Abstract
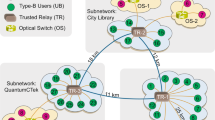
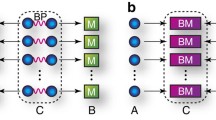
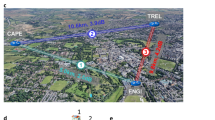
A hierarchical metropolitan quantum cryptography network upon the inner-city commercial telecom fiber cables is reported in this paper. The seven-user network contains a four-node backbone net with one node acting as the subnet gateway, a two-user subnet and a single-fiber access link, which is realized by the Faraday-Michelson interferometer set-ups. The techniques of the quantum router, optical switch and trusted relay are assembled here to guarantee the feasibility and expandability of the quantum cryptography network. Five nodes of the network are located in the government departments and the secure keys generated by the quantum key distribution network are utilized to encrypt the instant video, sound, text messages and confidential files transmitting between these bureaus. The whole implementation including the hierarchical quantum cryptographic communication network links and the corresponding application software shows a big step toward the practical user-oriented network with a high security level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muller A, Herzog T, Huttner B, et al. “Plug and play” systems for quantum cryptography. Appl Phys Lett, 1997, 70: 793–795
Gobby C, Yuan Z L, Shields A J. Quantum key distribution over 122 km of standard telecom fiber. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 84: 3762–3764
Mo X F, Zhu B, Han Z F, et al. Faraday-Michelson system for quantum cryptography. Opt Lett, 2005, 30: 2632–2634
Zhao Y, Qi B, Ma X F, et al. Experimental quantum key distribution with decoy states. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 96: 070502
Takesue H, Nam S W, Zhang Q, et al. Quantum key distribution over a 40-dB channel loss using superconducting single-photon detectors. Nat Photonics, 2007, 1: 343–348
Bennett C H, Brassard G. Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, 1984. 175–179
Gisin N, Ribordy G, Tittel W, et al. Quantum cryptography. Rev Mod Phys, 2002, 74: 145–195
Zeng G H, Keitel C H. Arbitrated quantum-signature scheme. Phys Rev A, 2002, 65: 042312
Chen K, Lo H K. Multi-partite quantum cryptographic protocols with noisy GHZ states. Quant Inform Comput, 2007, 7: 689–715
Xiao L, Long G L, Deng F G, et al. Efficient multiparty quantum-secret sharing schemes. Phys Rev A, 2004, 69: 052307
Yan F L, Gao T, Li Y C. Quantum secret sharing between multiparty and multiparty with four states. Sci China Ser G, 2007, 50: 572–580
Townsend P D, Phoenix S J D, Blow K J, et al. Quantum cryptography for multi-user passive optical networks. Electron Lett, 1994, 30: 1875
Townsend P D. Quantum cryptography on multi-user optical fibre networks. Nature, 1997, 385: 47–49
Elliott C. Building the quantum network. New J Phys, 2002, 4: 46.1–46.12
Chen W, Han Z F, Zhang T, et al. Field experimental “star type” metropolitan quantum key distribution network. IEEE Photonics Tech Lett, 2009, 21: 575–577
Poppe A, Peev M, Maurhart O. Outline of the SECOQC quantumkey- distribution network in Vienna. Int J Quantum Inf, 2008, 6: 209–218
Chen T Y, Liang H, Liu Y, et al. Field test of a practical secure communication network with decoy-state quantum cryptography. Optics Express, 2009, 17: 6540–6549
Han Z F, Mo X F, Gui Y Z, et al. Stability of phase-modulated quantum key distribution systems. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86: 221103
Chen W, Han Z F, Mo X F, et al. Active phase compensation of quantum key distribution system. Chinese Sci Bull, 2008, 53: 1310–1314
Subacius D, Zavriyev A, Trifonov A. Backscattering limitation for fiber-optic quantum key distribution systems. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86: 011103
Zhang T, Mo X F, Han Z F, et al. Extensible router for a quantum key distribution network. Phys Lett A, 2008, 372: 3957–3962
Tang X, Ma L J, Mink A, et al. Demonstration of an active quantum key distribution network. Proc SPIE, 2006, 6305: 630506
Wen H, Han Z F, Guo G C, et al. The queuing model for quantum key distribution network. Chin Phys B, 2009, 18: 46–50
Wang W Y, Wang C, Zhang G Y, et al. Arbitrarily long distance quantum communication using inspection and power insertion. Chinese Sci Bull, 2009, 54: 158–162
Wen H, Han Z F, Zhao Y B, et al. Multiple stochastic paths scheme on partially-trusted relay quantum key distribution network. Sci China Ser F, 2009, 52: 18–22
Hwang W Y. Quantum key distribution with high loss: Toward global secure communication. Phys Rev Lett, 2003, 91: 057901
Wang X B. Beating the photon-number-splitting attack in practical quantum cryptography. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 94: 230503
Lo H K, Ma X F, Chen K. Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 94: 230504
Wang X B. Decoy-state protocol for quantum cryptography with four different intensities of coherent light. Phys Rev A, 2005, 72: 012322
Gottesman D, Lo H K, Lutkenhaus N, et al. Security of quantum key distribution with imperfect devices. Quant Inform Comput, 2004, 5: 325–360
Ma X F, Qi B, Zhao Y, et al. Practical decoy state for quantum key distribution. Phys Rev A, 2005, 72: 012326
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported by the Wuhu Government and China Telecommunications Corporation, Wuhu Branch, and National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2006CB921900), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 60537020, 60621064) and Innovation Funds of Chinese Academy of Sciences
Electronic supplementary material
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Chen, W., Wang, S. et al. Field experiment on a robust hierarchical metropolitan quantum cryptography network. Chin. Sci. Bull. 54, 2991–2997 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0526-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0526-3