Abstract
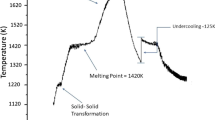
The high undercooling and rapid solidification of Ni-10%Cu-10%Fe-10%Co quaternary alloy were achieved by electromagnetic levitation and glass fluxing techniques. The maximum undercooling of 276 K (0.16TL) was obtained in the experiments. All the solidified samples are determined to be α-Ni single-phase solid solutions by DSC thermal analysis and X-ray diffraction analysis. The microstructure of the α-Ni solid solution phase transfers from dendrite to equiaxed grain with an increase in undercooling, accompanied by the grain refinement effect. When the undercooling is very large, the solute trapping effect becomes quite significant and the microsegregation is suppressed. The experimental measurement of α-Ni dendrite growth velocity indicates that it increases with undercooling according to the relation, V=8×10−2×ΔT 1.2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bisang U, Bilgram J H. Shape of the tip and the formation of sidebranches of xenon dendrites. Phys Rev E, 1996, 54(5): 5309–5326
Arnold C B, Aziz M J, Schwarz M, et al. Toward a parameter-free test of dendrite growth theory. Phys Rev B, 1999, 59(1): 334–343
Hürlimann E, Trittibach R, Risang U, et al. Intergral parameter of xenon dendrites. Phys Rev E, 1992, 46(10): 6579–6595
Lipton J, Kurz W, Trivedi R. Rapid dendrite growth in undercooled alloys. Acta Metall, 1987, 35(4): 957–964
Trivedi R, Lipton J, Kurz W. Effect of growth rate dependent partition coefficient on the dendritic growth in undercooled melts. Acta Metal, 1987, 35(4): 965–970
Yao W J, Han X J, Wei B. The undercooling and rapid dendritic growth of Cu-Sb in drop tube. Chin Sci Bull, 2002, 47(11): 824–828
Yao W J, Yang C, Han X J, et al. Rapid dendritic growth in an undercooled Ni-Cu alloy under the microgravity condition. Acta Physica Sinica, 2003, 52(2): 448–453
Hunziker O. Theory of plane front and dendritic growth in multicomponent alloys. Acta Mater, 2001, 49: 4191–4203
Ludwig A. The interface response-functions in multi-componental alloy solidification. Physica D, 1998, 124: 217–284
Ruan Y, Cao C D, Wei B. The rapid growth of ternary eutectic alloy at high undercooling. Sci China Ser G-Phys, 2004, 34(4): 392–402
Wang N, Wei B. Thermodynamic properties of highly undercooled liquid TiAl alloy. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 80(19): 3515–3517
Subramanian P R, Laughlin D E. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams (ed. Massalski T B), 1990. 1442
Swartzendruber L J, Itkin V P, Alock C B. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams (ed. Massalski T B), 1990. 1735
Nishizawa T, Lshida K. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams (ed. Massalski T B), 1990. 1215
Xie Y Q. Lattice constants of disordered and ordered phases in Au-Cu system. Acta Metall Sinica, 1998, 12(34): 1234–1242
Hofmeister W H, Bayuzick R J, Robinson M B. Dual purpose pyrometer for temperature and solidification velocity measurement. Rev Sci Instrum, 1990, 61: 222
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Wang, H., Ruan, Y. et al. Rapid dendrite growth in quaternary Ni-based alloys. CHINESE SCI BULL 51, 897–901 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-0897-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-0897-7



