Abstract
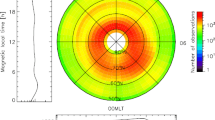
With energetic ion measurements on FAST satellite, the morphologic features of quiet-time ionospheric O+ ion upflowing at altitudes of 2000 to 4000 km are drawn out for the first time. The pre-noon cusp/cleft is the predominant region of upflowing occurrence for O+ with lower energy. Meanwhile the pre-dawn sector near the equatorward edge of the plasma convection dominates the occurrence for the higher energy O+ ions. No matter whether the energy is lower or higher, the upflows occur often over a wide MLT range of lower latitudes outside the auroral oval. The upflowing within the pre-midnight (21:00–22:00 MLT) auroral oval carrys larger energy fluxes, with extremely large fluxes for higher energy O+ appearing near the polar cap boundary. For altitudes of 2000–4200 km under observation, the ion conics occur much more frequently than ion beams. Ion beams are rarely found below 3000 km, while the conics occur uniformly over the observed altitudes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shelley E G, Johnson R G, Sharp R D. Satellite observations of energetic heavy ions during a geomagnetic storm. J Geophys Res, 1972, 77: 6104–6110
Shelley E G. Heavy ions in the magnetosphere. Space Sci Rev, 1979, 23: 465–497
Chappell C R, Giles B L, Moore T E, et al. The adequacy of the ionospheric source in supplying magnetospheric plama. J Atmos Terr Phys, 2000, 62: 421–436
Yau A W. Sources of ion outflow in the high latitude ionosphere. Space Sci Rev, 1997, 80: 1–25
Daglis I A. The role of magnetosphere-ionosphere coupling in magnetic storm dynamics. In: Tsurutani B T, Gonzalez W D, Kamide Y, et al. eds. Magnetic Storms, Geophysical Monograph 98-Magnetic storms. Washington, DC: AGU, 1997. 107–116
Klumpar D M, Transversely accelerated ions: an ionospheric source of hot magnetospheric ions. J Geophys Res, 1979, 84: 4229–4237
Gorney D J, Clarke A, Croley D, et al. The distribution of ion beams and conics below 8000 km. J Geophys Res, 1981, 86: 83–89
Yau A W, Beckwith P H, Peterson W K, et al. Long-term (solar-cycle) and seasonal variations of upflowing ionospheric ion events at DE-1 altitudes. J Geophys Res, 1985, 90: 6395–6407
Yau A W, Shelley E G, Peterson W K, et al. Energetic auroral and polar ion outflow at DE-1 altitudes: magnitude, composition, magnetic activity dependence and long-term variations. J Geophys Res, 1985, 90: 8417–8432
Kondo T, Whalen B A, Yau A W, et al. Statistical analysis of up-flowing ion beams and conic distributions at DE-1 altitudes. J Geophys Res, 1990, 95: 12091–12102
Thelin B, Aparicio B, Lundin R. Observations of upflowing ionospheric ions in the mid-altitude cusp/cleft region with the Viking satellite. J Geophys Res, 1990, 95: 5931–5939
Fuselier S A, Ghielmetti A G, Moore T E, et al. Ion outflow observed by IMAGE: implications for source regions and heating mechanisms. Geophys Res Lett, 2001, 28: 1163–1166
Pfaff R, Carlson C, Watzin J, et al. An overview of the fast auroral snapshot (FAST) satellite. Space Sci Rev, 2001, 98: 1–32
Möbius E, Tang L, Kistler L M, et al. Species dependent energies in upward directed ion beams over auroral ares as observed with FAST TEAMS. Geophys Res Lett, 1998, 25: 2029–2032
Lund E J, Möbius E, Klumpar D M, et al. Direct comparison of transverse ion acceleration mechanisms in the auroral region at solar minimum. J Geophys Res, 1999, 104: 22801–22805
Strangeway R J, Ergun R E, Su Y-J, et al. Factors controlling ionospheric outflows as observed at intermediate altitudes, J Geophys Res, 2005, 110(A03221): doi: 10.1029/2004JA010829
