Abstract
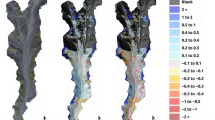
It is common to obtain the topography of tidal flats by the Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) photogrammetry, but this method is not applicable in tidal creeks. The residual water will lead to inaccurate depth inversion results, and the topography of tidal creeks mainly depends on manual survey. The present study took the tidal creek of Chuandong port in Jiangsu Province, China, as the research area and used UAV oblique photogrammetry to reconstruct the topography of the exposed part above the water after the ebb tide. It also proposed a Trend Prediction Fitting (TPF) method for the topography of the unexposed part below the water to obtain a complete 3D topography. The topography above the water measured by UAV has the vertical precision of 12 cm. When the TPF method is used, the cross-section should be perpendicular the central axis of the tidal creek. A polynomial function can be adapted to most shape of sections, while a Fourier function obtains better results in asymmetrical sections. Compared with the two-order function, the three-order function lends itself to more complex sections. Generally, the TPF method is more suitable for small, straight tidal creeks with clear texture and no vegetation cover.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akay S S, Ozcan O, Sen O L, 2019. Modeling morphodynamic processes in a meandering river with unmanned aerial vehicle-based measurements. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 13(4): 1–18.
Allen, J R L, 2000. Morphodynamics of Holocene salt marshes: A review sketch from the Atlantic and Southern North Sea coasts of Europe. Quaternary Science Reviews, 19(12): 1155–1231.
Bearman J A, Friedrichs C T, Jaffe B E et al., 2010. Spatial trends in tidal flat shape and associated environmental parameters in South San Francisco Bay. Journal of Coastal Research, 26(2): 342–349.
Brunier G, Fleury J, Anthony E J et al., 2016. Close-range airborne Structure-from-Motion photogrammetry for high-resolution beach morphometric surveys: Examples from an embayed rotating beach. Geomorphology, 261: 76–88.
Chen L C, 1998. Detection of shoreline changes for tideland areas using multi-temporal satellite images. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 19(17): 3383–3397.
Coco G, Zhou Z, van Maanen B et al., 2013. Morphodynamics of tidal networks: Advances and challenges. Marine Geology, 346: 1–16.
Dai W, Li H, Gong Z et al., 2019. Application of unmanned aerial vehicle technology in geomorphological evolution of tidal flat. Advances in Water Science, 30(3): 359–372. (in Chinese)
D’Alpaos A, Lanzoni S, Marani M et al., 2005. Tidal network ontogeny: Channel initiation and early development. Journal of Geophysical Research, 110: F02001.
Dash J, Pearse G, Watt M, 2018. UAV multispectral imagery can complement satellite data for monitoring forest health. Remote Sensing, 10(8): 1216.
Davies G, Woodroffe C D, 2010. Tidal estuary width convergence: Theory and form in North Australian estuaries. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 35(7): 737–749.
Dietrich J T, 2017. Bathymetric Structure-from-Motion: Extracting shallow stream bathymetry from multi-view stereo photogrammetry. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 42(2): 355–364.
Elgar S, Raubenheimer B, 2011. Currents in a small channel on a sandy tidal flat. Continental Shelf Research, 31(1): 9–14.
Fagherazzi S, Mariotti G, 2012. Mudflat runnels: Evidence and importance of very shallow flows in intertidal morphodynamics. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(14): L14402.
Fruergaard M, Andersen T J, Nielsen L H et al., 2011. Punctuated sediment record resulting from channel migration in a shallow sand-dominated micro-tidal lagoon, Northern Wadden Sea, Denmark. Marine Geology, 280: 91–104.
Gomez C, Hayakawa Y, Obanawa H, 2015. A study of Japanese landscapes using structure from motion derived DSMs and DEMs based on historical aerial photographs: New opportunities for vegetation monitoring and diachronic geomorphology. Geomorphology, 242: 11–20.
Gong Z, Wang Z B, Stive M J F et al., 2012. Process-based morphodynamic modeling of a schematized mudflat dominated by a long-shore tidal current at the Central Jiangsu Coast, China. Journal of Coastal Research, 28(6): 1381–1392.
