Abstract
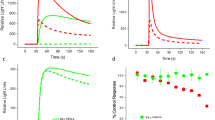
Na–K–Cl cotransporter 1 (NKCC1) cotransports Na+, K+, and Cl− ions across the plasma membrane into cells. Accumulation of Cl− ions in dorsal root ganglion neurons induces depolarizing GABAA receptors, which mediate presynaptic inhibition and filtration of sensory noise. The activity of the Na–K–Cl cotransporter is modulated by high-dose loop diuretics, such as furosemide and bumetanide. To identify NKCC1 modulators, we developed a functional cell-based assay feasible for high-throughput screening (HTS), in which the activity of NKCC1 was detected by a BTC-AM dye-based thallium transportation assay. We demonstrated that the influx of Tl+ was mediated by NKCC1, which required the existence of Cl− ions and could be inhibited by bumetanide and furosemide. Our results demonstrated that the assay was stable, reproducible, and suitable for HTS of negative modulators for NKCC1.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haas M (1989) Properties and diversity of Na–K–Cl cotransporters. Annu Rev Physiol 51:443–457
Lytle C, Forbush B 3rd (1996) Regulatory phosphorylation of the secretory Na–K–Cl cotransporter: modulation by cytoplasmic Cl. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 270:C437–C448
Palfrey HC, O’Donnell ME (1992) Characteristics and regulation of the Na–K–2Cl cotransporter. Cell Physiol Biochem 2:293–307
Palfrey HC, Greengard P (1981) Hormone-sensitive ion transport systems in erythrocytes as models for epithelial ion pathways. Ann N Y Acad Sci 372:291–308
Palfrey HC (1994) Protein phosphorylation control in the activity of volume sensitive transport systems. In: Strange K (ed) Cellular and molecular physiology of cell volume regulation. Boca Raton, Florida, pp 201–214
Lytle C (1997) Activation of the avian erythrocyte Na–K–Cl cotransport protein by cell shrinkage, cAMP, fluoride, and calyculin-A involves phosphorylation at common sites. J Biol Chem 272:15069–15077
Delpire E, Rauchman MI, Beier DR et al (1994) Molecular cloning and chromosome localization of a putative basolateral Na+–K+–2Cl− cotransporter from mouse inner medullary collecting duct (mIMCD-3) cells. J Biol Chem 269:25677–25683
Payne JA, Xu JC, Haas M et al (1995) Primary structure, functional expression, and chromosomal localization of the bumetanide-sensitive Na–K–Cl cotransporter in human colon. J Biol Chem 270:17977–17985
Alvarez-Leefmans FJ, Gamiño SM, Giraldez F et al (1988) Intracellular chloride regulation in amphibian dorsal root ganglion neurones studied with ion-selective microelectrodes. J Physiol 406:225–246
Sung KW, Kirby M, McDonald MP et al (2000) Abnormal GABAA receptor-mediated currents in dorsal root ganglion neurons isolated from Na–K–2Cl cotransporter null mice. J Neurosci 20:7531–7538
Willis WD Jr (1999) Dorsal root potentials and dorsal root reflexes: a double-edged sword. Exp Brain Res 124:395–421
Laird JM, García-Nicas E, Delpire EJ et al (2004) Presynaptic inhibition and spinal pain processing in mice: a possible role of the NKCC1 cation-chloride co-transporter in hyperalgesia. Neurosci Lett 361:200–203
Granados-Soto V, Arguelles CF, Alvarez-Leefmans FJ (2005) Peripheral and central antinociceptive action of Na+–K+–2Cl− cotransporter blockers on formalin-induced nociception in rats. Pain 114:231–238
Price TJ, Cervero F, de Koninck Y (2005) Role of cation-chloride-cotransporters (CCC) in pain and hyperalgesia. Curr Top Med Chem 5:547–555
Pieraut S, Laurent-Matha V, Sar C et al (2007) NKCC1 phosphorylation stimulates neurite growth of injured adult sensory neurons. J Neurosci 27:6751–6759
Rybak LP (1993) Ototoxicity of loop diuretics. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 26:829–844
Ikeda K, Oshima T, Hidaka H et al (1997) Molecular and clinical implications of loop diuretic ototoxicity. Hear Res 107:1–8
Delpire E, Lu J, England R et al (1999) Deafness and imbalance associated with inactivation of the secretory Na–K–2Cl co-transporter. Nat Genet 22:192–195
Delpire E, Days E, Lewis LM et al (2009) Small-molecule screen identifies inhibitors of the neuronal K–Cl cotransporter KCC2. Proc Natl Acad USA Sci 106:5383–5388
Schomberg SL, Bauer J, Kintner DB et al (2003) Cross talk between the GABAA receptor and the Na–K–Cl cotransporter is mediated by intracellular Cl−. J Neurophysiol 89:159–167
