Abstract
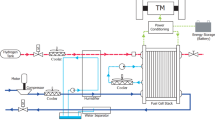
Constructed here is a mathematic model of PEM Fuel Cell Vehicle Power System which is composed of fuel supply model, fuel cell stack model and water-heat management model. The model was developed by Matlab/Simulink to evaluate how the major operating variables affect the output performances. It shows that the constructed model can represent characteristics of the power system closely by comparing modeling results with experimental data, and it can be used in the study and design of fuel cell vehicle power system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weber A Z, Newman J. Modeling transport in polymer-electrolyte fuel cells. Chem Rev, 2004 104(10): 4679–4726
Kim J, Lee S M, Srinivasan S. Modeling of proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance with an empirical equation. J Electrochem Soc, 1995 142(8): 2670–2674
del Real A J, Arce A, Bordons C. Development and experimental validation of a PEM fuel cell dynamic model. J Power Sources, 2007 173(1): 310–324
Bao C, Ouyang M G, Yi B L. Modeling and optimization of the air system in polymer exchange membrane fuel cell systems. J Power Sources, 2006 156(2): 232–243
Nguyen T V, White R E. A water and heat management model for proton-exchange-membrane fuel cells. J Electrochem Soc, 1993 140(8): 2178–2186
Amphlett J C, Baumert R M, Mann R F, et al. Performance modeling of the ballard mark IV solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell. J Electrochem Soc, 1995 142(1): 1–8
Mann R F, Amphlett J C, Hooper M A I, et al. Development and application of a generalised steady-state electrochemical model for a PEM fuel cell. J Power Sources, 2000 86(1–2): 173–180
Andujar J M, Segura F, Vasallo M J. A suitable model plant for control of the set fuel cell-DC/DC converter. Renew Energ, 2008 33(4): 813–826
Lin B. Conceptual design and modeling of a fuel cell scooter for urban Asia. J Power Sources, 2000 86(1–2): 202–213
Hirchenhofer J H. Fuel Cell Handbook. 5th ed. Morgantown, West Virginia: National Energy Technology Laboratory Press, 2000
Uzunoglu M, Alam M S. Dynamic modeling, design and simulation of a PEM fuel cell/ultra-capacitor hybrid system for vehicular applications. Energ Convers Manage, 2007 48(5): 1544–1553
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2007AA05Z145), State Key Development Program for Basic Research of China (Grant No. 2007cb209707) and Shanghai Science and Technology Project (Grant Nos. 06SN07115 and 07JC14024)
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Lin, Z. & Ma, Z. Process modeling of fuel cell vehicle power system. Chin. Sci. Bull. 54, 972–977 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0068-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0068-8