Abstract
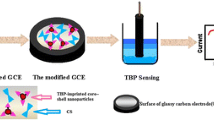
A sensitive nicotine sensor based on a molecularly imprinted electropolymer of o-aminophenol is proposed and its configuration and performance are studied in detail. On the condition of weak acidity, the sensitive layer was prepared by electropolymerization of o-aminophenol on a gold electrode in the presence of the template (nicotine). The sensor exhibits good selectivity and sensitivity to nicotine. The determination limit is 2.0×10−7 mol/L and a linear relationship between the current and concentration is found in the range of 4.0×10−7 ∼ 3.3 ×10−5 mol/L. The sensor has also been applied to the analysis of nicotine in tobacco samples with recovery rates ranging from 99.0% to 102%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Fang, Zheng HuaiLi, Shen Yi., The acid extracting and assembling spectrophotometry detection of nicotine in the tobacco. Chemical Word, 1997, 31(11): 597–600
Tan YiGuang, Yin Jian, Liang ChengDou, Peng Hui, Nie LiHua, Yao ShouZhuo, A study of a new TSM bio-mimetic sensor using a molecularly imprinted polymer coating and its application for the determination of nicotine in human serum and urine. Bioelectrochemistry, 2001, 53(2): 141–148
Liu JunQiu, Luo GuiMin., Molecularly Imprinted polymer and Its Application. Journal of functional polymers, 1998, 11(4): 561–565
Glad M., Reinholdsson P., Mosbach K., Molecularly imprinted composite polymers based on ttrimethylolpropane trimethacrylate (TRIM) particles for efficient enantiomeric sseparations. React. Polym., 1995, 25(1): 47–54
Seller G. B., Imprinted dispersion polymers: a new class of easily accessible affinity stationary phases. J. Chromatogr., 1994, 673(1): 133A–141A
Plunkett S. D., Amold F. H., Molecularly imprinted polymers on silica: selective supports for high-performance ligand-exchange chromatography. J. Chromatogr., 1995, 708(1): 19–29
Zuo YanJun, Yu JianHua, Huang QiBin., The preparation of poly(o-phenylenediamine) sarin acid imprinting nanometer layer and its structural characterization. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2003, 19(6): 528–532
Zhang AiQiang, Chen YanZhen, Tian ShaoWu, Studies of OAP electropolymer film. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2003, 19(6): 528–532
Kempe M., Mosbach K., Separation of amino acids, peptides and proteins on molecularly imprinted stationary phases. J. Chromatogr. A., 1995, 691(2): 317–323
Yoshizako K., Hosoya K., Iwakoshi Y., Kimata K., Tanaka N., Porogen imprinting effects. Anal. Chem., 1998, 70(2): 386–389
Yin YunRan, Feng GenXin, Yang Jun., Measuring of the dissociation constants of nicotine in aqueous solutions. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Nature Science), 1999, 22(S1): 181–184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Journal of Hunan university (Nature Science), 2005, 32(3) (in Chinese)
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Zhang, X., Yang, Y. et al. A sensitive nicotine sensor based on molecularly imprinted electropolymer of o-aminophenol. Front. Chem. China 1, 183–187 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11458-006-0004-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11458-006-0004-2