Wilson G R, Ober D M, Germany G A, et al. Nightside auroral zone and polar cap ion outflow as a function of substorm size and phase. J Geophys Res, 2004, 109(A02206): doi: 10.1029/2003JA009835
Andersson L, Peterson W K, McBryde K M. Dynamic coordinates for auroral ion outflow. J Geophys Res, 2004, 109(A08201): doi: 10.1029/2004JA010424
Andersson L, Peterson W K, McBryde K M. Estimates of the suprathermal O+ outflow characteristic energy and relative location in the auroral oval. Geophys Res Lett, 2005, 32(L09104): doi: 10.1029/2004GL021434
McFadden J P, Carlson C W, Ergun R E, et al. Spatial structure and gradients of ion beams observed by FAST. Geophys Res Lett, 1998, 25: 2021–2024
Klumpar D M, Möbius E, Kistler L M, et al. The time-of-flight energy, angle, mass spectrograph (TEAMS) experiment for FAST. Space Sci Rev, 2001, 98: 197–219
Carlson C W, Pfaff R F, Watzin J G. The fast auroral snapshot (FAST) mission. Geophys Res Lett, 1998, 25: 2013–2016
Tsyganenko N A. A model of the near magnetosphere with a dawn-dusk asymmetry: 1. Mathematical structure. J Geophys Res, 2002, 107(A8): doi: 10.1029/2001JA000219
Tsyganenko N A. A model of the near magnetosphere with a dawn-dusk asymmetry: 2. Parameterization and fitting to observations. J Geophys Res, 2002, 107(A8): doi: 10.1029/2001JA000220
Collin H L, Peterson W K, Lennartsson O W, et al. The seasonal variation of auroral ion beams. Geophys Res Lett, 1998, 25: 4071–4074
Janhunen P, Olsson A, Peterson W K. The occurrence frequency of upward ion beams in the auroral zone as a function of altitude using Polar/TIMAS and DE-1/EICS data. Ann Geophysicae, 2003, 21: 2059–2072
Feldstein Y I, Isaev S I, Lebedinsky A I, The phenomenology and morphology of aurorae. Ann IQSY, 1969, 4: 311–348
Seo Y, Caton R, Horwitz J L. Statistical relationship between high-latitude ionospheric F-region/topside upflows and their drivers: DE-2 observations. J Geophys Res, 1997, 102: 7493–7500
Liu C, Horwitz J L, Richards P G, Effects of convection ion heating and soft-electron precipitation on high-latitude F-region upflows. Geophys Res Lett, 1995, 22: 2713–2716
Su Y-J, Caton R G, Horwitz J L, et al. Systematic modeling of soft-electron precipitation effect on high-latitude F region and topside ionospheric upflows. J Geophys Res, 1999, 104: 153–163
Weimer D R. An improved model of ionospheric electric potentials including substorm perturbations and application to the Geospace Environment Modeling November 24, 1996 event. J Geophys Res, 2001, 106: 407–416
Horwitz J L, Moore T E. Four contemporary issues concerning ionospheric plasma flow to the magnetosphere. Space Sci Rev, 1997, 80: 49–76
Ma S Y, Liu H X, Schlegel K. A comparative study of magnetic storm effects on the ionosphere in the polar cap and auroral oval—F-region negative storm. Chin J Geophys (in Chinese), 2002, 45(2): 160–169
Liu H, Lu G. Velocity shear-related ion upflow in the low-altitude ionosphere. Ann Geophysicae, 2004, 22: 1149–1153
Ganguli G, Keskinen M J, Romero H, et al. Coupling of microprocesses and macroprocesses due to velocity shear: An application to the low-altitude ionosphere. Geophys Res Lett, 1986, 13: 893–896
Carpenter D, Lemaire J. The plasmasphere boundary layer. Ann Geophysicae, 2004, 22: 4291–4298
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 40390150)
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, G., Ma, S. & Zhou, Y. Morphology of polar ionospheric O+ ion upflow: FAST observations during quiet time. Chin. Sci. Bull. 52, 3403–3415 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0444-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0444-1