Abstract
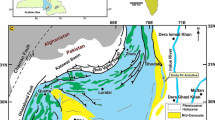
Detailed rock magnetic and paleomagnetic studies have been undertaken on borehole EY02-2 (70m in length) in the southern Yellow Sea (SYS). The main Curie point revealed by magnetic susceptibility-temperature (k-T) curve is 580–600°C indicating magnetite dominance. The hysteresis loop parameters show large variation of magnetic mineral size in different sedimentary contexts: it is larger in subtidal sediment than in terrigenous sediment and even larger than in shallow sea sediment. This trend is correlative with distance to sediment source and dynamic strength. Magnetostratigraphic results show that the M/B polarity boundary (MBPB) is at 63.29m and there are at least 7 polarity transitions (Nr1-7) in Brunhes chron that can be tentatively correlated with 6 named polarity reversals. Three positive polarity reversals occur in late Matuyama chron and the early two may be the record of Kamikatsura happening in 886±3 kaB.P. Magnetic susceptibility (MS) and sediment grain size behave so differently in some sedimentary facies that certain big environmental changes can be clearly revealed. Generally, the MS and grain size of subtidal and terrigenous sediments are larger than shallow sea sediments and MS value around 10×10−5SI and mean grain size of 7ϕ seems to be indicators of shallow sea sediments of deep water depth. However, the frequently used excellent climatic proxies such as MS and grain size in loess and deep sea sediments fail to record such climatic cycles revealed by oxygen isotope in continental sea. The various sediment sources, sedimentation dynamic and their complex changes between glacial and interglacial periods should be the cause of failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stokstad, E., Myriad ways to reconstruct past climate, Science, 2001, 292: 658–659.
Zhu, R. X., Hoffman, K. A., Potts, R. et al., Earliest presence of humans in northeast Asia, Nature, 2001, 413: 413–417.
Guo, Z. T., Ruddiman, W. F., Hao, Q. Z. et al., Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China, Nature, 2002, 416:159–163.
Heller, F., Liu, T. S., The magnetostratigraphy dating of Chinese loess deposits, Nature, 1982, 300: 431–433.
Ding, Z. L., Yang, S. L., Hou, S. S. et al., Magnetostratigraphy and sedimentology of the Jingchuan red clay section and correlation of the Tertiary eolian red clay sediments of the Chinese Loess Plateau, Journal of Geophysical Research, 2001, 106(B4): 6399–6408.
Heller, F., Liu, T. S., Paleoclimate of sedimentary history from magnetic susceptibility of loess in China, Geophysical Research Letter, 1986, 13(11): 1169–117.
Kukla, G., Heller, F., Liu, X. M. et al., Pleistocene climates in China dated by magnetic susceptibility, Geology, 1988, 16: 811–814.
Heller, F., Evans, M. E., Loess magnetism, Review Geophys., 1995, 33: 211–240.
Ding, Z. L., Yu, Z. W., Forcing mechanisms of paleomonsoons over east Asia, Quaternary Sciences (in Chinese), 1995, 1: 63–74.
Ding, Z. L., Sun, J. M., Yu, Z. W. et al., Paleoclimatic events recorded in Loess Plateau for the last 130ka, Chinese Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 1998, 43(6): 567–574.
Liu, D. S., Ding, Z. L., Comparison of Plio-Pleistocene climatic changes in different monsoonal regions and implications for human evolution, Quaternary Sciences (in Chinese), 1999, 4: 289–297.
Valet, J. P., Meynadier, L., Bassinot, F. C. et al., Relative paleointensity across the last geomagnetic reversal from sediments of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans. Geophysical Research Letter, 1994, 21(6): 485–488.
Meynadier, L., Valet, J. P., Shackleton, N. J., Relative geomagnetic intensity during the past 4 m.y. from the equatorial Pacific, Proc. Ocean Drill. Program, Sci. Results, 1995, 138: 779–795.
Robinson, S. G., Maslin, M. A., McCave, I. N., Magnetic susceptibility variations in Upper Pleistocene deep-sea sediments of the NE Atlantic: Implications for ice rafting and paleocirculation at the last glacial maximum, Paleoceanography, 1995, 10(2): 221–250.
