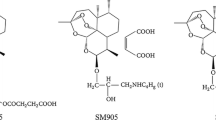
Abstract
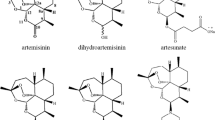
In the 1970s, artemisinin (“qinghaosu” in Chinese), a sesquiterpene lactone with an unusual peroxide bridge, was isolated from Artemisia annua L. It showed promising antimalarial activity, particularly by eliminating parasites resistant to chloroquine. For more than 30 years, artemisinin has contributed to worldwide health as a new type of antimalarial drug. Artemisinin and its analogs, such as dihydroartemisinin, artemether, artesunate, artemiside, artemisone, and arteether, possess not only potent antimalarial activity but also anti-viral, antifungal, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory properties. In this review, we discuss the current understanding of how artemisinin and its analogs affect the immune system and immune-related diseases.
摘要
青蒿素是由中国科学家1972 年首次从复合花序植物黄花蒿中提取的一种含过氧 基团的倍半萜内酯类化合物。它最初用于抗疟治疗, 对脑型疟疾和抗氯喹疟疾有很好的治疗效果, 并且具有速效和低毒的特点。除了抗虐活性外, 青蒿素与它的多种衍还显示出抗病毒、抗真菌、免疫调节以及抗肿瘤等功能。本文综述了目前青蒿素及其衍生物对免疫系统以及免疫相关疾病的影响和研究现状。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen XY, Xu Z (2016) Artemisinin and plant secondary metabolism. Sci Bull 61:1–2
Olliaro P, Djimde A, Dorsey G et al (2011) Hematologic parameters in pediatric uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in sub-Saharan Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg 85:619–625
Robert A, Benoit-Vical F, Claparols C et al (2005) The antimalarial drug artemisinin alkylates heme in infected mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13676–13680
Shi C, Li H (2015) Anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory functions of artemisinin and its derivatives. Mediat Inflamm 2015:435713
Vennerstrom JL, Arbe-Barnes S, Brun R et al (2004) Identification of an antimalarial synthetic trioxolane drug development candidate. Nature 430:900–904
Chen H, Maibach HI (1994) Topical application of artesunate on guinea pig allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermat 30:280–282
Cheng C, Ho WE, Goh FY et al (2011) Anti-malarial drug artesunate attenuates experimental allergic asthma via inhibition of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. PLoS One 6:e20932
Cheng C, Ng DS, Chan TK et al (2013) Anti-allergic action of anti-malarial drug artesunate in experimental mast cell-mediated anaphylactic models. Allergy 68:195–203
Cuzzocrea S, Saadat F, Di Paola R et al (2005) Artemether: a new therapeutic strategy in experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 27:615–630
Ho WE, Cheng C, Peh HY et al (2012) Anti-malarial drug artesunate ameliorates oxidative lung damage in experimental allergic asthma. Free Radic Biol Med 53:498–507
Hou LF, He SJ, Li X et al (2011) Oral administration of artemisinin analog SM934 ameliorates lupus syndromes in MRL/lpr mice by inhibiting Th1 and Th17 cell responses. Arthritis Rheum 63:2445–2455
Hou LF, He SJ, Wang JX et al (2009) SM934, a water-soluble derivative of arteminisin, exerts immunosuppressive functions in vitro and in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol 9:1509–1517
Jin O, Zhang H, Gu Z et al (2009) A pilot study of the therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of artesunate in the MRL/lpr murine model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Mol Immunol 6:461–467
Li B, Li J, Pan X et al (2010) Artesunate protects sepsis model mice challenged with Staphylococcus aureus by decreasing TNF-alpha release via inhibition TLR2 and Nod2 mRNA expressions and transcription factor NF-kappaB activation. Int Immunopharmacol 10:344–350
Li WD, Dong YJ, Tu YY et al (2006) Dihydroarteannuin ameliorates lupus symptom of BXSB mice by inhibiting production of TNF-alpha and blocking the signaling pathway NF-kappa B translocation. Int Immunopharmacol 6:1243–1250
Li Y, Wang S, Wang Y et al (2013) Inhibitory effect of the antimalarial agent artesunate on collagen-induced arthritis in rats through nuclear factor kappa B and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. J Lab Clin Med 161:89–98
Mirshafiey A, Saadat F, Attar M et al (2006) Design of a new line in treatment of experimental rheumatoid arthritis by artesunate. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 28:397–410
Shi JQ, Zhang CC, Sun XL et al (2013) Antimalarial drug artemisinin extenuates amyloidogenesis and neuroinflammation in APPswe/PS1dE9 transgenic mice via inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. CNS Neurosci Ther 19:262–268
