Abstract
Adaptation is one of the most fundamental issues in the studies of organismal evolution. Pancreatic ribonuclease is a very important digestive enzyme and secreted by the pancreas. Numerous studies have suggested that RNASE1 gene duplication is closely related to the functional adaptation of the digestive system in the intestinal fermentation herbivores. RNASE1 gene thus becomes one of the most important candidate genetic markers to study the molecular mechanism of adaptation of organisms to the feeding habit. Interestingly, RNASE1 gene duplication has also been found in some non-intestinal fermentation mammals, suggesting that RNASE1 gene may have produced novel tissue specificity or functions in these species. In this review, RNASE1 gene and its implications in adaptive evolution, especially in association with the feeding habit of organisms, are summarized.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nei M, Gu X, Sitnikova T. Evolution by the birth-and-death process in multigene families of the vertebrate immune system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1997, 94: 7799–7806
Nei M, Rogozin L B, Piontkivska H. Purifying selection and birth-and-death evolution in the ubiquitin gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2000, 97: 10866–10871
Zhang J, Rosenberg H F, Nei M. Positive Darwinian selection after gene duplication in primate ribonuclease genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1998, 95: 3708–3713
Shi P, Zhang J, Yang H, et al. Adaptive diversification of bitter taste receptor genes in mammalian evolution. Mol Biol Evol, 2003, 20: 805–814
Li X, Yang S, Peng L X, et al. Origin and evolution of new genes. Chinese Sci Bull, 2004, 49: 1120–1125
Robbins L S, Nadeau J H, Johnson K R, et al. Pigmentation phenotypes of variant extension locus alleles result from point mutations that alter MSH receptor function. Cell, 1993, 72: 827–834
Takeuchi S H, Suzuki S, Hirose Y, et al. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the chick melanocortin 1-receptor gene. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1996, 1306: 122–126
Rosenblum E B, Hoekstra H E, Nachman M W. Adaptive reptile color variation and the evolution of the Mc1r gene. Evolution, 2004, 58: 1794–1808
Gojobori J, Innan H. Potential of fish opsin gene duplications to evolve new adaptive functions. Trends Genet, 2009, 25: 198–202
Okoyama S, Yokoyama R. Adaptive evolution of photoreceptors and visual pigments in vertebrates. Annu Rev Ecol Syst, 1996, 27: 543–567
Shi P, Zhang J Z, Yang H, et al. Adaptive Diversification of bitter taste receptor genes in mammalian evolution. Mol Biol Evol, 2003, 20: 805–814
Shi P, Zhang J. Contrasting modes of evolution between vertebrate sweet/umami receptor genes and bitter receptor genes. Mol Biol Evol, 2006, 23: 292–300
Shi P, Zhang J. Comparative genomic analysis identifies an evolutionary shift of vomeronasal receptor gene repertoires in the vertebrate transition from water to land. Genome Res, 2007, 17: 166–174
Wu H H, Su B. Adaptive evolution of SCML1 in primates, a gene involved in male reproduction. BMC Evol Biol, 2008, 8: 192
Ota T, Nei M. Divergent evolution and evolution by the birth-and-death process in the immunoglobulin VH gene family. Mol Biol Evol, 1994, 11: 469–482
Makova K D, Li W H. Divergence in the spatial pattern of gene expression between human duplicate genes. Genome Res, 2003, 13: 1638–1645
Barnard E A. Biological function of pancreatic ribonuclease. Nature, 1969, 221: 340–344
Beintema J J, Gaastra W, Lenstra J A, et al. The molecular evolution of pancreatic ribonuclease. J Mol Evol, 1977, 10: 49–71
Beintema J J, Fitch W M, Carsana A. Molecular evolution of pancreatic-type ribonucleases. Mol Biol Evol, 1986, 3: 262–275
