Abstract
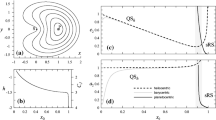
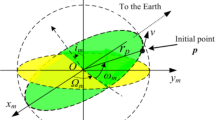
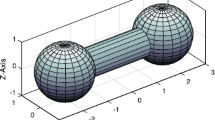
The double lunar swing-by orbits are a special kind of orbits in the Earth-Moon system. These orbits repeatedly pass through the vicinity of the Moon and change their shapes due to the Moon’s gravity. In the synodic frame of the circular restricted three-body problem consisting of the Earth and the Moon, these orbits are periodic, with two close approaches to the Moon in every orbit period. In this paper, these orbits are revisited. It is found that these orbits belong to the symmetric horseshoe periodic families which bifurcate from the planar Lyapunov family around the collinear libration point L3. Usually, the double lunar swing-by orbits have k=i+j loops, where i is the number of the inner loops and j is the number of outer loops. The genealogy of these orbits with different i and j is studied in this paper. That is, how these double lunar swing-by orbits are organized in the symmetric horseshoe periodic families is explored. In addition, the 2n lunar swing-by orbits (n⩾2) with 2n close approaches to the Moon in one orbit period are also studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farquhar R W, Dunham D W. A new trajectory concept for exploring the Earth’s geomagnetic tail. J Guid Control, 1981, 4: 192–196
Farquhar R W. The flight of ISEE-3/ICE: Origins mission history, and a legacy. J Astron Sci, 2001, 49: 23–73
Uesugi K, Hayashi T, Matsuo H. MUSES—a double lunar swingby mission. Acta Astron, 1988, 17: 495–502
Kawaguchi J, Yamakawa H, Uesugi T, et al. On making use of lunar and solar gravity assists in LUNAR-A, PLANET-B missions. Acta Astron, 1995, 35: 633–642
Uesugi T, Matsuo H, Kawaguchi J, et al. Japanese first double lunar swingby mission “Hiten”. Acta Astron, 1991, 25: 347–355
Farquhar R W. Halo-orbit and lunar-swingby missions of the 1990’s. Acta Astron, 1991, 24: 227–234
Nishida A. The geotail mission. Geophys Res Lett, 1994, 21: 2871–2873
Franz H, Sharer P, Ogilvie K, et al. WIND nominal mission performance and extended mission design. J Astron Sci, 2001, 49: 145–167
Edery A. Designing phase 2 for the double lunar swingby of the Magnetospheric Multiscale Mission (MMS). Adv Astron Sci, 2003, 114: 2089–2099
Stalos S. Calculation of double lunar swingby trajectories: I. Keplerian formulation. In: Flight Mechanics/Estimation Theory Symposium, Greenbelt, Ma, May, 1989
Stalos S. Calculation of double lunar swingby trajectories: II. Numerical solutions in the restricted problem of three bodies. In: Flight Mechanics/Estimation Theory Symposium, Greenbelt, Ma., Dec, 1990
Dunham D W, Jen S C, Lee T, et al. Double lunar-swingby trajectories for the spacecraft of the international solar-terrestrial physics program. Adv Astron Sci, 1989, 69: 285–301
Luo Z, Meng Y, Tang G. Correction methods analysis of double lunar-swingby trajectory (in Chinese). Chin J Theor Appl Mech, 2011, 43: 408–416
Folta D C, Sauter S L. ISEE-3 trajectory control utilizing multiple lunar swingbys. AIAA Paper, AIAA-84-1979, 1984
Wilson R S. Trajectory Design in the Sun-Earth-Moon Four Body Problem. Dissertation for Doctoral Degree. Lafayette: Purdue University, 1998
Hou X Y, Liu L. On Lyapunov families around collinear libration points. Astron J, 2009, 137: 4577–4585
Hou X Y, Liu L. The symmetric horseshoe periodic families and the Lyapunov planar around L3. Astron J, 2008, 136: 67–75
Szebehley V. Theory of Orbits. New York: Academic Press, 1967
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, X., Liu, L. Double lunar swing-by orbits revisited. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 57, 784–790 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-013-5361-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-013-5361-5