Abstract
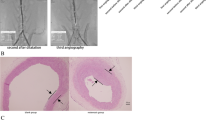
In this study, the effect of simvastatin on the atherosclerotic plaque stability and the angiogenesis in the atherosclerotic plaque of rabbits was observed. Thirty New Zealand rabbits were randomly divided into the normal control group, the model control group and the simvastatin group, 10 in each group. Rabbits in the normal control group were fed with normal forage, while rabbits in the rest two groups were fed with high fat forage. The balloon injury was performed two weeks later to establish an abdominal aortic atherosclerosis model, and then high fat forage was successively fed to them. Meanwhile, simvastatin at the daily dose of 2.5 mg/kg body weight was administered to rabbits in the simvastatin group. After 6 weeks of successive administration, levels of blood lipids were measured after blood sampling, and the serum high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) and matrix metalloproteinase-3,-9 (MMP-3,-9) were detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The macroscopically pathological indices of the plaque tissue were observed using hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining of abdominal aorta specimens under a light microscope, and the plaque area (PA), cross-sectional vascular area (CVA) and correcting plaque area (PA/CVA) were determined quantitatively using imaging software. The protein expressions of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), factor VIII related antigen (FVIIIRAg), MMP-3 and cluster of differentiation antigen 40 ligand (CD40L) in the plaque were detected with the immunohistochemical method. Compared with the model control group, the levels of VEGF, FVIIIRAg, MMP-3, CD40L protein expression and the serum expression levels of hsCRP, MMP-3, MMP-9 in the simvastatin group were significantly reduced (P<0.05, P<0.01). The ratio PA/CVA in the simvastatin group was more significantly reduced when compared with that in the model control group (P<0.01). The levels of serum total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL) were significantly reduced in the simvastatin group when compared with those in the model control group (P<0.05, P<0.01). Simvastatin plays a certain role in stabilizing the atherosclerotic plaque, and inhibiting the angiogenesis in the atherosclerotic plaque may be one of possible mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ross J, Staglian N, Donovan M, et al. Atheroselerosis and cancer: Common molecular pathways of disease development and progression. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2001, 947: 271–292
Sacco R L, Liao J K. Drug Insight: statins and stroke. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med, 2005, 2: 576–584
Wilson S H, Herrmann J, Lerman L O, et al. Simvastatin preserves the structure of coronary adventitial vasa vasorum in experimental hypercholesterolemia independent of lipid lowering. Circulation, 2002, 105: 415–418
Thrall G, Lane D, Carroll D, et al. A systematic review of the effects of acute psychological stress and physical activity on haemorheology, coagulation, fibrinolysis and platelet reactivity: Implications for the pathogenesis of acute coronary syndromes. Thromb Res, 2007, 120: 819–847
Sun L, Wei L X, Shi H Y, et al. The relation between angiogenesis and the plaque stability in the atherosclerotic plaque (in Chinese). Chin J Pathol, 2003, 32: 427–431
Xia C D, Yin H J. Progress of researches on pleiotropic effects of statins in improving endothelial functions (in Chinese). Adv Cardiovasc Dis, 2008, 29: 956–960
Rudd J H, Machac J, Favad Z A. Simvastatin and plaque inflammation. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2007, 48: 1825–1831
Schlager O, Exner M, Mlekusch W, et al. C-reactive protein predicts future cardiovascular events in patients with carotid stenosis. Stroke, 2007, 38: 1263–1268
Abilleira S, Bevan S, Markus H S. The role of genetic variants of matrix metalloproteinases in coronary and carotid atherosclerosis. J Med Genet, 2006, 43: 897–901
San Miguel Hernandez A, Inglada-Galiana L, Garcia Iglesias R, et al. Soluble CD40 ligand: a potential marker of cardiovascular risk. Rev Clin Esp, 2007, 207: 418–421
Caldwell R B, Bartoli M, Behzadian M A, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor and diabetic retinopathy: role of oxidative stress. Curr Drug Targets, 2005, 6: 511–524
Panutsopulos D, Papalambros E, Sigala F, et al. Protein and mRNA expression levels of VEGF-A and TGF-beta1 in different types of human coronary atherosclerotic lesions. Int J Mol Med, 2005, 15: 603–610
Galbusera M, Zoja C, Donadelli R, et al. Fluid shear stress modulates von Willebrand factor release from human vascular endothelium. Blood, 1997, 90: 1558–1564
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Key Basic Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2006CB504803)
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Jiang, Y., Xue, M. et al. Effect of simvastatin on the atherosclerotic plaque stability and the angiogenesis in the atherosclerotic plaque of rabbits. Chin. Sci. Bull. 54, 3061–3066 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0509-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0509-4