Abstract
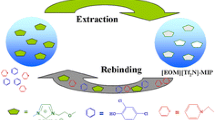
The uniform-sized spherical molecularly imprinted polymers were successfully prepared through molecular imprinting technology by two-step seed swelling and mini-emulsion polymerization in the aqueous condition using quinine as template molecules and methacrylic acid (MAA) as functional monomer. The polymers were characterized by IR spectra, thermal-weight analysis, scanning electron microscope and laser particle size analysis. The properties of imprinted polymers were investigated in different organic phases and aqueous media. In the organic media, results suggested that polar interactions (hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions) between acidic monomer/polymer and template molecules are mainly responsible for the binding and recognition; whereas in the aqueous medium, a considerable recognition effect was also obtained where the ionic (electrostatic) interaction and hydrophobic interaction play an important role. The experiments of binding different substrates indicated that the MIPs possessed an excellent rebinding ability and inherent selectivity to quinine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glad M, Reinholdsson P. and Mosbach K., Molecularly imprinted composite polymers based on trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate particles for efficient enantiomeric separations, React. Polym, 1995, 25: 47–54
Hwang C. C. and Lee W. C., Chromatographic resolution of the enantiomers of phenyl-propanolamine by using molecularly imprinted polymer as the stationary phase, J. Chromatogr., B, 2001, 765: 45–53
Lu Y., Li C., Zhang H. et al., Study on the mechanism of chiral recognition with molecularly imprinted polymers, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2003, 489: 33–43
Kazuyoshi Y. and Isao K., Molecularly imprinted polymers for biosensor application, Trends Anal. Chem., 1999, 18: 199–204
Bruggemann O., Chemical reaction engineering using molecularly imprinted polymeric catalysts, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2001, 435: 197–207
Ye L. and Mosbach K., Molecularly imprinted micro-spheres as antibody binding mimics. React. Funct. Polym, 2001, 48: 149–157
Baggiani C., Giovannoli C., Anfossi L. et al., Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction sorbent for the clean-up chlorinated phenoxyacids from aqueous samples, J. Chromatogr., A, 2001, 938: 35–44
Brambilla G., Fiori M., Rizzo B. et al., Use of molecularly imprinted polymers in the solid-phase extraction of clenbuterol from animal feeds and biological matrices, J. Chromatogr., B, 2001, 759: 27–32
Sergeyeva T. A., Matuschewski H., Piletsky S. A. et al., Molecularly imprinted polymer membranes for substance-selective solid-phase extraction from water by surface photo-grafting polymerization, J. Chromatogr., A, 2001, 907: 89–99
Zhang L. Y., Cheng G. X. and Fu C., Molecular selectivity of tyrosine-imprinted polymer prepared by seed swelling and suspension polymerization, Polym. Int., 2002, 51: 687–692
Vaihinger D., Landfester K., Krauter I. et al., Molecularly imprinted polymer nanospheres as synthetic affinity receptors obtained by mini-emulsion polymerization, Macromol. Chem. Phys., 2002, 203: 1965–1973
Hanginaka J. and Sakai Y., Uniform-sized molecularly imprinted polymer material for (S)-propranolol. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2000, 22: 899–907
Masci G., Aulenta F. and Crescenzi V., Uniform-sized clenbuterol molecularly imprinted polymers prepared with methacrylic acid or acrylamide as an interacting monomer, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2002, 83: 2660–2668
Meng Z. H., Wang J. W., Zhou L. M. et al., Beaded molecular imprinted polymer for stereo isomer separation, Chinese J. Chromatogr., 1999, 17: 323–325
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
__________
Translated from Zhongshan Dcocue Xuebao/Acta Scientianum Natralium University Sunyatseni, 2005, 44(3)(in Chinese)
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Liu, L., Yang, G. et al. Preparation, characterization and properties studies of quinine-imprinted polymer in the aqueous phase. Front. Chem. China 1, 211–216 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11458-006-0011-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11458-006-0011-3