Beintema J J. The primary structure of langur (Presbytis entellus) pancreatic ribonuclease: adaptive features in digestive enzymes in mammals. Mol Biol Evol, 1990, 7: 470–477
D’Alessio G, Floridi A, De Prisco R, et al. Bull semen ribonucleases 1 purification and physico-chemical properties of the major component. Eur J Biochem, 1972, 26: 153–161
Suzuki H, Parente A, Farina B, et al. Complete amino-acid sequence of bovine seminal ribonuclease, a dimeric protein from seminal plasma. Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler, 1987, 368: 1305–1312
Beintema J J, Neuteboom B. Origin of the duplicated ribonuclease gene in guinea-pig: Comparison of the amino acid sequences with those of two close relatives: capybara and cuis ribonuclease. J Mol Evol, 1983, 19: 145–152
Kleineidam R G, Pesole G, Breukelman H J, et al. Inclusion of cetaceans within the order Artiodactyla based on phylogenetic analysis of pancreatic ribonuclease genes. J Mol Evol, 1999, 48: 360–368
Breukelman H J, Jekel P A, Dubois J Y, et al. Secretory ribonucleases in the primitive ruminant chevrotain (Tragulus javanicus). Eur J Biochem, 2001, 268: 3890–3897
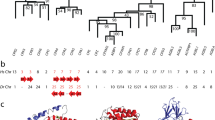
Dubois J Y, Jekel P A, Mulder P P, et al. Pancreatic-type ribonuclease 1 gene duplications in rat species. J Mol Evol, 2002, 55: 522–533
Dubois J Y, Ursing B M, Kolkman J A, et al. Molecular evolution of mammalian ribonucleases 1. Mol Phyl Evol, 2003, 27: 453–463
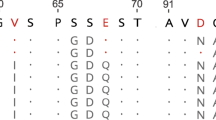
Zhang J, Zhang Y P, Rosenberg H F. Adaptive evolution of a duplicated pancreatic ribonuclease gene in a leaf-eating monkey. Nat Genet, 2002, 30: 411–415
Zhang J. Parallel adaptive origins of digestive RNases in Asian and African leaf monkeys. Nat Genet, 2006, 38: 819–823
Schienman J E, Holt R A, Auerbach M R, et al. Duplication and divergence of 2 distinct pancreatic ribonuclease genes in leaf-eating African and Asian colobine monkeys. Mol Biol Evol, 2006, 23: 1465–1479
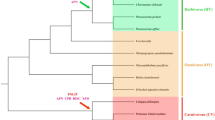
Yu L, Zhang Y P. The unusual adaptive expansion of pancreatic ribonuclease gene in carnivora. Mol Biol Evol, 2006, 23: 2326–2335
D’Alession G, Riordan J F. RNASEs Structures and Functions. New York: Academic Press, 1996
Beintema J J, Breukelman H J, Carsana A, et al. Evolution of vertebrate ribonucleases: ribonuclease A superfamily. In: D’Alessio G, Riordan J F, eds. Ribonucleases Structures and Functions. San Diego: Academic Press, 1997. 245–269
Beintema J J, Kleineidam R G. The ribonuclease A superfamily: General discussion. Cell Mol Life Sci, 1998, 54: 825–832
Cho S, Beintema J J, Zhang J. The ribonuclease A superfamily of mammals and birds: Identifying new members and tracing evolutionary histories. Genomics, 2005, 85: 208–220
Golding G B, Dean A M. The structural basis of molecular adaptation. Mol Biol Evol, 1998, 15: 355–396
Blackburn P, Moore S. Pancreatic ribonuclease. In: Boyer P D, ed. The Enzymes. Vol 15. New York: Academic Press, 1982
Beintema J J, Schuller C, Irie M, et al. Molecular evolution of the ribonuclease superfamily. Prog Biophys Mol Biol, 1988, 51: 165–192
Sasso M P, Carsana A, Confalone E, et al. Molecular cloning of the gene encoding the bovine brain ribonuclease and its expression in different regions of the brain. Nucleic Acids Res, 1991, 19: 6469–6474
Watanabe H, Katoh H, Ishii M, et al. Primary structure of a ribonuclease from bovine brain. J Biochem, 1988, 104: 939–945
Sasso M P, Lombardi M, Confalone E, et al. The differential pattern of tissue-specific expression of ruminant pancreatic type ribonucleases may help to understand the evolutionary history of their genes. Gene, 1999, 227: 205–212
Zhao W, Confalone E, Breukelman H J, et al. Ruminant brain ribonucleases. Expression and evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2001, 1547: 95–103
