Abstract
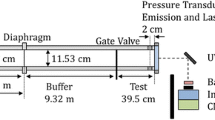
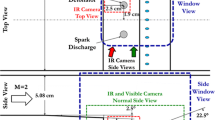
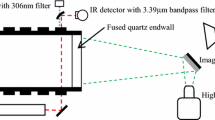
Ignition of methane/air mixture by the passage of a shock wave is an important issue for understanding more details of its gaseous detonation. The experiments of shock-induced ignition of stoichiometric methane/air mixture were conducted on a shock tube platform. The reaction zone structure in weak and strong ignition cases were investigated by digital chemiluminescence imaging and planar laser induced fluorescence (PLIF) techniques. Due to smaller gradients in induced time in weak ignition, which provided more time to nonlinear chemical reaction process, the results show that the reaction structures are highly nonuniform in those weak ignition cases, which become more regular while induced shock waves become stronger. In strong ignition case, it gives a typical detonation structure. The characteristics of reaction zone released by single-pulsed OH PLIF technique agreed well with other experimental measurements in this paper and were also in accord with the conclusions of previous researches. The successful implementation of the PLIF system has explored a new high temporally and spatially resolved method for the study of interaction between shock wave and gaseous matter in shock tube.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharpe G J, Short M. Ignition of thermally sensitive explosives between a contact surface and a shock. Phys of Fluid, 2007, 19: 126102
Oran E S, Young T R, Boris J P, et al. Weak and strong ignition. I. Numerical simulations of shock tube experiments. Comb & Flame, 1982, 48: 135–148
Cheng R K, Oppenheim A K. Autoignition in methane-hydrogen mixtures. Comb & Flame, 1984, 58: 125–139
Brown C J, Thomas G O. Experimental studies of shock induced ignition and transition to detonation in ethylene and propane mixture. Comb & Flame, 1999, 117: 861–870
Herzler J, Jerig L, Roth P. Shock tube study of the ignition of lean n-heptane/air mixtures at intermediate temperatures and high pressures. Proceed Comb Inst, 2005, 30: 1147–1153
Wang C J, Xu S L, Fei L S. Study on reaction zone structure of gaseous detonation wave by planar laser induced fluorescence technique. Acta Mech Sinica, 2007, 39: 661–667
Gray J. A shock tube with tunable, pulsed laser-based diagnostics. Rev Sci Instrum, 1990, 61: 071825
Seta T, Nakajima M, Miyoshi A, et al. Development of a technique for high-temperature chemical kinetics: Shock tube/pulsed laser-induced fluorescence imaging method. Rev Sci Instrum, 2005, 76: 064103
McMillin B K, Lee M P, Hanson R K. Planar laser-induced fluorescence imaging of shock-induced ignition. Proceed Comb Inst, 1990, 23: 1909–1914
Han Z Y, Wang Z Q, Yin X Z, et al. An experimental technique of electrically controlled double driver shock tube for studying head-on moving shock-bow shock interaction. Acta Mech Sinica, 1982, 4: 394–400
Oran E S, Gamezo V N. Origins of the deflagration to detonation transition in gas-phase combustion. Comb & Flame, 2007, 148: 4–47
Liang Z, Browne S, Shepherd J E, et al. Detonation front structure and competition for radicals. Proceed Comb Inst, 2007, 31: 2445–2453
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National High Technology R & D Program of China (Grant No. 2006AA05Z210) and Graduated Student Research Foundation of Chinese Acdemy Science
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Ma, C., Wang, B. et al. Direct observations of reaction zone structure in shock-induced ignition of methane air mixture. Chin. Sci. Bull. 54, 2247–2255 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0125-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0125-3