Abstract
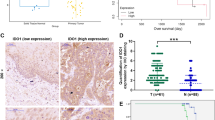
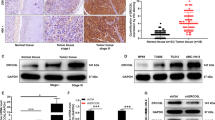
S100 calcium binding protein A8 (S100A8), a possible novel member of NF-kappa B signal pathway in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC), interacts with human leukocyte antigen B (HLA-B) which carries an NF-kappa B binding site within the enhancer A. The objective of this study was to explore the molecular mechanism of S100A8 in laryngeal carcinogenesis. RT-PCR, Western blotting and immunohistochemistry staining were applied to evaluate the expression levels of IKKα, P65, REL-B, S100A8, APAF-1 and BCL-2 genes. The signal transduction passway in which S100A8 might participate was explored by RNA interference. Flow cytometry, TUNEL assay and cell invasion in vitro were used to detect the biological behavior of Hep2 cells induced by S100A8 gene. Our results showed that high expression of S100A8 was related to tumorigenesis in LSCC and negatively correlated with the degree of differentiation, indicating that S100A8 gene could inhibit apoptosis and promote metastasis in LSCC. Additionally, the suppression of S100A8 by RNA interference down-regulated BCL-2 but not APAF-1, P65 and IKKα, while, the suppression of P65 could significantly down-regulate the expression of S100A8 gene. In conclusion, S100A8 plays an important role in P65/HLA-B/S100A8/BCL-2/Caspase-9 (−3) pathway in laryngeal carcinoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007, 57: 43–66
Busquets J M, Garcia H A, Trinidad-Pinedo J, et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in Puerto Ricans. P R Health Sci J, 2003, 22: 259–264
Marioni G, Marchese-Ragona R, Cartei G, et al. Current opinion in diagnosis and treatment of laryngeal carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev, 2006, 32(7): 504–515
Kerkhoff C, Klempt M, Sorg C. Novel insights into structure and function of MRP8 (S100A8) and MRP14 (S100A9). Biochim Biophys Acta, 1998, 1448: 200–211
Gebhardt C, Breitenbach U, Tuckermann J P, et al. Calgranulins S100A8 and S100A9 are negatively regulated by glucocorticoids in a c-Fosdependent manner and overexpressed throughout skin carcinogenesis. Oncogene, 2002, 21(27): 4266–4276
MacFarlane A J, Stover P J. Convergence of genetic, nutritional and inflammatory factors in gastrointestinal cancers. Nutr Rev, 2007, 65(12 Pt 2): S157–S166
Ishizuka M, Nagata H, Takagi K, et al. Inflammation-based prognostic score is a novel predictor of postoperative outcome in patients with colorectal cancer. Ann Surg, 2007, 246(6): 1047–1051
Stathopoulos G T, Sherrill T P, Cheng D S, et al. Epithelial NF-kappaB activation promotes urethane-induced lung carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007, 104(47): 18514–18519
Courtois G. The NF-kappaB signaling pathway in human genetic diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2005, 62(15): 1682–1691
Maeda S, Omata M. Inflammation and cancer: Role of nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Cancer Sci, 2008, 99(5): 836–842
Fu W, Guo Y, Huang D, et al. Novel partners of S100A8 identified in laryngeal cancer cell lines. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi (in Chinese), 2007, 24: 266–270
Gebhardt C, Németh J, Angel P, et al. S100A8 and S100A9 in inflammation and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol, 2006, 72(11): 1622–1631
Yao R, Davidson D D, Lopez-Beltran A, et al. The S100 proteins for screening and prognostic grading of bladder cancer. Histol Histopathol, 2007, 22(9): 1025–1032
El-Rifai W, Moskaluk C A, Abdrabbo M K, et al. Gastric cancers overexpress S100A calcium-binding proteins. Cancer Res, 2002, 62(23): 6823–6826
Seth A, Kitching R, Landberg G, et al. Gene expression profiling of ductal carcinomas in situ and invasive breast tumors. Anticancer Res, 2003, 23(3A): 2043–2051
Arai K, Teratani T, Nozawa R, et al. Immunohistochemical investigation of S100A9 expression in pulmonary adenocarcinoma: S100A9 expression is associated with tumor differentiation. Oncol Rep, 2001, 8(3): 591–596
