Abstract
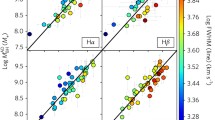
It has been suggested that the narrow cores of the Fe Kα emission lines in Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs) are likely produced in the torus, the inner radius of which can be measured by observing the lag time between the V and K band flux variations. In this paper, we compare the virial products of the infrared time lags, and the narrow Fe Kα widths for 10 type 1 AGNs, with the black hole masses from other techniques. We found the narrow Fe Kα line width is in average 2.6 +0.9−0.4 times broader than expected, assuming an isotropic velocity distribution of the torus at the distance measured by the infrared lags. We propose the thick disk model of the torus may explain the observed larger line width. Another possibility is the contamination by emission from the broad line region or the outer accretion disk. Alternatively, the narrow iron line might originate from the inner most part of the obscuring torus within the sublimation radius, while the infrared emission may be from the outer cooler part. We note the correlations between the black hole masses based on this new technique and those based on other known techniques are statistically insignificant. We argue that this could be attributed to the small sample size and the very large uncertainties in the measurements of iron K line widths. The next generation of X-ray observatories could help verify the origin of the narrow iron Kα line and the reliability of this new technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonucci R. Unified models for active galactic nuclei and quasars. Ann Rev Astron Astrophys, 1993, 31: 473–521
Jaffe W, Meisenheimer K, Röttgering H J A, et al. The central dusty torus in the active nucleus of NGC 1068. Nature, 2004, 429: 47–49
Suganuma M, Yoshii Y, Kobayashi Y, et al. The reverberation radius of the central dust hole in NGC 5548. Astrophys J, 2004, 612: L113–L116
Suganuma M, Yoshii Y, Kobayashi Y, et al. Reverberation measurements of the inner radius of the dust torus in nearby Seyfert 1 Galaxies. Astrophys J, 2006, 639: 46–63
Nelson B O. A correlated optical-infrared outburst of Markarian 744: The strongest evidence yet for thermal dust reverberation. Astrophys J, 1996, 465: L87–L90
Pounds K A, Nandra K, Stewart G C, et al. X-ray reflection from cold matter in the nuclei of active galaxies. Nature, 1990, 344: 132–133
Nandra K, Pounds K A. GINGA observations of the X-Ray spectra of Seyfert galaxies. Mon Not Roy Astron Soc, 1994, 268: 405–429
Reynolds C S, Nowak M A. Fluorescent iron lines as a probe of astrophysical black hole systems. Phys Rep, 2003, 377: 389–466
Yaqoob T, Padmanabhan U. The cores of the Fe K lines in Seyfert 1 galaxies observed by the Chandra high energy grating. Astrophys J, 2004, 604: 63–73
Page K L, O’Brien P T, Reeves J N, et al. An X-ray Baldwin effect for the narrow Fe Kα lines observed in active galactic nuclei. Mon Not Roy Astron Soc, 2004, 347: 316–322
Jiang P, Wang J X, Wang T G. On the X-Ray Baldwin effect for narrow Fe Kα emission lines. Astrophys J, 2006, 644: 725–732
Nandra K. On the origin of the iron Kα line cores in active galactic nuclei. Mon Not Roy Astron Soc, 2006, 368: L62–L66
Blandford R, McKee C F. Reverberation mapping of the emission line regions of Seyfert galaxies and quasars. Astrophys J, 1982, 255: 419–439
Peterson B M. Reverberation mapping of active galactic nuclei. Publ Astron Soc PAC, 1993, 105: 247–268
Ferrarese L, Merritt D. A fundamental relation between Supermassive black holes and their host galaxies. Astrophys J, 2000, 539: L9–L12
Gebhardt K, Bender R, Bower G, et al. A relationship between nuclear black hole mass and galaxy velocity dispersion. Astrophys J, 2000, 539: L13–L16
Ferrarese L, Pogge R W, Peterson B M, et al. Supermassive black holes in active galactic nuclei. I. The consistency of black hole masses in quiescent and active galaxies. Astrophys J, 2001, 555: L79–L82
Onken C A, Peterson B M, Dietrich M, et al. Black hole masses in three Seyfert galaxies. Astrophys J, 2003, 585: 121–127
Onken C A, Ferrarese L, Merritt D, et al. Supermassive black holes in active galactic nuclei. II. Calibration of the black hole mass-velocity dispersion relationship for active galactic nuclei. Astrophys J, 2004, 615: 645–651
Peterson B M, Ferrarese L, Gilbert K M, et al. Central masses and broadline region sizes of active galactic nuclei. II. A homogeneous analysis of a large reverberation-mapping database. Astrophys J, 2004, 613: 682–699
Clavel J, Wamsteker W, Glass I S. Hot dust on the outskirts of the broadline region in Fairall 9. Astrophys J, 1989, 337: 236–250
Maiolino R, Rieke G H. Low-luminosity and obscured Seyfert nuclei in nearby galaxies. Astrophys J, 1995, 454: 95–105
Glass I S. Infrared variability of the Seyfert galaxy NGC 3783. Mon Not Roy Astron Soc, 1992, 256: 23–27
Silk J, Rees MJ. Quasars and galaxy formation. Astron Astrophys, 1998, 331: L1–L4
Haehnelt M G, Kauffmann G. The correlation between black hole mass and bulge velocity dispersion in hierarchical galaxy formation models. Mon Not Roy Astron Soc, 2000, 318: L35–L38
Yaqoob T, George I M, Nandra K, et al. Physical diagnostics from a narrow Fe Kα emission line detected by Chandra in the Seyfert 1 galaxy NGC 5548. Astrophys J, 2001, 546: 759–768
Jefferys W H, Fitzpatrick M J, McArthur B E. GAUSSFIT — A system for least squares and robust estimation. Celest Mech, 1988, 41: 39–49
Tremaine S, Gebhardt K, Bender R, et al. The slope of the black hole mass versus velocity dispersion correlation. Astrophys J, 2002, 574: 740–753
Netzer H. In: Blandford R D, Netzer H, Woltjer L, eds. Active Galactic Nuclei. Berlin: Springer, 1990. 137
Yaqoob T, George I M, Kallman T R, et al. Fe XXV and Fe XXVI diagnostics of the black hole and accretion disk in active galaxies: Chandra time-resolved grating spectroscopy of NGC 7314. Astrophys J, 2003, 596: 85–104
Petrucci P O, Henri G, Maraschi L, et al. A rapidly variable narrow X-ray iron line in Mkn 841. Astron Astrophys, 2002, 388: L5–L8
Beckert T, Duschl W J. The dynamical state of a thick cloudy torus around an AGN. Astron Astrophys, 2004, 426: 445–454
Maiolino R, Rieke G H. Low-luminosity and obscured Seyfert nuclei in nearby galaxies. Astrophys J, 1995, 454: 95–105
Cackett E M, Horne K. Photoionized Hβ emission in NGC 5548: it breathes! Mon Not Roy Astron Soc, 2006, 365: 1180–1190
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by WANG JunXian (Editorial Board Member)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, P., Wang, J. & Shu, X. Weighing super-massive black holes with narrow Fe Kα line. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 54, 1354–1358 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-011-4352-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-011-4352-7