Abstract
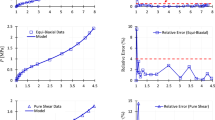
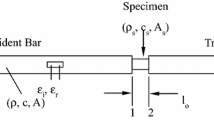
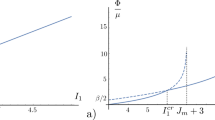
The present article is aimed to detect material-intrinsic indices that can be used to supervise the mechanical performance of general solid matter. The novelty carried in this article can be summarised as follows. Firstly, an inelastic deformation state of almost any solid matter can be treated as the combination of two fundamental modes due to different microscopic causation: Mode I inelastic distortion due to the movement of sliding types of defects and Mode II inelastic dilation due to the evolution of voids/bubbles. Secondly, each inelastic deformation mode is characterised by a single principal inelastic deformation descriptor (PIDD): Mode I by a newly introduced quantity of maximum distortional angle change α and Mode II by the logarithm of dilating magnification ω. In particular, the concept of maximum distortional angle change gives rise to a geometrically intuitive yield criterion of α > αc, which in situations of small deformation, is shown to asymptote von Mise’s, and to become Tresca’s in cases of plane stress. Thirdly, the deformation process of a solid matter under monotonic and ambient loads is formulated by means of trajectories of thermodynamic equilibria with respect to the PIDD pair. Then a pair of physical quantities which measure the stresses needed to change the local PIDD state are singled out. Being termed as inelastic deformation resistances (IDRs), these two quantities are shown to depend only on the onsite atomic configurations. It is also shown that key descriptive properties about the mechanical behaviours of materials, such as ductility, are encoded in IDRs as functions of PIDDs. Hence the IDR pair may serve as material performance indices that may be more intrinsic than conventional stress-strain relationships.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials, ASTM E8-03, 24 (2010).
L. P. Kubin, G. Canova, M. Condat, B. Devincre, V. Pontikis, and Y. Bréchet, Solid State Phenom. 23–24, 455 (1992).
D. Weygand, L. H. Friedman, E. V. Giessen, and A. Needleman, Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 10, 437 (2002).
H. M. Zbib, and T. Diaz de la Rubia, Int. J. Plast. 18, 1133 (2002).
A. Arsenlis, W. Cai, M. Tang, M. Rhee, T. Oppelstrup, G. Hommes, T. G. Pierce, and V. V. Bulatov, Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 15, 553 (2007).
J. A. El-Awady, S. Bulent Biner, and N. M. Ghoniem, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 56, 2019 (2008).
A. M. Hussein, and J. A. El-Awady, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 91, 126 (2016).
I. Groma, F. F. Csikor, and M. Zaiser, Acta Mater. 51, 1271 (2003).
T. Hochrainer, S. Sandfeld, M. Zaiser, and P. Gumbsch, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 63, 167 (2014).
H. S. Leung, P. S. S. Leung, B. Cheng, and A. H. W. Ngan, Int. J. Plast. 67, 1 (2015).
M. S. Mohamed, B. C. Larson, J. Z. Tischler, and A. El-Azab, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 82, 32 (2015).
Y. Zhu, and Y. Xiang, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 84, 230 (2015).
H. G. F. Wilsdorf, J. Electron. Mater. 4, 791 (1975).
A. A. Benzerga, and J.-B. Leblond, Adv. Appl. Mech. 44, 169 (2010).
D. Kondepudi, and I. Prigogine, Modern Thermodynamics: From Heat Engines to Dissipative Structures (John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, 2014).
B. Wang, Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 63, 124611 (2020).
B. Wang, Eng. Fract. Mech. 254, 107936 (2021).
E. H. Lee, J. Appl. Mech. 36, 1 (1969).
H. Hencky, Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 4, 323 (1924).
A. Nadai, J. Appl. Phys. 8, 205 (1937).
H. C. Wu, Continuum Mechanics and Plasticity, 1st ed. (Chapman and Hall/CRC, New York, 2004).
Y. L. Bai, M. F. Xia, and F. J. Ke, Statistical Meso-Mechanics of Damage and Failure: How Microdamage Induces Disaster, 1st ed. (Springer, Singapore, 2019).
A. L. Gurson, J. Eng. Mater. Tech. 99, 2 (1977).
V. Tvergaard, Int. J. Fract. 17, 389 (1981).
V. Tvergaard, and A. Needleman, Acta Metall. 32, 157 (1984).
A. Needleman, and V. Tvergaard, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 32, 461 (1984).
Y. Xiang, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 57, 728 (2009).
M. Zaiser, Philos. Mag. Lett. 93, 387 (2013).
P. M. Anderson, J. P. Hirth, and J. Lothe, Theory of Dislocations, 3rd ed. (Cambridge University Press, New York, 2017).
Y. Zhu, Y. Xiang, and K. Schulz, Scripta Mater. 116, 53 (2016).
Z. Zhou, Y. Zhu, J. Luo, X. Yang, and X. Guo, Int. J. Solids Struct. 198, 57 (2020).
M. Zaiser, Phys. Rev. B 92, 174120 (2015).
R. Wu, and M. Zaiser, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 159, 104735 (2022).
D. Hull, and D. J. Bacon, Introduction to Dislocations, 5th ed. (Elsevier, Oxford, 2011).
A. A. Griffith, and G. I. Taylor, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 221, 163 (1921).
G. A. Francfort, and J. J. Marigo, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 46, 1319 (1998).
B. Bourdin, G. A. Francfort, and J. J. Marigo, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 48, 797 (2000).
E. P. George, W. A. Curtin, and C. C. Tasan, Acta Mater. 188, 435 (2020).
A. Pineau, A. A. Benzerga, and T. Pardoen, Acta Mater. 107, 424 (2016).
J. W. Yoon, Y. Lou, J. Yoon, and M. V. Glazoff, Int. J. Plast. 56, 184 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Yichao Zhu was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12172074), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Chinese Universities (Grant No. DUT16RC(3)091). Biao Wang was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12150001, and 11832019).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Li, S. & Wang, B. Classification of inelastic deformation and material-intrinsic indices about mechanical performance of general solid matter. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 66, 114611 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-023-2167-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-023-2167-5