Bloemendal, J., DeMenocal, P. B., Evidence of a change in the periodicity of tropical climate cycles at 2.4 Myr from whole-core magnetic susceptibility measurements, Nature, 1989, 342, 897–900.
Thompson, R., Oldfield, F., Environmental Magnetism, London: Allen & Unwin, 1986.
Liu, M. H., Wu, S. Y., Wang, Y. J., Late Quaternary Geology in the Yellow Sea (in Chinese), Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1987.
Qin, Y. S., Zhao, Y. Y., Chen, L. R. et al., Geology of the Yellow Sea (in Chinese), Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1989.
Zhou, M. Q., Ge, Z. S., The magnetostratigraphy of unconsolidated sediments in South Yellow Sea and adjacent areas, Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology (in Chinese), 1990, 10: 21–32.
Zhu, R. X., Tschu, K. K., Studies on Paleomagnetism and Reversals of Geomagnetic Field in China, Beijing: Science Press, 2001.
Yang, S. Y., Jung, H. S., Lim, D. I. et al., A review on the provenance discrimination of sediments in the Yellow Sea, Earth-Science Reviews, 2003, 1289: 1–28.
Chough, S. K., Lee, H. J., Marine Geology of Korean Seas, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2000, 47–49.
Lee, H. J., Chough, S. K., Sediment distribution, dispersal and budget in the Yellow Sea, Marine Geology, 1989, 87: 195–205.
Roberts, A. P., Cui, Y., Verosub, K. L., Wasp-waisted hysteresis loops: mineral magnetic characteristics and discrimination of components in mixed magnetic systems, Journal Geophysical Research, 1995, 100(B9): 17909–17924.
Guo, B., Zhu, R. X., Yue, L. P. et al., The Cobb Mountain Event recorded in Chinese loess, Science in China, Ser. D (in Chinese), 1998, 28(4): 327–333.
Guo, B., Zhu, R. X., Florindo, F. et al., Pedogenesis affecting the Matuyama-Brunhes polarity transition recorded in Chinese loess? Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(12): 975–980.
Zhu, R. X., Guo, B., The reliability of secular variation of geomagnetic field of Lingtai profile in Gansu Province, Science in China, Ser. D (in Chinese), 2000, 30(3): 324–330.
Zhu, R. X., Shi, C. D., Suchy, V. et al., Magnetic properties and paleoclimatic implications of loess-paleosol sequences of Czech Republic, Science in China, Ser. D, 2001, 44(5): 385–394.
Florindo, F., Zhu, R. X., Guo, B. et al., Magnetic proxy climate results from the Duanjiapo loess section, southernmost extremity of the Chinese loess plateau, Journal of Geophysical Research, 1999, 104(B1): 645–659.
Kirschvink, J. L, The least-squares line and planed analysis of paleomagnetic data, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc., 1980, 62: 699–718.
Langeres, C. G., Dekkers, M. J., Lange, G. J. et al., Magnetostratigraphy and astronomical calibration of the last 1.1Myr from an eastern Mediterranean piston core and dating of short events in the Brunhes, Geophysical Journal of International, 1997, 129: 203–225.
Singer, B. S., Hoffman, K. A., Chauvin, A. et al., Dating transitionally magnetized lavas of the late Matuyama Chron: toward a new 40Ar/39Ar timescale of reversals and events, Journal Geophysical Research, 1999, 104: 679–693.
Zhuang, L. H., Chang, F. M., Li, T. G. et al., Foraminiferal faunas and Holocene sedimentation rates of core EY02-2 in the South Yellow Sea, Marine Geology and Quarternary Geology (in Chinese with English abstract), 2002, 4: 7–13.
Kent, D. V., Opydyke, N. D., Paleomagnetic field intensity variation recorded in a Brunhes epoch deep-sea sediment core, Nature, 1977, 266: 156–159.
