Abstract
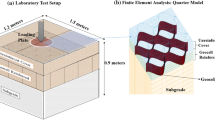
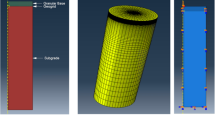
Geocell is a three-dimensional geosynthetic product that was originally developed to confine granular bases and minimize permanent deformation of unpaved roads. Many laboratory and field tests have demonstrated the effectiveness of geocell reinforcement in roadway constructions. However, the lack of a well-established design method that can quantify the benefit of geocell reinforcement has greatly limited the application of geocell in roadways. This paper presents the development of a three-dimensional mechanistic-empirical (M-E) model for geocell-reinforced unpaved roads. The constitutive equation for the tangential resilient modulus of the base material was derived under a general three-dimensional condition. Two analytical models were introduced to estimate the compaction- and repeated load-induced residual stresses in the base layer. These analytical models consider the material properties and construction effects in a rational way thus can be used for various situations. Finally, the proposed M-E model was validated against the test results from four unpaved road sections. Comparisons between the calculated results and the test data show that the three-dimensional M-E model effectively simulated the permanent deformation behavior of geocell-reinforced unpaved roads under a large number of load repetitions, given that the unpaved road was stable under a repeated load.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duncan JM, Seed RB (1986) Compaction-induced earth pressures under K0-condition. J Geotech Eng 122(1):1–22
Edil TB, Benson CH, Bin-Shafique MS, Tanyu BF, Kim W-H, Senol A (2002) Field evaluation of construction alternatives for roadways over soft subgrade. Trans Res Record J Trans Res Board 1786:36–48
Han J, Yang X, Leshchinsky D, Parsons RL (2008) Behavior of geocell-reinforced sand under a vertical load. Trans Res Record J Trans Res Board 2045:95–101
Han J, Pokharel SK, Yang X, Manandhar C, Leshchinsky D, Halahmi I, Parsons RL (2011) Performance of geocell-reinforced RAP bases over weak subgrade under full-scale moving wheel loads. J Mater Civ Eng ASCE 23(11):1525–1534
ARA, Inc. ERES Consultants Division (2004) Guide for mechanistic-empirical design of new and rehabilitated pavement structures. Final report, NCHRP 1-37A. Transportation Research Board, Washington, DC USA
Kwon J, Tutumluer E, Kim M (2007) Development of a mechanistic model for geosynthetic-reinforced flexible pavements. Geosynth Intern 12(6):310–320
Mengelt MJ, Edil TB, Benson CH (2000) Reinforcement of flexible pavements using geocells. Geo report no. 00-04, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, USA
Perkins SW, Ismeik M (1997) A synthesis and evaluation of geosynthetic-reinforced base layers in flexible pavements: part I. Geosynth Intern 4(6):549–604
Perkins SW, Christopher BR, Cuelho EL, Eiksund GR, Hoff I, Schwatz CW, Svano G, Watn A (2004) Development of design methods for geosynthetic reinforced flexible pavements. Report no. DTFH61-01-X-00068. Montana State University, Bozeman, MT, USA
Pokharel SK (2010) Experimental study on geocell-reinforced bases under static and dynamic loading. Ph.D. dissertation, the University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS, USA
Pokharel SK, Han J, Manandhar C, Yang X, Leshchinsky D, Halahmi I, Parsons RL (2011) Accelerated pavement testing of geocell-reinforced unpaved roads over weak subgrade. Trans Res Record J Trans Res Board 2204:67–75
Rondón HA, Wichtmann T, Triantafyllidis Th, Lizcano A (2007) Hypoplastic material constants for a well-graded granular material for base and subbase layers of flexible pavements. Acta Geotech 2(2):113–126
Salciarini D, Tamagnini C (2009) A hypoplastic model for shallow foundations under monotonic and cyclic loads. Acta Geotech 4:163–176
Seed RB (1983) Compaction-induced stresses and deflections on earth structure. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA
Yang X (2010) Numerical analyses of geocell-reinforced granular soils under static and repeated loads. Ph.D. Dissertation, the University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS, USA
Yang X, Han J, Pokharel SK, Manandhar C, Parsons RL, Leshchinsky D, Halahmi I (2012) Accelerated pavement testing of unpaved roads with geocell-reinforced sand bases. Geotext Geomembr 32:95–103
Acknowledgments
This research was jointly funded by the University of Kansas, Transportation Research Institute from Grant #DT0S59-06-G-00047, provided by the US Department of Transportation—Research and Innovative Technology Administration, PRS Mediterranean, Inc. in Israel, and the Geosynthetic Institute under its GSI Fellowship Program for the first author. The resilient modulus tests in this study were performed at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign with the help of Professor Erol Tutumluer and his students.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Han, J., Leshchinsky, D. et al. A three-dimensional mechanistic-empirical model for geocell-reinforced unpaved roads. Acta Geotech. 8, 201–213 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-012-0183-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-012-0183-6