Abstract
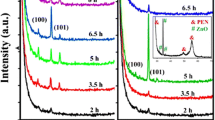
High-density well-aligned ZnO nanorods were successfully synthesized on ZnO-buffer-layer coated indium phosphide (InP) (100) substrates by a pulsed laser deposition (PLD) method. Scanning electron microscopy images show that the ZnO buffer layer formed uniform drip-like structure and ZnO nanorods were well-oriented perpendicular to the substrate surface. The sharp diffraction peak observed at 34.46° in X-ray diffraction scanning pattern suggests that the ZnO nanorods exhibit a (002)-preferred orientation. The PL spectra of ZnO samples shows a strong near band edge emission centered at about 380 nm and a weak deep level emission centered at around 495 nm, and it demonstrates that the ZnO nanorods produced in this work have high optical quality, which sheds light on further applications for nanodevices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Service R F. Will UV lasers beat blues? Science, 1997, 276: 895–895 [DOI]
Look D. C. Recent advances in ZnO materials and devices. Mater Sci Eng B, 2001, 80: 383–387[DOI]
Wan Q, Li Q H, Chen Y J, et al. Fabrication and ethanol sensing characteristics of ZnO nanowire gas sensors. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 84: 3654–3656[DOI]
Zhou J, Xu N S, Wang Z L. Dissolving behavior and stability of ZnO wires in biofluids: A study on biodegradability and biocompatibility of ZnO nanostructures. Adv Mater, 2006, 18: 2432–2435[DOI]
Shao G J, Qin X J, Liu R P, et al. Grain evolution of nano-crystals ZnO under HP and HT. Sci China Ser G-Phys Mech Astron, 2006, 49(3): 281–290[DOI]
Ye Z Z, Huang J Y, Xu W Z, et al. Catalyst-free MOCVD growth of aligned ZnO nanotip arrays on silicon substrate with controlled tip shape. Solid State Commun, 2007, 141: 464–466[DOI]
Gao H, Zhang X T, Zhou M Y, et al. Super-uniform ZnO nanohelices synthesized via thermal evaporation. Solid State Commun, 2006, 140:455–458[DOI]
Liang H W, Lu Y M, Shen D Z, et al. Growth of vertically aligned single crystal ZnO nanotubes by plasma-molecular beam epitaxy. Solid State Commun, 2006, 137: 182–186[DOI]
Okada T, Kawashima K, Nakata Y. Nano-wire pig-tailed ZnO nano-rods synthesized by laser ablation. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 506–507: 274–277[DOI]
Wang Z L, Kong X Y, Ding Y, et al. Semiconducting and piezoelectric oxide nanostructures induced by polar surfaces. Adv Funt Mater, 2004, 14(10): 943–956[DOI]
Gao P X, Ding Y, Mai W J, et al. Conversion of zinc oxide nanobelts into superlattice-structured nanohelices. Science, 2005, 309:1700–1704[DOI]
Vayssieres L. Growth of arrayed nanorods and nanowires of ZnO from aqueous solutions. Adv Mater, 2003, 15: 464–466[DOI]
Chen Y J, Zhu C L, Xiao G. Reduced-temperature ethanol sensing characteristics of flower-like ZnO nanorods synthesized by a sonochemical method. Nanotechnology, 2006, 17: 4537–4541[DOI]
Huang M H, Mao S, Feick H, et al. Room-temperature ultraviolet nanowire nanolasers. Science, 2001, 292: 1897–1899[DOI]
Lyu S C, Zhang Y, Ruh H, et al. Low temperature growth and photoluminescence of well-aligned zinc oxide nanowires. Chem Phys Lett, 2002, 363: 134–138[DOI]
Vanheusden K, Warren W L, Seager C H, et al. Mechanisms behind green photoluminescence in ZnO phosphor powders. J Appl Phys, 1996, 79: 7983–7990[DOI]
Shalish H, Temhin H, Narayanamurti V, et al. Size-dependent surface luminescence in ZnO nanowires. Phys Rev B, 2004, 69: 245401–245405[DOI]
Sun J C, Bian J M, Liang H W, et al. Realization of controllable etching for ZnO film by NH4Cl aqueous solution and its influence on optical and electrical properties. Appl Sur Sci, 2007, 253: 5161–5165[DOI]
Godlewski M, Goldys E M, Phillips M R, et al. Influence of the surface morphology on the yellow and “edge” emissions in wurtzite GaN. Appl Phys Lett, 1998, 73: 3686–3688[DOI]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 50532080), the Science & Technology Foundation for Key Laboratory of Liaoning Province (Grant No. 20060131), and the Doctoral Project by China Ministry of Education (Grant No. 20070141038)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, D., Hu, L., Li, J. et al. Self-catalyst synthesis of aligned ZnO nanorods by pulsed laser deposition. Sci. China Ser. G-Phys. Mech. Astron. 52, 207–211 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-009-0040-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-009-0040-2