Sun XZ (1991) Experimental study on the immunosuppressive effects of qinghaosu and its derivative. Chin J Mod Dev Tradit Med 11:37–38 (in Chinese)
Wang J, Zhou H, Zheng J et al (2006) The antimalarial artemisinin synergizes with antibiotics to protect against lethal live Escherichia coli challenge by decreasing proinflammatory cytokine release. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:2420–2427
Wang JX, Tang W, Zhou R et al (2008) The new water-soluble artemisinin derivative SM905 ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis by suppression of inflammatory and Th17 responses. Br J Pharmacol 153:1303–1310
Wang X, Fang K, Wang XQ et al (2011) Inhibition effect and mechanism of artemisnin on surgically induced endometriosis. J Sichuan Univ Med Sci Ed 42:364–368 (in Chinese)
Wang XQ, Liu HL, Wang GB et al (2011) Effect of artesunate on endotoxin-induced uveitis in rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:916–919
Wang YY, Liu YX, Xie QB et al (2012) Effects of dihydroartemisinin on collagen II-induced arthritis in rats model. J Sichuan Univ Med Sci Ed 43:851–854 (in Chinese)
Wang Z, Qiu J, Guo TB et al (2007) Anti-inflammatory properties and regulatory mechanism of a novel derivative of artemisinin in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 179:5958–5965
Yang Z, Ding J, Yang C et al (2012) Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties of artesunate in experimental colitis. Curr Med Chem 19:4541–4551
Zhao YG, Wang Y, Guo Z et al (2012) Dihydroartemisinin ameliorates inflammatory disease by its reciprocal effects on Th and regulatory T cell function via modulating the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. J Immunol 189:4417–4425
Zwang J, Ndiaye JL, Djimde A et al (2012) Comparing changes in haematologic parameters occurring in patients included in randomized controlled trials of artesunate-amodiaquine vs single and combination treatments of uncomplicated falciparum in sub-Saharan Africa. Malar J 11:25
Gasasira AF, Kamya MR, Achan J et al (2008) High risk of neutropenia in HIV-infected children following treatment with artesunate plus amodiaquine for uncomplicated malaria in Uganda. Clin Infect Dis 46:985–991
Borrmann S, Adegnika AA, Moussavou F et al (2005) Short-course regimens of artesunate-fosmidomycin in treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:3749–3754
Guruprasad B, Chaudhary P, Choedon T et al (2015) Artesunate ameliorates functional limitations in Freund’s complete adjuvant-induced monoarthritis in rat by maintaining oxidative homeostasis and inhibiting COX-2 expression. Inflammation 38:1028–1035
Hunt S, Yoshida M, Davis CE et al (2015) An extract of the medicinal plant Artemisia annua modulates production of inflammatory markers in activated neutrophils. J Inflamm Res 8:9–14
Cao TH, Jin SG, Fei DS et al (2016) Artesunate protects against sepsis-induced lung injury via heme oxygenase-1 modulation. Inflammation 39:651–662
Wenisch C, Parschalk B, Zedwitz-Liebenstein K et al (1997) The effect of artemisinin on granulocyte function assessed by flow cytometry. J Antimicrob Chemother 39:99–101
Perlmann P, Troye-Blomberg M (2002) Malaria and the immune system in humans. Chem Immunol 80:229–242
Fujiwara N, Kobayashi K (2005) Macrophages in inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 4:281–286
Pahl HL (1999) Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-kB transcription factors. Oncogene 18:6853–6866
Prato M, Gallo V, Giribaldi G et al (2010) Role of the NF-kB transcription pathway in the haemozoin- and 15-HETE-mediated activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human adherent monocytes. Cell Microbiol 12:1780–1791
Shakir L, Hussain M, Javeed A et al (2011) Artemisinins and immune system. Eur J Pharmacol 668:6–14
Yu WY, Kan WJ, Yu PX et al (2012) Anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of artemisinin and dihydroartemisinin. China J Chin Mater Med 37:2618–2621 (in Chinese)
Wang Y, Huang ZQ, Wang CQ et al (2011) Artemisinin inhibits extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression via a protein kinase Cdelta/p38/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in phorbol myristate acetate-induced THP-1 macrophages. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 38:11–18
Li B, Zhang R, Li J et al (2008) Antimalarial artesunate protects sepsis model mice against heat-killed Escherichia coli challenge by decreasing TLR4, TLR9 mRNA expressions and transcription factor NF-kappa B activation. Int Immunopharmacol 8:379–389