Horng, C. S., Roberts, A. P., Liang, W. T., A 2.14Myr astronomically tuned record of relative geomagnetic paleointensity from the western Philippine Sea, Journal Geophysical Research, 2003, 108(B1): 8-1–8-15.
Liu, X. M., Liu, T. S., Xu, T. C. et al., A preliminary study on magnetostratigraphy of a loess profile in Xifeng area, Gansu Province, Aspects of Loess Research (ed. Liu, T. S., in Chinese), Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1987, 151–164.
Yang, Z. G., Lin, H. M., Zhang, G. W., The Quaternary sequences in continental sea of Yellow Sea, the Quaternary Sequences and International Correlation (ed. Yang, Z. G., Lin, H. M., in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1996, 31–55.
Morner, N. A., Lanser, J. P., Gothenberg magnetic ‘flip’, Nature, 1974, 251: 408–409.
Dansgaard, W., White, J. W. C., Johnsen, S. J., The abrupt termination of the Younger Dryas climate event, Nature, 1989, 339(15): 532–533.
Liddicoat, J. C., Mono lake geomagnetic excursion, Journal Geophysical Research, 1979, 10(B1): 261–271.
Zhu, R. X., Pan, Y. X., Liu, Q. S., Geomagnetic excursions recorded in Chinese loess in the last 70000 years, Geophysical Research Letter, 1999, 26(4): 505–508.
Li, P. Y., Wang, Y. J., Liu, Z. X., Chronostratigraphy and deposition rates in the Okinawa Trough region, Science in China, Ser. D (in Chinese), 1999, 29(1): 50–55.
Chappell, J., Omura, A., Esat, T. et al., reconciliation of late Quaternary sea levels derived from coral terraces at Huon Peninsula with deep sea oxygen isotope records, Earth Planetary Science Letter, 1996, 141: 227–236.
Guyodo, Y., Richter, C., Valet, J. P., Paleointensity record from Pleistocene sediments(1.4-0Ma) off the California Margin, Journal Geophysical Research, 1999, 104(B10): 22953–22964.
Harrison, C. G. A., The paleomagnetic record from deep-sea sediment cores, Earth Planetary Science Letter, 1974, 10: 1–36.
Chen, F. H., Wang, S. M., Li, J. J. et al., Magnetostratigraphy of Ruoergai lake in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, Science in China, Ser. B (in Chinese), 1995, 25(7): 772–777.
Ge, S. L., Shi, X. F., Han, Y. B., Distribution characteristics of magnetic susceptibility of the surface sediments in the southern Yellow Sea, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(supp): 37–41.
Liu, J., Li, S. Q., Wang, S. J. et al., A rock-magnetic study of the last deglacial to Holocene sedimentary sequence in the YSDP105 core on the northeast shelf of the south Yellow Sea, Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology (in Chinese with English abstract), 1997, 17(4): 13–22.
Martinson, D. G., Pisias, N. G., Hays, J. D. et al., Age dating and the orbital theory of the ice ages: development of a high-resolution 0-2300000-year chrono-stratigraphy, Quaternary Research, 1987, 27: 1–29.
Su, Y. S., A survey of geographic environment, circulation system and the central fishing grounds in the Huanghai Sea and East China Sea, Journal of Shandong College of Oceanology (in Chinese with English abstract), 1986, 16: 12–28.
Xu, Q. Q., Lin, H. M., Six transgressions in the east of China since Middle Pleistocene and the astroclimatological interpretation, Marine Geology and Quarternary Geology (in Chinese with English abstract), 1993, 13(1): 11–17.
Imbrie, J., The orbital theory of Pleistocene climate: support from a revised chronology of the marine δ 18O record, Milankovitch and Climate (ed. Berger, A. L., Imbrie, J., Hays, J. et al.), Dordrecht: Reidel Publishing Company, 1984: 269–305.
Zheng, G. Y., Quaternary Stratigraphic Correlation in Southern Yellow Sea (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, S., Shi, X., Zhu, R. et al. Magnetostratigraphy of borehole EY02-2 in the southern Yellow Sea and its paleoenvironmental significance. CHINESE SCI BULL 51, 855–865 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-0855-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-0855-4