Abstract
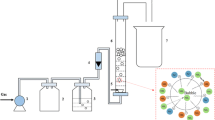
Based on the traditional method of high concentration ammonia removal from wastewater, a mixture mainly consisting of ethyl lactate and acetic acid is used as an aid for ammonia removal by air stripping. The effect of dosage, the depth of air nozzle in water and other conditions for ammonia removal were investigated. The results show that under the conditions that denitrification reagent is in the dosage of 30 mg/L, pH value is 9–11, blowing depth is 400 mm, stripping time is greater than 2.5 h, and the temperature is normal (25°C), the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in wastewater can be reduced from 21006.0 mg/L to 10.6 mg/L. The ammonia nitrogen removal rate is up to 99.95%. At the temperature of 45°C, the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in wastewater can be decreased from 21006 mg/L to 0.2 mg/L. The ammonia nitrogen removal rate is up to 99.999%. When the wastewater ammonia concentration is between 800–30000 mg/L, the ammonia is air stripped under the above mentioned conditions, the residual concentration can be below 15 mg/L. The stripped ammonia can be absorbed without secondary pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deng T, Qu Y X, Che Y K. Mass transfer properties of aqueous organic mixtures under conditions of purging (in Chinese). J Beijing Univ Chem Technol, 2006, 33: 89–92
Hamanoi O, Kudo A. Reduction of nitrate and nitrite ions over Ni-ZnS photocatalyst under visible light irradiation in the presence of a sacrificial reagent. Chem Lett, 2002, 8: 838–839
Hu Y L, Zhang J C, Zhai W, et al. The test of air stripping of ammoniac wastewater from pharmaceutical industry (in Chinese). Ind Water Treat, 1999, 19: 192–211
Kato H, Kudo A. Photocatalytic reduction of nitrate ions over tantalate photocatalysts. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2002, 4: 2833–2838
Khin T, Annachhatre A P. Novel microbial nitrogen removal processes. Biotechnol Adv, 2004, 22: 519–532
Kominami H. Selective photocatalytic reduction nitrate to nitrogen Molecule in an aqueous suspension of metal loaded titanium(IV) oxide particle. Chem Commun, 2005, 23: 2293–2295
Li X T, Liu L F, Yang F L, et al. Nitrogen removal via coupled ammonia oxidation and nitrite reduction using Pt/TiO2 and photocatalysis (in Chinese). Chin J Inorg Chem, 2006, 22: 1180–1186
Li Y, Zhang R, Li H S, et al. Catalytic wet air oxidation of ammonia in landfill leachates in the presence of Co/Bi catalyst (in Chinese). Chem Res Chin Univ, 2005, 26: 430–435
Lukow T, Diekmann H. Aerobic denitrification by a newly isolated heterotrophic bacterium strain TL1. Biotechnol Lett, 1997, 11: 1157–1159
Shen X Y, Sun J J, Ma Z Y, et al. Influence of surfactants on the evaporation of naphthalene from static water (in Chinese). China Environ Sci, 2004, 24: 196–200.
Shen X Y, Sun J J, Ma Z Y, et al. Effect of surfactant on the evaporation of BTEX from static water (in Chinese). Environ Sci, 2005, 26: 122–126.
Wang Q, Zhang Y, Miao Q, et al. Initio study on nH2O…mNH3 hydrogen-bonded clusters (in Chinese). Comput Appl Chem, 2002, 19: 267–269
Wang Y L. Treatment of ammonia nitrogen wastewater by ultrasonic stripping (in Chinese). Tech Equip Environ Pollut, 2001, 2: 59–63
Wu S, Ling S P, Duan J G. Removal of basic nitrogen in coking gatch by means of compound denitrogenating agent (in Chinese). J Daqing Pet Inst, 2007, 31: 54–57
Xu G Q, Zeng G M, Yin Z W, et al. Recent advances on the treatment technologies of ammonia-nitrogen wastewater (in Chinese). Hunan Nonferr Met, 2002, 18: 29–33
Xu Y P, Chen D H, Xu H Q. Experimental study on the treatment of ammonium chloride wastewater by reverse osmosis (in Chinese). Ind Water Treat, 2005, 25: 29–30
Zhang H Z, Yan Q Z, Fang S M, et al. Treatment of ammonia nitrogen in landfill leachate by combined membranes-anionic surfactant method (in Chinese). Chem Eng (China), 2008, 36: 37–40
Zhang Y, Wang Q, Hong X, et al. Initio study on hydrogen bonding networks in acetic acid-water clusters (in Chinese). Comput Appl Chem, 2002, 19: 441–444
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, C., Ma, J., Li, D. et al. Composite denitrification reagent for high concentration ammonia removal by air stripping. Chin. Sci. Bull. 55, 2657–2661 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-3587-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-3587-4