Hou LF, He SJ, Li X et al (2012) SM934 treated lupus-prone NZB × NZW F1 mice by enhancing macrophage interleukin-10 production and suppressing pathogenic T cell development. PLoS One 7:e32424
Gu Y, Wang X, Wu G et al (2012) Artemisinin suppresses sympathetic hyperinnervation following myocardial infarction via anti-inflammatory effects. J Mol Histol 43:737–743
Wu B, Hu K, Li S et al (2012) Dihydroartiminisin inhibits the growth and metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep 27:101–108
Li B, Yu M, Pan X et al (2014) Artesunate reduces serum lipopolysaccharide in cecal ligation/puncture mice via enhanced LPS internalization by macrophages through increased mRNA expression of scavenger receptors. Int J Mol Sci 15:1143–1161
Magenta D, Sangiovanni E, Basilico N et al (2014) Inhibition of metalloproteinase-9 secretion and gene expression by artemisinin derivatives. Acta Trop 140:77–83
Kim HG, Yang JH, Han EH et al (2013) Inhibitory effect of dihydroartemisinin against phorbol ester-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages. Food Chem Toxicol 56:93–99
Park KH, Yoon YD, Han SB et al (2012) Artemisinin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced interferon-beta production in RAW 264.7 cells: implications on signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 signaling and nitric oxide production. Int Immunopharmacol 14:580–584
Cho YC, Lee SH, Lee M et al (2012) Enhanced IL-12p40 production in LPS-stimulated macrophages by inhibiting JNK activation by artemisinin. Arch Pharmacal Res 35:1961–1968
Wang JX, Hou LF, Yang Y et al (2009) SM905, an artemisinin derivative, inhibited NO and pro-inflammatory cytokine production by suppressing MAPK and NF-kB pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30:1428–1435
Konkimalla VB, Blunder M, Korn B et al (2008) Effect of artemisinins and other endoperoxides on nitric oxide-related signaling pathway in RAW 264.7 mouse macrophage cells. Nitric Oxide 19:184–191
Sen R, Ganguly S, Saha P et al (2010) Efficacy of artemisinin in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Int J Antimicrob Agents 36:43–49
Xueqin H, Zhijun X, Fenfen L et al (2014) Dihydroartemisinin inhibits activation of the Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway and production of type I interferon in spleen cells from lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice. Int Immunopharmacol 22:266–272
Wang JX, Tang W, Shi LP et al (2007) Investigation of the immunosuppressive activity of artemether on T-cell activation and proliferation. Br J Pharmacol 150:652–661
Tatfeng YM, Ihongbe JC, Okodua M et al (2007) CD4 count, viral load and parasite density of HIV positive individuals undergoing malaria treatment with dihydroartemisinin in Benin City, Edo state, Nigeria. J Vector Borne Dis 44:111–115
Mota TC, Cardoso PC, Gomes LM et al (2011) In vitro evaluation of the genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of artesunate, an antimalarial drug, in human lymphocytes. Environ Mol Mutagen 52:590–594
Yang ZS, Zhou WL, Sui Y et al (2005) Synthesis and immunosuppressive activity of new artemisinin derivatives. 1. [12(beta or alpha)-dihydroartemisininoxy]phen(ox)yl aliphatic acids and esters. J Med Chem 48:4608–4617
Veerasubramanian P, Gosi P, Limsomwong C et al (2006) Artesunate and a major metabolite, dihydroartemisinin, diminish mitogen-induced lymphocyte proliferation and activation. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 37:838–847
Lee SH, Cho YC, Kim KH et al (2015) Artesunate inhibits proliferation of naive CD4(+) T cells but enhances function of effector T cells. Arch Pharm Res 38:1195–1203
Zhou WL, Wu JM, Wu QL et al (2005) A novel artemisinin derivative, 3-(12-beta-artemisininoxy) phenoxyl succinic acid (SM735), mediates immunosuppressive effects in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol Sin 26:1352–1358
Wang JX, Tang W, Yang ZS et al (2007) Suppressive effect of a novel water-soluble artemisinin derivative SM905 on T cell activation and proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 564:211–218
Li X, Li TT, Zhang XH et al (2013) Artemisinin analogue SM934 ameliorates murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through enhancing the expansion and functions of regulatory T cell. PLoS One 8:e74108
Li TT, Zhang XH, Jing JF et al (2015) Artemisinin analogue SM934 ameliorates the proteinuria and renal fibrosis in rat experimental membranous nephropathy. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36:188–199
