Abstract
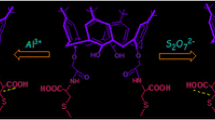
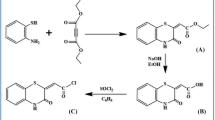
A novel calix[4]arene-based fluorescent chemosensor bearing a 2-aminopyridine moiety and a naphthalenic fluorophore was synthesized The chemical structure of the product was elucidated by FT-IR, MS-FAB, NMR and elemental analyses. Then, the properties and identification mechanism of the synthesized chemosensor were investigated. The results show that the chemosensor exhibits selective fluorescent quenching in the presence of aromatic organic acid in acetonitrile solution, and that the binding ability of the chemosensor with organic acid is in the order of p-cyanic-benzyl acid > p-chloric-benzyl acid > p-methoxyl-benzyl acid > benzyl acid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steed J W, Atwood J L. Supramolecular chemistry. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons Ltd, 2000
Schneider H J, Yatsimirsky A. Principles and methods in supramolecular chemistry. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons Ltd, 2000
Desvergne J P, Czarnik A W. Chemosensors of ion and molecule recognition. Dordrecht: NATO ASI Series, Kluwer Academic, 1997
Czarnik A W. Fluorescent Chemosensors for Ion and Molecule Recognition. ACS Symposium Series No 538. Washington: American Chemical Society, 1992
Zhang M Q, Shen H F, Yang Z R, Chen H Q, Wong K Y. Development of oxygen sensor based on luminescence quenching (I)-Synthesis and Selection of Indicators. Journal of South China University of Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2001, 29(1): 51–55 (in Chinese)
Ikeda A, Shinkai S. Novel cavity design using calix [n] arene skeletons: Toward molecular recognition and metal binding. Chem Rev, 1997, 97(5): 1713–1734
Goswami S, Ghosh K, Dasgupta S. Troger’s base molecular scaffolds in dicarboxylic acid recognition. J Org Chem, 2000, 65(7): 1907–1914
Benito H M, Gomez-Garcia M, Jimenez Blanco J L, Ortiz Mellet C, Garcia Fernandez J M. Carbohydrate-based receptors with multiple thiourea binding sites: Multipoint hydrogen bond recognition of dicarboxylates and monosaccharides. J Org Chem, 2001, 66(4): 1366–1369
Watanabe S, Higashi N, Kobayashi M, Hamanaka K, Takata Y, Yoshida K. Stereoselective optical sensing of dicarboxylate anions by an inducedfit type Ru (II) receptor. Tetrahedron Lett, 2000, 41(21): 4583–4586
Carr J D, Coles S J, Hursthouse M B, Light M E, James H R, Westwood T J. Redoxswitched control of binding strength in hydrogen-bonded metallocene complexes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2000, 39(18): 3296–3299
Albert J S, Goodman M S, Hamilton A D. Molecular recognition of proteins: Sequence-selective binding of aspartate pairs in helical pep tides. J Am Chem Soc, 1995, 117(3): 1143–1144
Lakowicz J R. Princip les of fluorescence spectroscopy. 2nd ed. New York: Kluwer A cademico Plenum Publishers, 1999
Jaime C, De Mendoza Javier, Prados P, Nieto P M, Sanchez C. Carbon-13NMR chemical shifts: a single rule to determine the conformation of calix[4]arenes. J Org Chem, 1991, 56(10): 3372–3376
Matsumoto H, Shinkai S. Metal-induced conformational change in pyrene-appended calix[4] crown-4 which is useful for metal sensing and guest tweezing. Tetrahedron Lett, 1996, 37(1): 77–80
Krauss R, Weinig H G, Seydack M, Bendig J, Koert U. Molecular signal transduction through conformational transmission of a perhydroanthracene transducer. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2000, 39(10): 1835–1837
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 35(4): 20–24 [译自: 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版)]
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Bu, J., Liu, J. et al. Calix[4]arene based selective fluorescent chemosensor for organic acid recognition. Front. Chem. China 3, 348–352 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11458-008-0048-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11458-008-0048-6