Abstract
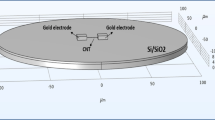
Patterned flow sensor cell consisting of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) network and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) are fabricated, based on the process of vacuum filtration, photolithography, and plasma etching. The sensor cell is a composite thin film and packaged to form a flow sensor, and then tested in different flow rates with different liquids, such as deionized (DI) water and NaCl solution. The induced-voltage increases with increasing flowing velocity and liquid concentration. The relation between induced-voltage and sensor cell conductivity is tested in the same liquid at the same flow rate. The higher the conductivity is, the higher the induced-voltage is. Some of the SWCNTs are fixed in the PDMS matrix, simultaneously some of them protrude above the composite thin film, which are exposed to the liquid and contribute to the voltage generation. The fabrication method can make the flow sensor scaled down to dimensions on the order of micrometers, which makes it suitable in very small liquid volumes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iijima S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature, 1991, 354: 56–58
Barone P W, Baik S, Heller D A, et al. Near-infrared optical sensors based on single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nat Mater, 2005, 4: 86–92
Thess A, Lee R, Nikolaev P, et al. Crystalline ropes of metallic carbon nanotubes. Science, 1996, 273: 483–487
Artukovic E, Kaempgen M, Hecht D S, et al. Transparent and flexible carbon nanotube transistors. Nano Lett, 2005, 5: 757–760
Im J, Kang J, Lee M, et al. Selective adsorption and alignment behaviors of double- and multiwalled carbon nanotubes on bare Au and SiO2 surfaces. J Phys Chem B, 2006, 110: 12839–12842
Hu L, Hecht D S, Gruner G. Percolation in transparent and conducting carbon nanotube networks. Nano Lett, 2004, 4: 2513–2517
Moore V C, Strano M S, Haroz E H, et al. Individually suspended single-walled carbon nanotubes in various surfactants. Nano Lett, 2004, 3: 1379–1382
Hu L B, Gruner G. Electrowetting devices with transparent single-walled carbon nanotube electrodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90: 093124
Zhou Y X, Hu L B, Gruner G. A method of printing carbon nanotube thin films. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 88: 123109
Ghosh S, Sood A K, Kumar N. Carbon nanotube flow sensors. Science, 2003, 299: 1042–1044
Ghosh S, Sood A K, Ramaswamy S, et al. Flow-induced voltage and current generation in carbon nanotubes. Phys Rev B, 2004, 70: 205423
Liu J W, Dai L M, Baur J W. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes for flow-induced voltage generation. J Appl Phys, 2007, 101: 064312
Andrew M H Ng, Hartadi L T, Tan H W, et al. Efficient coating of transparent and conductive carbon nanotube thin films on plastic substrates. Nanotechnology, 2008, 19: 205703
Lu S, Panchapakesan B. Nanotube micro-optomechanical actuators. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 88: 253107
Bernards D A, Biegala T, Samuels Z A, et al. Organic light-emitting devices with laminated top contacts. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 84: 3675–3677
Reyes D R, Lossifidis D, Auroux P A, et al. Micro total analysis systems. 1. Introduction, theory, and technology. Anal Chem, 2002, 74: 2623–2636
Kral P, Shapiro M. Nanotube electron drag in flowing liquids. Phys Rev Lett, 2001, 86: 131–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, H., Lü, Q., Song, X. et al. Fabrication and characterization of patterned carbon nanotube flow sensor cell. Chin. Sci. Bull. 55, 2579–2583 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-010-3024-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-010-3024-8