Abstract
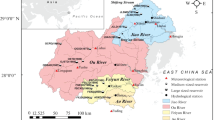
This paper applied wavelet analysis to examining change tendency, multi-time scale variations, periodic and abrupt change characteristics of suspended sediment flux (SSF) of the Panlong basin in the Upper Red River, China. The results indicated that the SSF had increased from 1951 to 1997, but declined since 1998. The variations of the SSF had multi-time scale characteristics and the fluctuations varied in different time periods. Three periodic time scales, 4, 7 and 22 years, were determined. The 22-year periodic time scale, which was the most obvious one among the three time scales, extended through the whole research period, whereas the 4-and 7-year time scales were obvious only in certain time periods. There were 27 times of abrupt changes across the 4-year time scale, 16 times across the 7-year time scale and 5 times across the 22-year time scale, respectively. On the basis of social statistical and climate data analysis, we concluded that the human activities were the main reason that led to the changing tendency of the SSF, but the characteristics of the multi-time scale, periodic and abrupt change were mainly influenced by climate variations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fu R S, Yu Z Y, Jin L, et al. Variation trend of runoff and sediment load in Yangtze River. J Hydr Engin (in Chinese), 2003, 34(11):21–29
Li Y, Li G X, Pan X D. Change on characteristics of runoff and sediment in the main stem of the Yellow River. J Sed Res (in Chinese), 2002, (4): 1–7
Ding W R, Wu Y D. Suspended sediment concentration (SSC) change characteristic and countermeasures of two kinds of landform of Yunnan province. Res Soil Water Conserv (in Chinese), 2007, 14(2): 106–107
He D M, Wu S H, Peng H, et al. A study of ecosystem changes in Longitudinal Range-Gorge Region and transboundary eco-security in southwest China. Adv Earth Sci (in Chinese), 2005, 20(3): 338–344
Zhu Y M, Lu X X, Zhou Y. Suspended sediment flux modeling with artificial neural network: An example of the Longchuanjiang River in the Upper Yangtze Catchment, China. Geomorphology, 2007, 84: 111–125
Zhu Y M, Lu X X, Zhou Y, et al. Runoff sensitivity to climate change in the Longitudinal Range-Gorge Region (LRGR): An example of the Longchuanjiang Basin in the Upper Yangtze. Chin Sci Bull, 2006, 51(Suppl.): 88–96
Merritt W S, Letcher R A, Jakeman A J. A review of erosion and sediment transport models. Environ Model Software, 2003, 18(8):761–799
Singh V P, Woolhiser D A. Mathematical modeling of watershed hydrology. J Hydrol Engin, 2002, 7(4): 270–292
Iadanza C, Napolitano F. Sediment transport time series in the Tiber River. Phys Chem Earth, 2006, 31(18): 1212–1227
Zhang S W, He W, Wang W S. Study on variation characters in ultra-Long period of annual natural flow of the Yellow River. Yellow River (in Chinese), 2004, 26(8): 10–12
Nakken M. Wavelet analysis of rainfall-runoff variability isolating climatic from anthropogenic patterns. Environ Model Software, 1999, 14(4): 283–295
Zhang J T, Li Z, Zheng D. Wavelet analysis of temperature and precipitation changes and their environmental effects. Geograph Res (in Chinese), 2002, 21(1): 54–60
Labat D, Goddéris Y, Probst J L. Evidence for global runoff increase related to climate warming. Adv Water Res, 2004, 27(6): 631–642
Liu H Y, Lin Z S, Zhang M Y. Wavelet Analysis of area affected by flood disaster in China after 1949. Sci Geograph Sin (in Chinese), 2005, 25(1): 43–48
Wang H R, Ye L T, Liu C M. Existed problems and improvement ways for wavelet periodical analysis of Hydrological sequence. Prog Nat Sci (in Chinese), 2006, 16(8): 1002–1008
Wang W S, Ding J, Li Y Q. Hydrology Wavelet Analysis (in Chinese). Beijing: Chemical Industrial Press, 2005. 64
Kumar P, Foufoula-Geogiou E. Wavelet analysis for geophysical applications. Rev Geophys, 1997, 35(4): 385–412
Wang W S, Ding J. Wavelet Network model and its application to the prediction of hydrology. Nat Sci, 2003, 1(1): 67–71
You W H. Multiscale Diagnosis Analyses and Forecast Methods of Climate Changes (in Chinese). Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 1998. 9–20
Ji Z P, Gu D J. Multiple time scales analysis of climate variation in Guangzhou during the last 100 years. J Trop Meteor (in Chinese), 1999, 15(1): 48–55
Lu X X, Higgitt D L. Sediment yields variability in the Upper Yangtze. Earth Surface Proc Landforms, 1999, 24(11): 1077–1093
Lu X X. Spatial variability and temporal change of water discharge and sediment flux in the lower Jinsha tributary: Impact of environmental changes. River Rese Appl, 2005, 21: 229–243
Ding W R, Zhou Y, Lu X X. Climate variation characteristic of the Panlong Basin during the last 50 years. J Hydraulic Engineering (in Chinese), submitted
Lu X X, Higgitt D L. Recent changes of sediment yield in the Upper Yangtze, China. Environ Manag, 1998, 22(5): 697–709
Lemke K A. Transfer function models of suspended sediment concentration. Water Res Rese, 1991, 27(3): 293–305
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the China 973 Program (Grant No. 2003CB415105-6)
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, W., Zhou, Y. & Lü, X. Suspended sediment flux of river: Wavelet analysis in the Panlong basin of the Upper Red River (Honghe River), China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 52 (Suppl 2), 172–179 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-7013-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-7013-5