Hayakawa Y S, Obanawa H, 2020. Volumetric change detection in bedrock coastal cliffs using terrestrial laser scanning and UAS-based SfM. Sensors, 20(12): 3403.
Hibma A, Stive M J F, Wang Z B, 2004. Estuarine morphodynamics. Coastal Engineering, 51: 765–778.
Hood W G, 2010. Tidal channel meander formation by depositional rather than erosional processes: Examples from the prograding Skagit River Delta (Washington, USA). Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 35(3): 319–330.
Hughes Z J, 2012. Tidal channels on tidal flats and marshes. In: Richard A Fuller, Robert W Dalrymple eds. Principles of Tidal Sedimentology. Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer 269–300.
Ichoku C, Chorowicz J, 1994. A numerical approach to the analysis and classification of channel network patterns. Water Resources Research, 30(2): 161–174.
van Iersel W, Straatsma M, Middelkoop H et al., 2018. Multitemporal classification of river floodplain vegetation using time series of UAV images. Remote Sensing, 10(7): 1144.
Ishiguro S, Yamano H, Oguma H, 2016. Evaluation of DSMs generated from multi-temporal aerial photographs using emerging structure from motion-multi-view stereo technology. Geomorphology, 268: 64–71.
Kasvi E, Salmela J, Lotsari E et al., 2019. Comparison of remote sensing based approaches for mapping bathymetry of shallow, clear water rivers. Geomorphology, 333: 180–197.
Lanzoni S, D’Alpaos A, 2015. On funneling of tidal channels. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 120(3): 433–452.
Li C X, Z J Q, Fan D et al., 2001. Holocene regression and the tidal radial sand ridge system formation in the Jiangsu coastal zone, East China. Marine Geology, 173: 97–120.
Liu Y X, Zhou M X, Zhao S S et al., 2015. Automated extraction of tidal creeks from airborne laser altimetry data. Journal of Hydrology, 527: 1006–1020.
Magolan, J L, Halls J N, 2020. A multi-decadal investigation of tidal creek wetland changes, water level rise, and ghost forests. Remote Sensing, 12(7): 1141.
Mallin M A, Lewitus A J, 2004. The importance of tidal creek ecosystems. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 298(2): 145–149.
Mancini F, Dubbini M, Gattelli M et al., 2013. Using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) for high-resolution reconstruction of topography: The structure from motion approach on coastal environments. Remote Sensing, 5(12): 6880–6898.
Mariotti G, Fagherazzi S, 2012. Channels-tidal flat sediment exchange: The channel spillover mechanism. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 117: C03032.
Mason D C, Davenport I J, Flather R A, 1997. Interpolation of an intertidal digital elevation model from heighted shorelines: A case study in the Western Wash. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 45(5): 599–612.
Mason D C, Davenport I J, Flather R A et al., 1998. A digital elevation model of the inter-tidal areas of the Wash, England, produced by the waterline method. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 19(8): 1455–1460.
Mason D C, Scott T R, H-J Wang. 2006. Extraction of tidal channel networks from airborne scanning laser altimetry. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing, 61: 67–83.
Meinen B U, Robinson D T, 2020. Mapping erosion and deposition in an agricultural landscape: Optimization of UAV image acquisition schemes for SfM-MVS. Remote Sensing of Environment, 239: 111666.
Mohamad N, Abdul Khanan M F, Ahmad A et al., 2019. Evaluating water level changes at different tidal phases using UAV photogrammetry and GNSS vertical data. Sensors, 19(17): 3778.
d’Oleire-Oltmanns S, Marzolff I, Peter K et al., 2012. Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) for monitoring soil erosion in Morocco. Remote Sensing, 4(11): 3390–3416.
Perillo G M E, 2009. Tidal courses: Classification, origin and functionality. In: Coastal Wetlands: An Integrated Ecosystem Approach. New York: Elsevier Science, 185–209.
Rao W B, Mao C P, Wang Y G et al., 2015. Geochemical constraints on the provenance of surface sediments of radial sand ridges off the Jiangsu coastal zone, East China. Marine Geology, 359: 35–49.
Shi B W, Cooper J R, Pratolongo P D et al., 2017. Erosion and accretion on a mudflat: The importance of very shallow - water effects. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 122(12): 9476–9499.
