, MD, USA: Springer, 1993, 449–452
Yun C H, Ishii T, Nakamura K, et al. A high power ultrasonic linear motor with a longitudinal-bending hybrid transducer for high-speed and precise drive of a heavy stage. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium. Atlanta, GA, USA: Springer, 2001: 537–540
Senjyu T, Kashigawi T, Uezato K. Position control of ultrasonic motors using MRAC and dead-zone compensation with fuzzy inference. IEEE Trans Power Electr, 2002, 17(2): 265–272
Yasuhide K, Tetsuya K, Shigeo Y. Robust speed control of ultrasonic motor based on H-infinity control with repetitive compensator. JSME International Journal, 1999, Series C, 42(4): 884–890
Kandare G, Wallaschek J. Deviaton and validation of a mathematical model for traveling-wave ultrasonic motors. Smart Mater Struct, 2002, (11): 565–574
Lin F J, Wai R J, Hong C M. LLCC resonant inverter for piezoelectric ultrasonic motor drive. In: IEEE Proc Electr Power. Budapest, Hungary: Springer, 1999, 146(5): 479–487
Miyazawa O. Drive control unit for an ultrasonic step motor. US Patent, 5229678, 1993-07-20
Kusakabe C, Takehiro T, Tomikawa Y. Driving and controlling of a watch device ultrasonic motor by two phase pulse signals. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1991, 30(2): 206–208
Wang Guiqin. Study on self-correction ultrasonic motor using standing wave. Dissertaion for the Master Degree. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 1999 (in Chinese)
Chen Y, Zhou T Y, Zhang Q, et al. A study on the friction of a self-correction ultrasonic stepping motor. Ultrasonics, 2002, (39): 667–671
Jin Yong, Ji Feng, Ji Kehui. Stepping-positioning control of ultrasonic motor. Mechanical & Electrical Engineering Magazine, 2003, 20(6): 25–29 (in Chinese)
Chu Xiangcheng, Xing Zengping, Li Longtu, et al. High resolution miniaturized stepper ultrasonic motor using differential composite motion. Ultrasonics, 2004, 41(9): 737–741
Jin Jiamei, Zhao Chunsheng. Distortion and rotation of vibrational shape in the stator rings of ultrasonic motors. Piezoelectectrics & Acoustooptics 2007, 29(3): 354–355 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2006, 38(5): 600–604 [译自: 南京航空航天大学学报]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, J., Zhao, C. Bi-modes alternation stepping ultrasonic motors. Front. Mech. Eng. China 3, 101–105 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-008-0018-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-008-0018-1