Beintema J J, Scheffer A J, Van Dijk H, et al. Pancreatic ribonuclease distribution and comparisons in mammals. Nat New Biol, 1973, 241: 76–78
Futami J, Tsushima Y, Murato Y, et al. Tissue-specific expression of pancreatictype RNases and RNase inhibitor. DNA Cell Biol, 1997, 16: 413–419
Libonati M, Floridi A. Breakdown of double-stranded RNA by bull semen ribonuclease. Eur J Biochem, 1969, 8: 81–87
Sorrentino S, Libonati M. Structure-function relationships in human ribonucleases: Main distinctive features of the major RNASE types. FEBS Lett, 1997, 404: 1–5
Libonati M, Sorrentino S. Degradation of double-stranded RNA by mammalian pancreatic-type ribonucleases. Methods Enzymol, 2001, 341: 234–248
Weickmann J L, Glitz D G. Human ribonucleases: Quantitation of pancreatic like enzymes in serum, urine and organ preparations. J Biol Chem, 1982, 257: 8705–8710
Beintema J J, Blank A, Schieven G L, et al. Differences in glycosylation pattern of human secretory ribonucleases. Biochem J, 1988, 255: 501–505
Ohno S. Evolution by Gene Duplication. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 1970
Clegg M T, Cummings M P, Durbin M L. The evolution of plant nuclear genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1997, 94: 7791–7798
Force A, Lynch M, Pickett F, et al. Preservation of duplicate genes by complementary degenerative mutations. Genetics, 1999, 151: 1531–1545
Zhang J. Evolution by gene duplication: an update. Trends Ecol Evol, 2003, 18: 292–298
Sorrentino S, Naddeo M, Russo A, et al. Degradation of double-stranded RNA by human pancreatic ribonuclease: crucial role of noncatalytic basic amino acid residues. Biochemistry, 2003, 42: 10182–10190
Zhang J. Parallel functional changes in the digestive RNases of ruminants and colobines by divergent amino acid substitutions. Mol Biol Evol, 2003, 20: 1310–1317
Kay R N B, Davies A G. Digestive physiology. In: Davies A G, Olates J F, eds. Colobine Monkeys: Their Ecology, Behaviour and Evolution. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1994
Delson E. Evolutionary history of the colobine monkeys in paleoenvironmental perspective. In: Davies A G, Oates J F, eds. Colobine Monkeys: Their Ecology, Behaviour, and Evolution. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1994
Stewart C B, Wilson A C. Sequence convergence and functional adaptation of stomach lysozymes from foregut fermenters. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol, 1987, 52: 891–899
Schaller G B, Teng Q T, Johnson K G, et al. The feeding ecology of giant pandas and Asiatic black bears in the Tanjiahe Reserve, China. In: Gittleman J L, ed. Carnivore Behavior, Ecology and Evolution. New York: Cornell University Press, 1989. 212–241
Neil A S, Kimberly D, Zhang J Z, et al. Rapid evolution of the ribonuclease a superfamily: adaptive expansion of independent gene clusters in rats and mice. J Mol Evol, 1999, 49: 721–728
Dubois J Y, Catzeflis F M, Beintema J J. The phylogenetic position of “Acomyinae” (Rodentia, Mammalia) as sistergroup of a murinae1 gerbillinae clade: evidence from the nuclear ribonuclease gene. Mol Phyl Evol, 1999, 13: 181–192
Beintema J J, Lenstra J A. Evolution of mammalian pancreatic ribonucleases. In: Goodman M, ed. Macromolecular Sequences in Systematic and Evolutionary Biology. New York: Plenum, 1982. 43–73
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This work was supported by the State Key Basic Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2007CB411600) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U0836603).
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Li, N., Yu, L. et al. Duplication and functional diversification of pancreatic ribonuclease (RNASE1) gene. Chin. Sci. Bull. 55, 2–6 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0717-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0717-y