Snavely N, Seitz S M, Szeliski R, 2008. Modeling the world from internet photo collections. International Journal of Computer Vision, 80(2): 189–210.
Stefanon L, Carniello L, D’Alpaos A et al., 2012. Signatures of sea level changes on tidal geomorphology: Experiments on network incision and retreat. Geophysical Research Letters, 39: L12402.
Stevenson J A, Sun X F, Mitchell N C, 2010. Despeckling SRTM and other topographic data with a denoising algorithm. Geomorphology, 114: 238–252.
Tong X H, Liu X F, Chen P et al., 2015. Integration of UAV-based photogrammetry and terrestrial laser scanning for the three-dimensional mapping and monitoring of open-pit mine areas. Remote Sensing, 7(6): 6635–6662.
Um I, Park S, Kim H T et al., 2020. Configuring RTK-GPS architecture for system redundancy in multi-drone operations. IEEE Access, 8: 76228–76242.
Vandenbruwaene W, Meire P, Temmerman S, 2012. Formation and evolution of a tidal channel network within a constructed tidal marsh. Geomorphology, 151/152: 114–125.
Vlaswinkel B M, Cantelli A, 2011. Geometric characteristics and evolution of a tidal channel network in experimental setting. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 36: 739–752.
Wang X Y, Ke X K, 1997. Grain-size characteristics of the extant tidal flat sediments along the Jiangsu coast, China. Sedimentary Geology, 112: 105–122.
Wang Y, Zhu D K, You K Y et al., 1999. Evolution of radiative sand ridge field of the South Yellow Sea and its sedimentary characteristics. Science in China Series D Earth Sciences, 42: 97–112.
Wang, Y P, Gao S, Jia J J et al., 2012. Sediment transport over an accretional intertidal flat with influences of reclamation, Jiangsu coast, China. Marine Geology, 291–294: 147–161.
Watts A C, Ambrosia V G, Hinkley E A, 2012. Unmanned aircraft systems in remote sensing and scientific research: Classification and considerations of use. Remote Sensing, 4(6): 1671–1692.
Westoby M J, Alfieri J, Glasser N F et al., 2012. ‘Structure-from-Motion’ photogrammetry: A low-cost, effective tool for geoscience applications. Geomorphology, 179: 300–314.
Xing F, Wang Y P, Wang H V, 2012. Tidal hydrodynamics and fine-grained sediment transport on the radial sand ridge system in the southern Yellow Sea. Marine Geology, 291–294: 192–210.
Yin Y H, 1997. Actuality and advances in tidal creeks. Marine Geology Letters, 1–4. (in Chinese)
Zhang C K, Xu M P, Zhou Z et al., 2018. Advances in cross-shore profile characteristics and sediment sorting dynamics of tidal flats. Advances in Water Science, 29(2): 269–282. (in Chinese)
Zhang R S, 1992. Suspended sediment transport processes on tidal mud flat in Jiangsu Province, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 35(3): 225–233.
Zhang S M, Zhao G X, 2019. A harmonious satellite-unmanned aerial vehicle-ground measurement inversion method for monitoring salinity in coastal saline soil. Remote Sensing, 11(14): 1700.
Zhao B X, Liu Y X, Xu W X et al., 2019. Morphological characteristics of tidal creeks in the central coastal region of Jiangsu, China, using LiDAR. Remote Sensing, 11(20): 2426.
Zhou Z, Stefanon L, Olabarrieta M et al., 2014. Analysis of the drainage density of experimental and modelled tidal networks. Earth Surface Dynamics, 2: 105–116.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Kun Zhao, Xiaoyan Zhang, Zhiyuan Li and Huatao Yang for their efforts in collecting the UAV imagery and measuring data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation
China National Funds for Distinguished Young Scientists, No.51925905; National Natural Science Foundation of China, No.41401371
Author
Zhang Xuhui (1996–), Master Candidate, specialized in tidal flats and remote sensing, E-mail: zhangxuhui_hhu@163.com
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Li, H., Gong, Z. et al. Method for UAV-based 3D topography reconstruction of tidal creeks. J. Geogr. Sci. 31, 1852–1872 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-021-1926-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-021-1926-9