Abstract
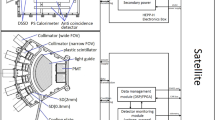
Using the data measured by energetic particle detector on board CBERS-01 and-02 for the past five years, statistics was made to show the general features of MeV electrons and protons along a solar synchronous orbit at an altitude of 780 km. This height is in the bottom region of the Earth’s radiation belts. Detectors are inside the satellite cabinet and such continuous monitoring of particle radiation environment inside a satellite has seldom conducted so far. After a proper and careful treatment, it is indicated that the data inside satellite are well correlated with the radiation environment outside. Besides the agreement of the general distribution characteristics of energetic electrons and protons with similar observations from other satellites, attention is particularly paid to the disturbed conditions. Variations of particle fluxes are closely related with solar proton events, in general, electron fluxes of outer belt are well correlated with Dst index after three days’ delay while the electron injection occurred almost at the same day during great magnetic storms. It is confirmed that both energetic electrons and protons appear in the Polar Cap region only after the solar proton events.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xiao Z, Zou J Q, Zou H, et al. Energetic particle detector on board ‘ZY-1’ satellite. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis (in Chinese), 2003, 39: 361–369
Baker D N. What is space weather? Adv Space Res, 1998, 22: 7–16
Garrett H B, Whittlesey A C. Spacecraft charging, an update. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci, 2000, 28: 2017–2028
Lauriente M, Koga R, Vampola A L, et al. Analysis of spacecraft anomalies due to the radiation environment. J Spacecraft Rockets, 1999, 36: 902–906
Zhu G W, Li B Q. Space environment effect and countermeasure research on spacecraft. Aerospace Shanghai (in Chinese), 2002, 18(4): 1–7
Baker D N, Mason G M, Figueroa O, et al. An overview of the Solar Anomalous, and Magnetospheric Particle Explorer (SAMPEX) mission. IEEE Trans Geosci and Remote Sensing, 1993, 31: 531–541
Wang S J, Zhu G W, Liang J B, et al. FY-1C space particle composition monitor and the results detected. Aerospace Shanghai (in Chinese), 2001, 18(2): 24–28
Li X, Baker D N, Kanekal S G, et al. Long term measurements of radiation belts by SAMPEX and their variations. Geophys Res Lett, 2001, 28: 3827–3830
Li X, Temerin M A. The electron radiation belt. Space Sci Rev, 2001, 95: 569–580
Baker D N, Klebesadel R W, Higbie P R, et al. Highly relativistic electrons in the earth’s outer magnetosphere: I — Lifetimes and temporal history 1979–1984. J Geophys Res, 1986, 91: 4265–4276
Baker D N, Blake J B, Callis L B, et al. Relativistic electron acceleration and decay time scales in the inner and outer radiation belts: SAMPEX. Geophys Res Lett, 1994, 21: 409–412
Li X, Baker D N, Temerin M, et al. Are energetic electrons in the solar wind the source of the outer radiation belt? Geophys Res Lett, 1997, 24: 923–926
Patterson J D, Armstrong T P, Laird C M, et al. Correlation of solar energetic protons and polar cap absorption. J Geophys Res, 2001, 106: 149–164
Kavanagh A, Marple S, Honary F, et al. On solar protons and polar cap absorption: constraints on an empirical relationship. Ann Geophys, 2004, 22: 1133–1147
Li X, Roth I, Temerin M, et al. Simulation of the prompt energization and transport of radiation belt particles during the March 24, 1991 SSC Geophys Res Lett, 1993, 20: 2423–2426
Li X, Baker D N, Elkington S, et al. Energetic particle injections in the inner magne tosphere as a response to an interplanetary shock. J Atmos Terr Phys, 2003, 65: 233–244
Baker D N, Kanekal S G, Li X, et al. An extreme distortion of the Van Allen belt arising from the ‘Halloween’ solar storm in 2003. Nature, 2004, 432: 878–881
Sheldon R B, Spence H E, Sullivan J D, et al. The discovery of trapped energetic electrons in the outer cusp. Geophys Res Lett, 1998, 25: 1825–1828
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 40636032, 40674089 and 40310223)
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, Y., Xiao, Z., Zou, H. et al. Energetic particle radiations measured by particle detector on board CBERS-1 satellite. CHINESE SCI BULL 52, 665–670 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0087-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0087-2