Weaver CD, Harden D, Dworetzky SI et al (2004) A thallium sensitive, fluorescence-based assay for detecting and characterizing potassium channel modulators in mammalian cells. J Biomol Screen 9:671–677
Zhang JH, Chung TD, Oldenburg KR (1999) A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J Biomol Screen 4:67–73
Payne JA (1997) Functional characterization of the neuronal-specific K–Cl cotransporter: implications for [K+]o regulation. Am J Physiol 273:C1516–C1525
Holtzman EJ, Kumar S, Faaland CA et al (1998) Cloning, characterization, and gene organization of K–Cl cotransporter from pig and human kidney and C. elegans. Am J Physiol 275:F550–F564
Xu JC, Lytle C, Zhu TT et al (1994) Molecular cloning and functional expression of the bumetanide-sensitive Na–K–Cl cotransporter. Proc Natl Acad USA Sci 91:2201–2205
Williams JR, Payne JA (2004) Cation transport by the neuronal K+–Cl− cotransporter KCC2: thermodynamics and kinetics of alternate transport modes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 287:C919–C931
Isenring P, Jacoby SC, Payne JA et al (1998) Comparison of Na–K–Cl cotransporters: NKCC1, NKCC2, and the HEK cell Na–K–Cl cotransporter. J Biol Chem 273:11295–11301
Nardou R, Ben-Ari Y, Khalilov I (2009) Bumetanide, an NKCC1 antagonist, does not prevent formation of epileptogenic focus but blocks epileptic focus seizures in immature rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 101:2878–2888
Lee HA, Jeong H, Kim EY et al (2003) Bumetanide, the specific inhibitor of Na+–K+–2Cl− cotransport, inhibits 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced osteoclastogenesis in a mouse co-culture system. Exp Physiol 88:569–574
Gillen CM, Forbush B 3rd (1999) Functional interaction of the K–Cl cotransporter (KCC1) with the Na–K–Cl cotransporter in HEK293 cells. Am J Physiol 276:C328–C336
Gamba G (2005) Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of electroneutral cation-chloride cotransporters. Physiol Rev 85:423–493
Keller AF, Beggs S, Salter MW et al (2007) Transformation of the output of spinal lamina I neurons after nerve injury and microglia stimulation underlying neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 3:27
Ma LH, Deng Y, Zhang B et al (2012) Pinacidil, a Katp channel opener, identified as a novel agonist for TRPA1. Chin Sci Bull 57:1810–1817
Yin Q, Zhuang DM, Jiang YQ et al (2010) Establishment of a high-throughput screening system for universal anti-HIV targets. Chin Sci Bull 55:937–942
Willis EF, Clough GF, Church MK (2004) Investigation into the mechanisms by which nedocromil sodium, frusemide and bumetanide inhibit the histamine-induced itch and flare response in human skin in vivo. Clin Exp Allergy 34:450–455
Mazzone SB, McGovern AE (2006) Na+–K+–2Cl− cotransporters and Cl− channels regulate citric acid cough in guinea pigs. J Appl Physiol 101:635–643
Haas M, McBrayer D, Lytle C (1995) [Cl−]i dependent phosphorylation of the Na–K–Cl cotransport protein of dog tracheal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 270:28955–28961
Lytle C, Forbush B 3rd (1992) The Na–K–Cl cotransport protein of shark rectal gland. II. Regulation by direct phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 267:25438–25443
Lytle C, McManus T (2002) Coordinate modulation of Na–K–2Cl cotransporter and K–Cl cotransporter by cell volume and chloride. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:C1422–C1431
Zhang D, Gopalakrishnan SM, Freiberg G et al (2010) A thallium transport FLIPR-based assay for the identification of KCC2-positive modulators. J Biomol Screen 15:177–184
Carmosino M, Rizzo F, Torretta S et al (2013) High-throughput fluorescent-based NKCC functional assay in adherent epithelial cells. BMC Cell Biol 14:16
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by “Significant new drugs creation” science and technology major special “Twelfth Five” plan, and Key Technology Research of GPCR targeting Drug Screening and Mechanism of Action Studies Project (2012ZX09301003-003). We thank HD Biosciences for providing the instruments and compounds used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Y., Ma, L. & Li, S. Development of a functional cell-based HTS assay for identification of NKCC1-negative modulators. Chin. Sci. Bull. 59, 630–638 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-013-0083-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-013-0083-7