Yang DM, Liew FY (1993) Effects of qinghaosu (artemisinin) and its derivatives on experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. Parasitology 106(Pt 1):7–11
Utoh-Nedosa AU, Akah PA, Okoye TC et al (2009) Evaluation of the toxic effects of dihydroartemisinin on the vital organs of Wistar albino rats. Am J Pharmacol Toxicol 4:169–173
Li-Min XU, Chen XR (2002) Effect of hydroartemisinin on lupus BXSB mice. Chin J Dermatovenerol Integr Tradit West Med 1:19–20
Langroudi L, Hassan ZM, Ebtekar M et al (2010) A comparison of low-dose cyclophosphamide treatment with artemisinin treatment in reducing the number of regulatory T cells in murine breast cancer model. Int Immunopharmacol 10:1055–1061
Botros SS, Mahmoud MR, Moussa MM et al (2007) Immunohistopathological and biochemical changes in Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice treated with artemether. J Infect 55:470–477
Zhang LX, Liu ZN, Ye J et al (2014) Artesunate exerts an anti-immunosuppressive effect on cervical cancer by inhibiting PGE2 production and Foxp3 expression. Cell Biol Int 38:639–646
Azimi Mohamadabadi M, Hassan ZM, Zavaran Hosseini A et al (2013) Arteether exerts antitumor activity and reduces CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ T-reg cells in vivo. Iran J Immunol 10:139–149
Noori S, Hassan ZM (2011) Dihydroartemisinin shift the immune response towards Th1, inhibit the tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Cell Immunol 271:67–72
Ramacher M, Umansky V, Efferth T (2009) Effect of artesunate on immune cells in ret-transgenic mouse melanoma model. Anti Cancer Drug 20:910–917
Ho WE, Peh HY, Chan TK et al (2014) Artemisinins: pharmacological actions beyond anti-malarial. Pharmacol Ther 142:126–139
Tawfik AF, Bishop SJ, Ayalp A et al (1990) Effects of artemisinin, dihydroartemisinin and arteether on immune responses of normal mice. Int J Immunopharmacol 12:385–389
Hou L, Block KE, Huang H (2014) Artesunate abolishes germinal center B cells and inhibits autoimmune arthritis. PLoS One 9:e104762
Yang ZS, Wang JX, Zhou Y et al (2006) Synthesis and immunosuppressive activity of new artemisinin derivatives. Part 2: 2-[12(beta or alpha)-dihydroartemisinoxymethyl(or 1′-ethyl)]phenoxyl propionic acids and esters. Bioorg Med Chem 14:8043–8049
Zhang JX, Wang JX, Zhang Y et al (2006) Synthesis and immunosuppressive activity of new artemisinin derivatives containing polyethylene glycol group. Acta Pharm Sin B 41:65–70 (in Chinese)
Wu Y, He S, Bai B et al (2016) Therapeutic effects of the artemisinin analog SM934 on lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice via inhibition of TLR-triggered B-cell activation and plasma cell formation. Cell Mol Immunol 13:379–390
Zhou ZH, Chen FX, Xu WR et al (2013) Enhancement effect of dihydroartemisinin on human gammadelta T cell proliferation and killing pancreatic cancer cells. Int Immunopharmacol 17:850–857
Clark RL, Brannen KC, Sanders JE et al (2011) Artesunate and artelinic acid: association of embryotoxicity, reticulocytopenia, and delayed stimulation of hematopoiesis in pregnant rats. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol 92:52–68
Li LN, Zhang HD, Yuan SJ et al (2008) Differential sensitivity of colorectal cancer cell lines to artesunate is associated with expression of beta-catenin and E-cadherin. Eur J Pharmacol 588:1–8
Xu H, He Y, Yang X et al (2007) Anti-malarial agent artesunate inhibits TNF-alpha-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines via inhibition of NF-kappaB and PI3 kinase/Akt signal pathway in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology 46:920–926
Lei Y, Yang C, Li C et al (2016) Recent advances in biosynthesis of bioactive compounds in traditional Chinese medicinal plants. Sci Bull 61:3–17
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91529305, 81427805, 81302507, 81302809, 31401611, 81573161, and 81502122), the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2014AA020524), the CAS/SAFEA International Partnership Program for Creative Research Teams of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (14391901800), and the Key Laboratory of Food Safety Research of INS, SIBS, CAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, W., Wang, F. & Wang, H. Immunomodulation of artemisinin and its derivatives. Sci. Bull. 61, 1399–1406 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1105-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1105-z