Abstract
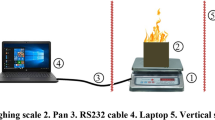
The use of water mist to extinguish fire is a problem of particular interest since the banning of halogen-based agents for environmental reasons. This interest is reflected in the large number of researches performed on the main fire-extinguishing mechanisms of water mist: heat extraction, oxygen displacement and attenuation of heat fluxes. In contrast, there are still little known about the chemical and some other aspects of water mist addition on the pool fire. In this paper, a phenomenological study was conducted of the effect of water mist addition on the kerosene pool fire through the measurement of the heat release rate, CO, CO2 and O2 species concentration in combustion. The experimental results show that there is a significant enhancement effect at the beginning stage of water mist addition. Then, the flame size was decreased abruptly. By physical suppression effect combined with chemical effect, the experiments’ results are explained especially. The study of effects of water mist on pool fire will be useful for optimizing designation of water mist fire-suppression system, improving the fire suppression efficiency and extending their application field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robert E T. Halon fire extinguishing substitutes. Fire Saf Mag, 2001, 6–11
Yang W H, Robert J K. The Effect of monodispersed water mists on the structure, burning velocity, and extinction behavior of freely propagating, stoichiometric, premixed, methane-air flames. Comb Flam, 2002, 130(4): 322–335
Zhou X M, Liao G X, Cai B. Improvement of water mist fire-extinguishing efficiency with MC additive. Fire Saf J, 2006, 41(1): 39–45
Heskestad G. Extinction of gas and liquid pool fires with water sprays. Fire Saf J, 2003, 38(4): 301–317
Richard J, Garo J P, Souil J M, et al. On the flame structure at the base of a pool fire interacting with a water mist. Exp Therm Fluid Sci, 2003, 27(4): 439–448
Prasad K, Patnaik G, Kailasanath K. A numerical study of water-mist suppression of large scale compartment fires. Fire Saf J, 2002, 37 (6): 569–589
Jiang Z, Chow W K, Tang J, et al. Preliminary study on the suppression chemistry of water mists on poly(methylmethacrylate) flames. Polym Degrad Stab, 2004, 86(2): 293–300
Manzello S L, Yang J C, Cleary T G. On the interaction of a liquid droplet with a pool of hot cooking oil. Fire Saf J, 2003, 38(7): 651–659
Yang W H, Parker T, Ladouceur H D, et al. The interaction of thermal radiation and water mist in fire suppression. Fire Saf J, 2004, 39(1): 41–66
Lian Z X, Chao X, Li F. Numerical simulation of water-mist in confined space. Mech Manage Dev, 2008, 23(1): 27–28
Atreya A, Crompton T, Such J. A study of the chemical and physical mechanisms of fire suppression by water. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium. July 5–9, 1999, Poitiers, France, 1999, 7: 493–504
Morita M, Minami T, Kikkawn A. Suppression mechanism of water mist for poll fire. Fift Meet UJNR Pan Fire Res Saf, 2000, (1): 273–279
Liu Z, Kim A K. A review of water mist fire suppression systems-fundamental studies. J Fire Prot Eng, 2000, 10(3): 32–50
Qin J, Liao G X, Wang X S, et al. Water mists measurement of the flow field of the water mist by 3D LDV. Chin J Quant Electron, 2001, 18(3): 281–284
Qin J, Weng W G. Preliminary study of water mist suppressing ghee flame in historical building in the northwest China. J Cult Her, 2006, 7(4): 329–333
ASTM. Standard Test Method for Health and Visible Smoke Release Rates for Materials and Products Using an Oxygen Consumption Calorimeter. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, 1990
Liang Q S, Liang Q Q, Xu W Y. Water mist characteristics and its fire suppression mechanism. Fire Sci Tech, 2005, 24(4): 447–451
Liu Z G, Kim A K, Carpenter D. A study of portable water mist fire extinguishers used for extinguishment of multiple fire types. Fire Saf J, 2007, 42(1): 25–42
Richard J, Garo J P, Souil J M, et al. On the flame structure at the base of a pool fire interacting with a water mist. Exp Therm Fluid Sci, 2003, 27(4): 439–448
Liu C, Jia C G. Numerical study of water spray suppression of single room fire by zone model. J Comb Sci Tech, 2004, 10(4): 308–313
Wang X S, Liao G X, Qin J, et al. Experimental study on effectiveness of extinction of a pool fire with water mist. J Fire Sci, 2002, 20(4): 279–295
Richard J, Garo J P, Souil J M, et al. Chemical and physical effects of water vapor addition on diffusion flames. Fire Saf J, 2003, 38(6): 569–587
Schofield D P, Kjaergard H G. High-level ab initio studies of the electronic excited states of the hydroxyl radical and water-hydroxyl complex. J Chem Phys, 2004, 120(15): 6930–6934
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2001CB409600) and Opening Fund of State Key Laboratory of fire Science, University of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. HZ2006-KF10)
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Qin, J. & Liao, G. Effects of water mist addition on kerosene pool fire. Chin. Sci. Bull. 53, 3240–3246 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0437-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0437-8