Abstract
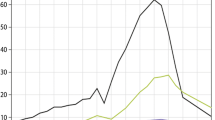
Acid rain has been recognized as a serious environmental problem in China since the 1980s, but little is known about the effects of the climatic change in regional precipitation on the temporal and spatial variability of severe acid rain. We present the effects of the regional precipitation trend change on the area and intensity of severe acid rain in southern China, and the spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of SO2 and NO2 concentrations are analyzed on the basis of SO2 and NO2 column concentration data. The results are as follows. (1) The emission levels of SO2 and NO2 have reached or passed the precipitation scavenging capacity in parts of southern China owing to the emission totals of SO2 and NO2 increasing from 1993 to 2004. (2) Notable changes in the proportion of cities subject to severe acid rain occurred mainly in the south of the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River during 1993–2004. With an abrupt change in 1999, the severe acid rain regions were mainly located in central and western China during 1993–1999 and moved obviously eastward to the south of the lower-middle reaches of the Yangtze River with the proportion of cities subject to severe acid rain increasing significantly from 2000 to 2004. (3) The spatial distribution and variation in the seasonal precipitation change rate of more than 10 mm/10a are similar to those of severe acid rain in southern China. An abrupt change in 1999 is seen for winter and summer precipitation, the same as for the proportion of cities subject to severe acid rain in southern China. The significant increase in summer storm precipitation from 1991 to 1999 mitigated the annual precipitation acidity in the south of the Yangtze River and reduced the area of severe acid rainfall. On the other hand, the decrease in storm rainfall in summer expanded the area of severe acid rainfall in the south of the Yangtze River in 2000–2006. Therefore, the change in seasonal precipitation is an important factor in the severe acid rain regions moving eastward and expanding in southern China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beamish R J, Harvey H H, 1972. Acidification of the La Cloche Mountain Lakes, Ontario, and resulting fish mortalities. J. Fish Res. Board Can., 29: 1131–1143.
Chen Yu, Gao Ge, Ren Guoyu et al., 2005. Spatial and temporal variation of precipitation over ten major basins in China between 1956 and 2000. Journal of Natural Resources, 20(5): 637–643. (in Chinese)
Cheng Xinjin, Sun Jiming, Lei Hengchi et al., 2004. Evaluation of SO2 emission control in China. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 28(2): 174–186. (in Chinese)
Cowling E B, 1982. Acid precipitation in historical perspective. Environmental Science & Technology, 16(2): 110–123.
Ding Guoan, Xu Xiaobin, Fang Xiumei, 1997. Current status and future of acid rain in China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 42(2): 169–173. (in Chinese)
Gao Huiwang, Huang Meiyuan, Chen Xinjin, 1998. A study on sulfur deposition features in East Asia. Research of Environmental Sciences, 11(5): 37–40. (in Chinese)
Gorham E, 1957. The chemical composition of lake waters in Halifax County, Nova Scotia. Limnology and Oceanography, 2(1): 12–21.
He Xicheng, Ding Yihui, He Jinhai et al., 2006. An analysis on anomalous precipitation in southern China during winter monsoons. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 64(5): 594–604. (in Chinese)
Huang Meiyuan, Shen Zhilai, Liu Shuairen et al., 1995. A study on the formation processes of acid rain in some areas of Southwest China. Scientia Atmopherica Sinica, 19(3): 359–366. (in Chinese)
Huang Meiyuan, Wang Zifa, He Dongyang et al., 1996. Modeling studies on sulfur deposition and transport among different areas in China in summer and winter. Chinese Science Bulletin, 41(11): 1013–1016. (in Chinese)
Liu Jiaqi, 1996. Research on precipitation background value and definition of acid rain. Environmental Monitoring in China, 12(5): 5–9. (in Chinese)
Olendrzynski K, Berge E, Bartnicki J, 2000. EMEP Eulerian acid deposition model and its applications. European Journal of Operational Research, 122: 426–439.
Quan Jiannong, Zhang Xiaoshan, Duan Ning et al., 2007. Numerical modeling of sulfur deposition in south and southwest China. Plateau Meteorology, 26(2): 326–332. (in Chinese)
Ren Guoyu, Wu Hong, Chen Zhenhong, 2000. Spatial patterns of change trend in rainfall of China. Quarterly Journal Applied Meteorology, 11(3): 322–330. (in Chinese)
SEPA. Report on the status quo of the environment in China from 1990 to 2006. http://www.zhb.gov.cn.
Shi Neng, Chen Jiaqi, 1995. 4-phase climate change features in the last 100 years over China. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 53(4): 431–439. (in Chinese)
Thorjørn Larssen, Espen Lydersen, Tang Dagang et al., 2006. Acid rain in China. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(2): 418–425.
Tian Hezhong, Lu Yongqi, Hao Jiming et al., 2001. Control courses and progress of acid rain and SO2 pollution in China. Electric Power, 34(3): 51–56. (in Chinese)
Tomlinson G H, 1983. Air pollution and forest decline. Environmental Science & Technology, 17(6): 246–256.
Ulrich B, 1990. Waldsterben: Forest decline in West Germany. Environmental Science & Technology, 24(4): 436–441.
Wang Wenxing, 1994. Study on the origin of acid rain formation in China. China Environmental Science, 14(5): 323–329. (in Chinese)
Wang Wenxing, Zhang Wanhua, Shi Quan et al., 1993. Study on factors related to acidity of rain water in China. China Environmental Science, 13(6): 401–407. (in Chinese)
Wang Ying, Shi Neng, Gu Junqiang et al., 2006. Climatic variations of wet days in China. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 30(1): 162–170. (in Chinese)
Xu Yaxuan, Duan Ning, Chai Fahe et al., 2006. Numerical simulation of sulfur deposition in China. Research of Environmental Sciences, 19(5): 1–10. (in Chinese)
Yang Xinxing, Gao Qingxian, Jiang Zhenyuan et al., 1998. Research on the transportation and precipitation regular pattern of sulphur pollutants in China. Research of Environmental Sciences, 11(4): 27–34. (in Chinese)
Zhang Xinling, An Junling, Cheng Xinjin et al., 2003. Effect of evolutions of source emissions and meteorological factors on SO2 distribution and sulfur deposition in China. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 27(5): 939–947. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation: Concentrated fund item of national science and technology foundation work, No.2005DKA31700-06-20; Special fund from China Meteorological Administration, No.CCSF2006-32
Author: Xie Zhiqing (1977–), Master’s degree and Engineer, specializing in meteorological disaster prevention and reduction and climate change.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Z., Du, Y., Zeng, Y. et al. Effects of precipitation variation on severe acid rain in southern China. J. Geogr. Sci. 19, 489–501 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-009-0489-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-009-0489-y