Abstract
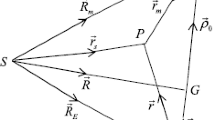
From Kaula’s Earth gravitational potential written in classical orbital elements, the unified ideal model of mean motion resonance of artificial satellites due to geopotential perturbations is developed in this paper first, through a suitable sequence of canonical transformations constructed by implicit functions. This unified ideal orbital resonance model is valid for all the commensurabilities between the rotational angular velocity of the Earth and the angular velocities of mean orbital motion of artificial satellites with arbitrary inclination and small eccentricity, and can be also transformed into Garfinkel’s general expression of ideal resonance problem. Then 1/1 resonance of the 24-hour satellite with arbitrary inclination and small eccentricity is analyzed under the effect of harmonics of J 2 and J 22 of the geopotential, based on the unified ideal model of mean motion resonance. The analytical expressions of the libration period and libration half width of the 1/1 resonance of the 24-hour satellite with arbitrary inclination and small eccentricity are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garfinkel B. Formal solution in the problem of small divisors. Astron J, 1966, 71: 657–669
Jupp A H. A solution of the ideal resonance problem for the case of libration. Astron J, 1969, 74: 35–43
Garfinkel B. Global solution of the ideal resonance problem. Celest Mech, 1973, 8: 207–212
Henrard J, Wauthier P. A geometric approach to the ideal resonance problem. Celest Mech, 1988, 44: 227–238
Erdi B, Kovacs J. A fourth-order solution of the ideal resonace problem. Celest Mech Dyn Astron, 1993, 56: 221–230
Ferraz-Mello S. Ideal resonance problem: the post-post-pendulum approximation. Celest Mech Dyn Astron, 2002, 83: 275–289
Garfinkel B. A theory of libration. Celest Mech, 1976, 13: 229–246
Liu L, Innanen K A, Zhang S P. Studies on orbital resonance. I. Astron J, 1985, 90: 877–886
Liu L, Innanen K A. Studies on orbital resonance. II. Astron J, 1985, 90: 887–891
Liu L. Orbital resonance. Progr Astron, 1986, 4: 43–52
Liu L, Liao X H, Zhao C Y. The orbital resonances on the motions of artificial satellites. Progr Astron, 1991, 9: 298–308
Zhao C Y, Liu L. Some discussions about the ideal resonance. Acta Astron Sin, 1991, 32: 268–276
Lima Jr P H C L. Sistemas ressonantes a altas excentricidades no movimento de satélites artificiais. Tese de Doutorado, Instituto tecnológico de aeronáutica, São José dos Campos, São Paulo, 1998
Formiga J K S. Estudo de ressonâncias no movimento orbital de satélites artificiais. Faculdade de Engenharia do Campus de Guaratinguetá, Universidade Estadual Paulista, Guaratinguetá, São Paulo, 2005
Formiga J K S, Vilhena de Moraes R. Dynamical systems: an integrable kernel for resonance effects. J Comput Interdisc Sci, 2009, 1: 89–94
Sampaio J C, Vilhena de Moraes R, Fernandes S S. Artifical satellites dynamics: resonance effects. Proceedings of the 22nd International Symposium on Space Flight Dynamics, São José dos Campos, Brazil, 2011
Formiga J K S, Vilhena de Moraes R. 15:1 resonance effects on the orbital motion of artificial satellites. J Aerosp Technol Manag, 2011, 3: 251–258
Kaula W M. Theory of Satellite Geodesy: Application of Satellites to Geodesy. London: Blaisdell Publishing Company, 1966
Yi Z H. An Introduction to Celestial Mechanics (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 1978
Mei F X, Liu R, Luo Y. Advanced Analytical Mechanics (in Chinese). Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 1991
Liu L. Celestial Mechanics Method (in Chinese). Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 1998
Tapley B D, Watkins M M, Ries J C, et al. The joint gravity model 3. J Geophys Res, 1996, 101, 28029–28049
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Zhao, C., Xiong, Y. et al. The unified ideal model of mean motion resonance of artificial satellites due to geopotential perturbations. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 56, 840–847 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-013-5022-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-013-5022-8