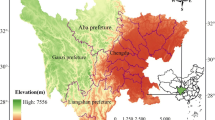
Abstract
The expansion of agriculture is posited as one of the main dynamics of forest landscape change globally, and the robust modeling of these processes is important for policy as well as academic concern. This paper concerns a relatively small area of Yiluo River catchment where considerable attention has been paid to slow down the process of the expansion of agriculture into the remaining natural forests. In the present study, we reconstructed the former forest landscape structure and elucidated the landscape change during a period of about 15 years. Three sets (1987, 1996 and 2002) of maps derived from Landsat-5 images were used for analyses. The result showed that there was a decrease in the area of the forest landscape from 995.60 km2 in 1987 to 650.50 km2 in 2002. Then we examined the degree to which forest landscape conversion could be attributed to a set of factors identified as significant at broader scales, namely topography, distribution of the village clusters (centroids), distance from villages (centroids), and distance from forest edge (1987). By using “spatial analysis” in Arc/gis 8.3, the correlation between forest landscape change and driving factors was constructed. This study found that forest landscape conversion in this region was largely explained by elevation, slope and proximity to village.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang Jie, Li Huidian, Huang Yujie et al., 2004. Spatial structure change of land use on middle-sized basin on RS and GIS: a case study of Luoning County in central Yiluo River basin. Journal of Institute of Surveying and Mapping, 21(1): 42–45. (in Chinese)
Ding Shengyan, Qian Lexiang, Cao Xinxiang et al., 2003. Forest landscape pattern dynamics of Yihe-Luohe River Basin. Acta Geographica Sinica, 58(3): 354–362. (in Chinese)
Editorial Committee of China Encyclopedia, 1990. China Encyclopedia. Beijing: Encyclopedia of China Publishing House. (in Chinese)
Geist H, Lambin E F, 2002. Proximate causes and underlying driving forces of tropical deforestation. BioScience, 52(2): 143–150.
Goudie A, Viles H, 1997. The Earth Transformed: An Introduction to Human Impacts on the Environment. Oxford: Blackwell.
Kaimowitz D, Angelsen, A, 1996. A Guide to Economic Models of Tropical Deforestation. Centre for International Forestry Research, Jakarta.
Kim Y M, Zerb S, Kowarik I, 2002. Human impact on flora and habitats in Korean rural settlements. Preslia, Praha, 74: 409–419.
Krausmann F, Haberl H, Schulz N B et al., 2003. Land-use change and socio-economic metabolism in Austria. Part I. Driving forces of land-use change: 1950–1995. Land Use Policy, 20: 1–20.
Lambin E F, 1994. Modelling of deforestation processes: a review. TREES Publication Series B. Research Report No. 1. European Commission, Brussels, EUR 15744 EN.
Lambin E F, Baulies X, Bockstael N et al., 1999. Land use and cover change implementation strategy. IGBP Report No. 48/IHDP, Report No. 10. IGBP, Stockholm.
Lambin E F, Turner II B L, Geist H J et al., 2001. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: moving beyond the myths. Global Environmental Change, 11: 261–269.
Li X J, Jim P, Liu G J et al., 2001. Assessing regional sustainability: the case of land use and land cover change in the middle Yiluo River catchment of the Yellow River basin, China. Applied Geography, 21: 87–106.
Liu Jingyu, Chang Jie, Zhao Hhuifeng, 2005. Studies of human driving force of cultivated land change: a case study of Luoning County. Agricultural Science of Henan Province, 9: 58–61. (in Chinese)
Mertens B, Lambin E F, 2000. Land-cover-change trajectories in southern Cameroon. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr., 90(3): 467–494.
Qian Lexiang, Li Shuang, Zhang Xiaowei, 2005. Change on the vegetation landscape pattern in the typical Yiluo River River valley: a case study from Luoning County, Henan Province. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 13(1): 49–52. (in Chinese)
Turner M G, 1990. Spatial and temporal analysis of landscape patterns. Landscape Ecology, 4(1): 21–30.
Turner II B L, Moss R H, Skole D L, 1993. Relating land use and global land-cover change: a proposal for IGBP-HDP Core Product. IGBP Report 24, Stockholm, Sweden, HDP Report 5.
Veldkamp A, Lambin E, 2001. Predicting land use change. Agriculture Ecosystem and Environment, 85(1–3): 1–6.
Vitousek P M, 1992. Global environmental change: an introduction. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst., 23: 1–14.
Vitousek P M, Mooney H A, Lubchenko J et al., 1997. Human domination of earth’s ecosystems. Science, 277: 494–499.
Yellow River Conservancy Commission, 1989. The Atlas of Yellow River Basin. Beijing: China Cartographic Publishing House. (in Chinese)
Wrbka T, Erb K H, Schulz N B et al., 2004. Linking pattern and process in cultural landscapes: an empirical study based on spatially explicit indicators. Land Use Policy, 21: 289–306.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation: National Natural Science Foundation of China, No.30570301, No.40671175; Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province, No.0111070100
Author: Liang Guofu (1973–), master, specialized in landscape ecology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, G., Ding, S. Driving factors of forest landscape change in Yiluo River basin. J GEOGR SCI 16, 415–422 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-006-0404-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-006-0404-8