Abstract
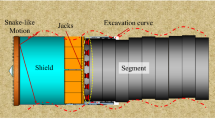
The earth pressure balance (EPB) shield cutterhead structure, which features an opening ratio and opening distribution as a core, seriously affects tunneling stability and tunneling efficiency. This paper presents a new model for the soil using visco-plastic fluid theory, and then introduces the model into the computational-fluid-dynamics model to comprehensively analyze the cutterhead structure, which consists of the soil, the cutterhead, the working chamber, and the screw conveyor. Based on this model, the stability situation and tunneling performance of multiple schemes of the cutting head structure are analyzed by changing the opening ratio and the opening distribution on the cutterhead. In this study, a new method for design and analysis of the EPB-shield cutterhead structure is proposed that fits changes in geologic conditions. The results will be helpful for engineers and manufacturers of more efficient machines and for carrying out tunneling projects with more stable EPB-shield cutterheads, and it will reduce the influences of changing geologic conditions during all stages of tunnel construction.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang HY, Shi H, Gong GF et al (2009) Earth pressure balance control for EPB shield. Sci China Ser E Technol Sci 52:2840–2848
Burger W (2007) Design principles for soft ground cutterheads. Proc Rapid Excav Tunn 784–792
Maidl U (1999) Design features of the Botlek Rail Tunnel in the Betuweroute. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 14:135–140
Motai T (1969) Mechanical shield tunnelling of two-track tunnel in Kintetsu-Namba line. Planning and recent construction progress. J Jpn Soc Civil Eng 54:10–16
Xu QW, Zhu HH, Ding WQ et al (2011) Laboratory model tests and field investigations of EPB shield machine tunnelling in soft ground in Shanghai. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 26:1–14
Shi H, Yang HY, Gong GF et al (2011) Determination of the cutterhead torque for EPB shield tunneling machine. Autom Construct 20:1087–1095
Wen WL, Feng PF, Wu ZJ et al (2009) Study on external load domain of shield machine cutterhead. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5928, pp 1176–1182
Qu F Z, Wu L, Sun W (2009) Analysis of chamber pressure for earth pressure balance shield machine by discrete numerical model. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5298, pp 402–411
Wu L, Qu FZ (2009) Discrete element simulation of mechanical characteristic of conditioned sands in earth pressure balance shield tunneling. J Cent South Univ 16:1028–1033
Liu JQ, Guo W, Huang BQ et al (2011) Relationship between aperture ratio and fore-and-back pressure of EPB shield cutterhead. Trans Tianjin Univ 44:659–664 (in Chinese)
Karmakar S, Ashrafizadeh SR, Kushwaha RL (2009) Experimental validation of computational fluid dynamics modeling for narrow tillage tool draft. J Terramech 46:277–283
Karmakar S, Kushwaha RL (2005) Simulation of soil deformation around a tillage tool using computational fluid dynamics. Trans ASAE 48:923–932
Karmakar S, Kushwaha RL, Lague C (2007) Numerical modeling of soil stress and pressure distribution on a flat tillage tool using computational fluid dynamics. Biosyst Eng 97:407–414
Aluko OB, Chandler HW (2004) Characterisation and modelling of brittle fracture in two-dimensional soil cutting. Biosyst Eng 88:369–381
Aluko OB, Seig DA (2000) An experimental investigation of the characteristics and conditions for brittle fracture in two-dimensional soil cutting. Soil Tillage Res 57:143–157
Hogg AJ, Matson GP (2009) Slumps of viscoplastic fluids on slopes. J Non-Newton Fluid 158:101–112
Chen RP, Zhu J, Liu W et al (2011) Ground movement induced by parallel EPB tunnels in silty soils. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 26:163–171
Qiao JL, Liu JQ, Guo W et al (2010) Artificial neural network to predict the surface maximum settlement by shield tunneling. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6424, pp 257–265
Anagnostou G, Kovari K (1996) Face stability conditions with earth pressure balanced shields. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 11:165–173
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51275339, 2013CB035402).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Hu, J. & Liu, J. The scheme design for the earth pressure balance shield cutterhead structure. Chin. Sci. Bull. 59, 4589–4599 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0492-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0492-2