Abstract
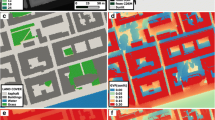
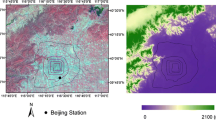
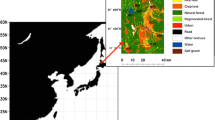
An urban net all-wave radiation parameterization scheme is evaluated using annual datasets for 2010 recorded at a Beijing urban observation site. The statistical relationship between observed data and simulation data of net radiation has a correlation coefficient of 0.98 and model efficiency of 0.93. Therefore, it can be used to simulate the radiation balance of Beijing. This study analyzes the variation in the radiation balance for different underlying surfaces. To simulate radiation balance differences, we set four pure land-cover types (forest, grass, roads, and buildings). Keeping all other conditions inputted unchanged, we model the radiation balance by changing the land-cover type. The results show that the effects of different underlying surfaces on radiation differ, and that there is much upward long-wave radiation, accounting for 84.3% of the total radiation energy falling incident on the land surface. The annual averages of net radiation for the four land-cover types are in the range of 38.2–53.4 W/m2. The net radiation of the grass surface is minimal while that of the roads surface is maximal. Additionally, with urbanization the net radiation values of common types of land-cover change, such as conversion from forest to roads, grass to roads, and grass to buildings, all have increasing trends, indicating that net radiation usually increases with urban sprawl.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Yin Y H, Wu S H, Dai E F. Determining factors in potential evapotranspiration changes over China in the period 1971–2008. Chin Sci Bull, 2010, 55: 3329–3337
Dabberdt W F, Lenschow D H, Horst T W, et al. Atmosphere-surface exchange measurements. Science, 1993, 260: 1472–1481
Arnfield A J. Two decades of urban climate research: A review of turbulence, exchanges of energy and water, and the urban heat island. Int J Climatol, 2003, 23: 1–26
Wang X Q, Gong Y B. The impact of an urban dry island on the summer heat wave and sultry weather in Beijing City. Chin Sci Bull, 2010, 55: 1657–1661
Zhang H Y, Rao S, Chi Y Y, et al. Advances in the impacts of urban landscape pattern on urban air environment (in Chinese). Adv Earth Sci, 2006, 21: 1025–1032
Tong H, Chan J C L, Sang J G. A study of the urban boundary layer model and its applicatin in the Hong Kong area (in Chinese). Chin J Atmos Sci, 2004, 28: 957–978
White J M, Eaton F D, Auer A H. The net radiation budget of the St. Louis metropolitan area. J Appl Meteorol, 1978, 17: 593–599
Christen A, Vogt R. Energy and radiation balance of a central European city. Int J Climatol, 2004, 24: 1395–1421
Peng J L, Wu X, Jiang Z H, et al. Characteristics analysis of energ budget over urban and suburban underlying surfaces in Nanjing (in Chinese). Sci Meteorol Sin, 2008, 28: 21–29
Offerle B, Grimmond C S B, Oke T R. Parameterization of net all-wave radiation for urban areas. J Appl Meteorol, 2003, 42: 1157–1173
U.S. Environmental Proection Agency. Pcrammet User’s Guide, Technical Report. In: U.S. Environmental Proection Agency, Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards, Emissions, Monitoring, and Analysis Division. 1999. 95
Prata A. A new long-wave formula for estimating downward clear-sky radiation at the surface. Q J Roy Meteor Soc, 1996, 122: 1127–1151
Batlles F J, Olmo F J, Tovar J, et al. Comparison of cloudless sky parameterizations of solar irradianceat various spanish midlatitude Locations. Theor Appl Climatol, 2000, 66: 81–93
Loridan T, Grimoond C S B, Offerle B D, et al. Local-scale urban meteorological parameterization scheme (LUMPS): Longwave radiation parameterization and seasonality-related developments. J Appl Meteorol Climatol, 2011, 50: 185–202
Holtslag A A M, van Ulden A P. A simple scheme for daytime estimates of the surface fluxes from routine weather data. J Appl Meteorol, 1983, 22: 517–529
van Ulden A P, Holtslag A A M. Estimation of atmospheric boundary layer parameters for diffusion applications. J Clim Appl Meteorol, 1985, 24: 1196–1207
de Rooy W, Holtslag A A M. Estimation of surface radiation and energy flux densities from single-level weather data. J Appl Meteorol, 1999, 38: 526–540
Grimmond C S B, Oke T R. Turbulent heat fluxes in urban areas: Observations and a local-scale urban meteorological parameterization scheme (LUMPS). J Appl Meteorol, 2002, 41: 792–810
Oke T R. The heat island of the urban boundary layer: Characteristics, causes and effects. In: Cermak J E, Davenport A G, Plate E J, et al., eds. Wind Climate in Cities. Waldbronn: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1995. 81–107
Grimmond C, Blackett M, Best M, et al. Initial results from Phase 2 of the international urban energy balance comparison project. Int J Climatol, 2011, 31: 244–272
Oke T R. Boundary Layer Climate. London: Routledge Press, 1987
Zhou S Z, Shu T. Urban Climatology (in Chinese). Beijing: Chinese Meteorological Press, 1994. 156
Grimmond C S B, Blackett M, Best M J, et al. The international urban energy balance models comparison project: First results from phase 1. J Appl Meteorol Climatol, 2010, 49: 1268–1292
Wang X, Zhou G Y, Sun G, et al. Characteristic of radiation flux of coniferous and broadleaved mixed forest in low subtropical China (in Chinese). J Beijing Forestry Univ, 2006, 28: 28–34
Oke T R, Shen J Z (translator). A review on water, radiation, and energy balance in urban climate (in Chinese). Prog Geogr, 1983, 2: 25–30
Badescu V. Verification of some very simple clear and cloudy sky models to evaluate global solar irradiance. Sol Energy, 1998, 61: 251–264
Crawford T M, Duchon C E. An improved parameterization for estimating effective atmospheric emissivity for use in calculating daytime down-welling, long-wave radiation. J Appl Meteorol, 1999, 38: 474–480
Niemelä S, Räisänen P, Savijärvi H. Comparison of surface radiative flux parameterizations: Part II. Shortwave radiation. Atmos Res, 2001, 58: 141–154
Sailor D J, Fan H. Modeling the diurnal variability of effective albedo for cities. Atmos Environ, 2002, 36: 713–725
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Y., Liu, J., Hu, Y. et al. Modeling the radiation balance of different urban underlying surfaces. Chin. Sci. Bull. 57, 1046–1054 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-011-4933-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-011-4933-x