Abstract
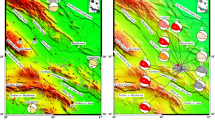
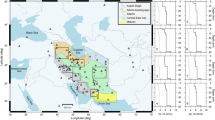
Moment tensor solutions of 88 earthquakes were determined by using the broadband waveform data recorded in six stations within 450 km around the Wenchuan Earthquake sequence by means of the time domain moment tensor inversion method. It was found that the type of the focal mechanism solution is characteristic of obvious spatial segmentation. There are six segments along the main rupture zone from southwest to northeast, where initially the focal mechanism is of main thrust type, finally of main right-lateral strike-slip type and between these two areas there is a transition zone characterized in multiple types of focal mechanisms appearing in turn. Earthquakes of left-lateral strike-slip type perpendicular to the main rupture zone occurred near Xiaoyudong Town. The stress field of each segment is inversed by means of the FMSI program, and it was found that, along the main rupture zone from southwest to northeast, the direction of the maximum principal stress is gradually changing from near EW to NW-SE, and finally changing back to near EW.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang P Z, Xu X W, Wen X Z, et al. Slip rates and recurrence intervals of the Longmen Shan active fault zone, and tectonic implications for the mechanism of the May 12 Wenchuan earthquake, 2008, Sichuan, China (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 2008, 51: 1066–1073
Xu X W, Wen X Z, Yu S E, et al. Discovery of the Wenchuan M8.0 earthquake surface ruptures and discussion for its seismogenic structure (in Chinese). Seismol Geol, 2008, 30: 597–629
Wang C Y, Herrmann R B. A numerical study of P, SV, SH-wavegeneration in a plane layered medium. Bull Seism Soc Am, 1980, 70: 1015–1036
Herrmann R B, Wang C Y. A comparison of synthetic seismograms. Bull Seism Soc Am, 1985, 75: 41–56
Tajima F, Mégnin F, Dreger D S. Feasibility of real-time broadband waveform inversion for simultaneous moment tensor and centroid location determination. Bull Seism Soc Am, 2002, 92: 739–750
Gephart J W, Forsyth D W. An improved method for determining the regional stress tensor using earthquake focal mechanism data: application to the San Fernando earthquake sequence. J Geophys Res, 1984, 89: 9305–9320
Gephart J W. Stress and the direction of slip on fault planes. Tectnics, 1990, 845–858
Wyss M B, Lu Z. Plate boundary segment by stress directions: Southern San Andreas fault, California. Geophys Res Lett, 1995, 22: 547–550
Wyss M B, Liang W R, Wu X. Comparison of orientations of stress and strain tensors based on fault plane solutions in Kaoiki, Hawaii. J Geophys Res, 1992, 97: 4769–4790
Wang C Y, Wu J P, Lou H, et al. P-wave crustal structure in western Sichuan and eastern Tibetan region (in Chinese). Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 2003, 46(Supp): 254–265
Wang Ch Y, Mooney W D, Wang X L, et al. A study on 3-D velocity structure of crust and upper mantle in Sichuan-Yunnan region (in Chinese). Acta Seismol Sin, 2002, 24: 1–16
Fukuyama E, Dreger D S. Performance test of an automated moment tensor determination system for the future “tokai” earthquake. Earth Planet Space, 2000, 52: 383–39
Pasyanos M E, Dreger D S, Romanowicz. Towards real-time determination of regional moment tensors. Bull Seism Soc Am, 1996, 86: 1255–1269
Romanowicz B, Dreger D S, Pasyanos M, et al. Monitoring of strain release in central and northern California using broadband data. Geophys Res Let, 1993, 20: 1634–1646
Zoback M L. First- and second-order patterns of stress in the lithosphere: the world stress map project. J Geophys Res, 1992, 97: 11703–11728
Zhou S Y, Xu Z H, Chen X F. Analysis on the source characteristics of the 1997 Jiashi swarm, Western China (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 2001, 44: 654–662
Zhu A L, Xu X W, Zhou Y S, et al. Relocation of the small earthquakes in western Sichuan, China and its implications for active tectonics (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 2005, 48: 629–636
Ratchkovski N A. Change in stress direction along the central Denali fault, Alaska after the 2002 earthquake sequence. Geophys Res Lett, 2003, 30: 2017, doi:10.1029/2003gl017905
Wang Q, Zhang P Z, Freymueller J T, et al. Present-day crustal deformation in China constrained by Global Positioning System (GPS) measurements. Science, 2001, 294: 574–577
Wang Q, Zhang P Z, Ma Z J, et al. GPS database and velocity field of contemporary tectonic deformation in continental china. Earth Sci Front, 2002, 9: 415–429
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Key Project of Scientific and Technical Supporting Programs Funded by Ministry of Science & Technology of China (Grant No. 2008BAC38B02 and 2006BAC01B02), National Department Public Benefit Research Foundation (Grant No. 200708026)
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Chen, Z. & Zheng, S. Spatial segmentation characteristic of focal mechanism of aftershock sequence of Wenchuan Earthquake. Chin. Sci. Bull. 54, 2263–2270 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0367-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0367-0