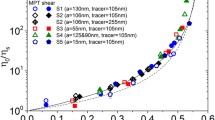
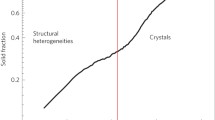
Abstract
Since Mr. Tsien brought up his idea of physical mechanics, as a new field in engineering science, to public attention in the early 50’s of the 20th century, innumerable application examples of physical mechanics approach in diverse fields have manifested its strong vitality increasingly. One of important aspects in applications of physical mechanics is to appropriately choose the microscopic quantity for the system in consideration and build a bridge to connect its relevant microscopic information to its desired macroscopic properties. We present two unique cases of using the physical mechanics approach to study colloidal stability. In the first case we measured the outcomes from artificially induced collisions at individual particle levels, by means of directly observing artificially induced collisions with the aid of optical tweezers. In the second case, by using T-matrix method, the microscopic quantity extinction cross section of the doublet can be accurately evaluated and therefore the measurement range and accuracy of the turbidity methodology for determining the CRC are greatly improved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsien H S. Physical mechanics, a new field in engineering science. J Amer Rocket Soc, 1953, 23: 17–24
Tsien H S. The properties of pure liquids. J Amer Rocket Soc, 1953, 23: 14–16
Tsien H S. Lennard-Jones and Devonshire Theory for dense gas. Jet Propulsion, 1955, 25: 471–478
Qian X S. The Lectures on Physical Mechanics (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 1962
Zhu R Z. Physical mechanics pioneered by H. S. Tsien. Adv Mech, 2001, 31: 489–499
Poon W. Colloids as big atoms. Science, 2004, 304: 830–831
Arora A K, Tata B V R. Ordering and Phase Transitions in Charged Colloids. New York: VCH Publishers, 1996
Anderson V J, Lekkerkerker H N W. Insights into phase transition kinetics from colloid science. Nature, 2002, 416: 811–815
Vold R D, Vold M J. Colloid and Interface Chemistry. London: Addison-Wesley, 1983
von Smoluchowski M. Versuch einer mathematischen Theorie der Koagulationskinetik kolloider Lösungen. Z Phys Chem, 1917, 92: 129–168
Sun Z W, Liu J, Xu S H. Study on improving the turbidity measurement of the absolute coagulation rate constant. Langmuir, 2006, 22: 4946–4951
Gillies G, Lin W, Borkovec M. Charging and aggregation of positively charged latex particles in the presence of anionic polyelectrolytes. J Phys Chem B, 2007, 111: 8626–8633
Sonntag H, Strenge K. Coagulation Kinetics and Structure Formation. Berlin: VEB Deutscher Verlag der Wissenschaften, 1987
Hunter R J. Zeta Potential in Colloid Science: Principles and Applications. London: Academic Press, 1981
Fuchs N. Über die Stabilität und Aufladung der Aerosole. Z Phys, 1934, 89: 736–743
Han M Y, Lee H K, Lawler D F, et al. Collision efficiency factor in Brownian coagulation (αBr) including hydrodynamics and interparticle forces. Water Sci Technol, 1997, 36: 69–75
Han M Y, Lee H K. Collision efficiency factor in Brownian coagulation (αBr): Calculation and experimental verification. Colloids Surf A, 2002, 202: 23–31
Mellema M, van Opheusden J H J, van Vliet T. Relating colloidal particle interactions to gel structure using Brownian dynamics simulations and the Fuchs stability ratio. J Chem Phys, 1999, 111: 6129–6135
Ashkin A. Acceleration and trapping of particles by radiation pressure. Phys Rev Lett, 1970, 24: 156–159
Ashkin A, Dziedzic J M, Brorkholm J E, et al. Observation of a single-beam gradient force optical trap for dielectric particles. Opt Lett, 1986, 11: 288–290
Sun Z W, Xu S H, Dai G L, et al. A microscopic approach to studying colloidal stability. J Chem Phys, 2003, 119: 2399–2405
Xu S H, Lou L R, Li Y M, et al. On the aggregation kinetics of two particles trapped in an optical tweezers. Colloids Surf A, 2005, 255: 159–163
Xu S H, Li Y M, Lou L R, et al. Computer simulation of the collision frequency of two particles in optical tweezers. Chin Phys, 2005, 14: 382–385
Sun Z W, Xu S H, Liu J, et al. Improved procedure on the microscopic approach to determine colloidal stability. J Chem Phys, 2005, 122: 184904
Xu S H, Sun Z W. Computer simulation on the collision-sticking dynamics of two colloidal particles in an optical trap. J Chem Phys, 2007, 126: 144903
Elimelech M, Gregory J, Jia X, et al. Particle Deposition and Aggregation. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann, 1995
Lichtenbelt J W T, Ras H J M C, Wiersema P H. Turbidity of coagulating lyophobic sols. J Colloid Interface Sci, 1974, 46: 522–527
Holthoff H, Schmitt A, Fernandez-Barbero A, et al. Measurement of absolute coagulation rate constants for colloidal particles: Comparison of single and multiparticle light scattering techniques. J Colloid Interface Sci, 1997, 192: 463–470
Puertas A M, de las Nieves F J. A new method for calculating kinetic constants with the Rayleigh-Gans-Debye approximation from turbidity measurements. J Phys-Condens Matter, 1997, 9: 3313–3320
Xu S H, Liu J, Sun Z W. Optical factors determined by the T-matrix method in turbidity measurement of absolute coagulation rate constants. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2006, 304: 107–114
Xu S H, Sun Z W. Progress in coagulation rate measurements of colloidal dispersions. Soft Matter, 2011, 7: 11298–11308
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Xu, S. Two examples of using physical mechanics approach to evaluate colloidal stability. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 55, 933–939 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-012-4725-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-012-4725-6