Luo A, Kong J, Hu G, et al. Discovery of Ca2+-relevant and differentiation-associated genes downregulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using cDNA microarray. Oncogene, 2004, 23(6): 1291–1299
Stulik J, Osterreicher J, Koupilova K, et al. The analysis of S100A9 and S100A8 expression in matched sets of macroscopically normal colon mucosa and colorectal carcinoma: the S100A9 and S100A8 positive cells underlie and invade tumor mass. Electrophoresis, 1999, 20(4/5): 1047–1054
Shen J, Person M D, Zhu J, et al. Protein expression profiles in pancreatic adenocarcinoma compared with normal pancreatic tissue and tissue affected by pancreatitis as detected by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Cancer Res, 2004, 64(24): 9018–9026
Cross S S, Hamdy F C, Deloulme J C, et al. Expression of S100 proteins in normal human tissues and common cancers using tissue microarrays: S100A6, S100A8, S100A9 and S100A11 are all overexpressed in common cancers. Histopathology, 2005, 46(3): 256–269
Carlsson H, Petersson S, Enerback C. Cluster analysis of S100 gene expression and genes correlating to psoriasin (S100A7) expression at different stages of breast cancer development. Int J Oncol, 2005, 27(6): 1473–1481
Hermani A, Hess J, De Servi B, et al. Calcium-binding proteins S100A8 and S100A9 as novel diagnostic markers in human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res, 2005, 11(14): 5146–5152
Yui S, Nakatni Y, Mikami M. Calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9), an inflammatory protein complex from neutrophils with a broad apoptosis-inducing activity. Biol Pharm Bull, 2003, 26(6): 753–760
Newton R A, Hogg N. The human S100 protein MRP-14 is a novel activator of thebeta 2 integrin Mac-1 on neutrophils. J Immunol, 1998, 160: 1427–1435.
Kerkhoff C, Eue I, Sorg C. The regulatory role of MRP8 (S100A8) and MRP14 (S100A9) in the transendothelial migration of human leukocytes. Pathobiology, 1999, 67: 230–232
Gebhardt C, Breitenbach U, Tuckermann J P, et al. Calgranulins S100A8 and S100A9 are negatively regulated by glucocorticoids in a c-Fosdependent manner and overexpressed throughout skin carcinogenesis. Oncogene, 2002, 21(27): 4266–4276
Coultas L, Strasser A. The role of the Bcl-2 protein family in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol, 2003, 13: 115–123
Viemann D, Barczyk K, Vogl T, et al. MRP8/MRP14 impairs endothelial integrity and induces a caspase-dependent and-independent cell death program. Blood, 2007, 109(6): 2453–2460
Ott H W, Lindner H, Sarg B, et al. Calgranulins in cystic fluid and serum from patients with ovarian carcinomas. Cancer Res, 2003, 63: 7507–7514
Gobin S J, Keijsers V, van Zutphen M, et al. The role of enhancer A in the locus-specific transactivation of classical and nonclassical HLA class I genes by nuclear factor kappa B. J Immunol, 1998, 161: 2276–2283
Guo Y, Liu J, Xu Z, et al. HLA-B gene participates in NF-κB signal pathway partly by regulating S100A8 in the laryngeal carcinoma cell line Hep2. Oncol Rep. 2008, 19(6): 1453–1460
Yen T, Harrison C A, Devery J M, et al. Induction of the S100 chemotactic protein, CP-10, in murine microvascular endothelial cells by proinflammatory stimuli. Blood, 1997, 90(12): 4812–4821
Xu K, Geczy C L. IFN-gamma and TNF regulate macrophage expression of the chemotactic S100 protein S100A8. J Immunol, 2000, 164(9): 4916–4923
Klempt M, Melkonyan H, Hofmann H A, et al. Identification of epithelial and myeloid-specific DNA elements regulating MRP14 gene transcription. J Cell Biochem, 1999, 73(1): 49–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contributed equally to this work
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30171008) and National 863 Project of China (Grant No. 2002BA711A08-18)
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, D., Fu, W., Guo, Y. et al. S100A8 mediates the activation of P65/HLA-B/S100A8/BCL-2/Caspase-9 (−3) pathway in laryngeal carcinogenesis. Chin. Sci. Bull. 53, 2017–2024 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0238-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0238-0