Abstract
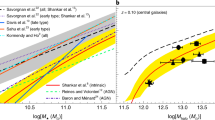
Narrow-line Seyfert 1 (NLS1) galaxies are believed to harbor low-mass black holes accreting at high rates, and they are therefore important targets when studying the nature of black hole growth, galaxy evolution, and accretion physics. We have rigorously studied the physical properties of a sample of NLS1 galaxies. We briefly review previous findings and present new results, including: (1) The locus of NLS1 galaxies on the M BH-σ plane, which we find to follow the relation of non-active galaxies after removing objects obviously dominated by outflows. (2) The presence of “blue outliers” which hint at extreme outflows as they would be predicted from merger models. (3) More subtle evidence for winds and outflows across the whole NLS1 population. (4) New correlations and trends which link black hole mass, Eddington ratio and physical parameters of the emission-line region. A new element is added to the eigenvector 1 space based on a principal component analysis, which aims at identifying the main drivers of AGN correlation properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boroson T A, Green R F. The emission-line properties of low-redshift quasi-stellar objects. Astrophys J Suppl, 1992, 80: 109–135
Komossa S. Narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies. Revista Mexicana de Astronomia y Astrofisica (Serie de Conferencias), 2008, 32: 86–92
Abazajian K, Adelman-McCarthy J K, Agüeros M A, et al. The third data release of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Astron J, 2005, 129: 1755–1759
Xu D W, Komossa S, Zhou H Y, et al. The narrow-line region of narrow-line and broad-line type 1 active galactic nuclei. I. A zone of avoidance in density. Astrophys J, 2007, 670: 60–73
Véron-Cetty M P, Véron P. A catalogue of quasars and active nuclei: 11th edition. Astron Astrophy, 2003, 412: 399–403
Boroson T A. Does the narrow [O III] λ5007 line reflect the stellar velocity dispersion in active galactic nuclei? Astrophys J, 2003, 585: 647–652
Kaspi S, Maoz D, Netzer H, et al. The relationship between luminosity and broad-line region size in active galactic nuclei. Astrophys J, 2005, 629: 61–71
Mathur S, Kuraszkiewicz J, Czerny B. Evolution of active galaxies: black-hole mass-bulge relations for narrow line objects. New Astron, 2001, 6: 321–329
Grupe D, Mathur S. M BH-σ relation for a complete sample of soft X-ray-selected AGNs. Astrophys J, 2004, 606: L41–L44
Bian W, Zhao Y. The black hole-bulge relation in active galactic nuclei. Mon Not Roy Astron Soc, 2004, 347: 607–612
Wang T, Lu Y. Black hole mass and velocity dispersion of narrow line region in active galactic nuclei and narrow line Seyfert 1 galaxies. Astron Astrophys, 2001, 377: 52–59
Tremaine S, Gebhardt K, Bender R, et al. The slope of the black hole mass versus velocity dispersion correlation. Astrophys J, 2002, 574: 740–753
Ferrarese L, Ford H. Supermassive black holes in galactic nuclei: past, present and future research. Space Sci Rev, 2005, 116: 563–624
Komossa S, Xu D. Narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies and the M BH-σ relation. Astron J, 2007, 667: L33–L36
Zhou H, Wang T, Yuan W, et al. A comprehensive study of 2000 narrow line Seyfert 1 galaxies from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. I. The sample. Astrophys J Suppl, 2006, 166: 128–153
Botte V, Ciroi S, Rafanelli P, et al. Exploring narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies through the physical properties of their hosts. Astron J, 2004, 127: 3168–3179
Hu J. The black hole mass-stellar velocity dispersion correlation: bulges versus pseudo-bulges. Mon Not Roy Astron Soc, 2008, 386: 2242–2252
Komossa S, Xu D, Zhou H, et al. On the nature of Seyfert galaxies with high [O III] λ5007 blueshifts. Astrophys J, 2008, 680: 926–938
Boroson T A. Black hole mass and Eddington ratio as drivers for the observable properties of radio-loud and radio-quiet QSOs. Astrophys J, 2002, 565: 78–85
Sulentic J W, Zamfir S, Marziani P, et al. Average quasar spectra in the context of eigenvector 1. Astrophys J, 2002, 566: L71–L75
Xu D W, Komossa S, Wei J Y, et al. An active galactic nucleus sample with high X-ray-to-optical flux ratio from RASS. II. Optical emission line properties of Seyfert 1-type active galactic nuclei. Astrophys J, 2003, 590: 73–85
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This work is supported by the National Basic Research Program of China-973 (Grant No. 2009CB824800) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 10873017).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, D., Komossa, S. New insights into AGNs with low-mass black holes and high accretion rates: the case of narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 53 (Suppl 1), 216–219 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-010-0060-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-010-0060-y