Abstract
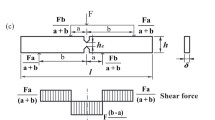
This paper presents the SEM micrographs for the three-point bending fracture surfaces of Zr-based, Ce-based and Mg-based bulk metallic glasses (BMGs), which show the dimple structures in the three kinds of BMGs. The shapes of the giant plastic deformation domain on the fracture surface are similar but the sizes are different. The fracture toughness K C and the dimple structure size of the Zr-based BMG are both the largest, and those of the Mg-based BMG are the smallest. The fracture toughness K C and the dimple structure size of the Ce-based BMG are between those of the Zr-based and the Mg-based BMG. Through analyzing the data of different fracture toughnesses of the BMGs, we find that the plastic zone width follows w = (K C/σ Y)2/(6π).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Courtney T H. Mechanical Behavior of Materials. Beijing: Mechanical Industry Press, 2004
Yu Z S. Metal Physics. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1981
Xi X K, Zhao D Q, Pan M X, et al. Fracture of brittle metallic glasses: Brittleness or plasticity. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 94: 125510-1–4
Wang W H. Correlations between elastic moduli and properties in bulk metallic glasses. J Appl Phys, 2006, 99: 093506-1–10
Wang W H, Dong C, Shek C H. Bulk metallic glass. Mater Sci Eng R, 2004, 44: 45–89
Xiao H X, Chen G. Preparation of plate Fe-based bulk amorphous alloy and measurement of its fracture toughness. Ordn Mater Sci Eng, 2004, 27(02): 23–26
Wang G, Wang Y T, Liu Y H, et al. The evolution of nanoscale morphology on fracture surface of brittle metallic glass. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89(12): 1909–1916
Li J X, Chu W Y, Gao K W, et al. In situ SEM study of initiating of shear band and microcrack in bulk metallic grass. Acta Metall Sin, 2003, 39(4): 359–363
Heilmaier M. Deformation behavior of Zr-based metallic glasses. J Mater Pro Tech, 2001, 117(24): 374–380
Bakke E, Johnson W L. The viscosity of the Zr46.75Ti8.25Cu7.5Ni10-Be27.5 bulk metallic glass forming alloy in the supercooled liquid. Appl Phy Lett, 1995, 67(22): 3260–3262
Deng Y F, Yang F, Yang J L, et al. Direct observations of localized free volume increases in a bulk metallic glass fractured by uniaxial compression at room temperature. Acta Metall Sin, 2006, 46(22): 2662–2678
Zarzycki J. Glass and Amorphous Materials (V9). Beijing: Science Press, 2001
Rabinovitch A, Frid V, Bahat D. Wallner lines revisited. J Appl Phys, 2006, 99: 76102-1–3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Z., Zheng, Z. & Jiao, Z. Three-point bending fracture characteristics of bulk metallic glasses. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 53, 654–657 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-010-0155-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-010-0155-5