Abstract
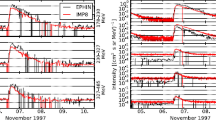
The space particle component detector on Fengyun-1 satellite which works at the sun-synchronous orbit of about 870 km altitude has detected relativistic electrons for a long time. In comparison with the SAMPEX satellite observations during 1999–2004, the relativistic electron data from Fengyun-1 satellite from June 1999 to 2005 are used to analyze the relativistic electron enhancement (REE) events at the low earth orbit, and the possible correlation among REE events at the low earth orbit, high-speed solar wind and geomagnetic storms is discussed. The statistical result presents that 45 REE events are found in total during this time period, and the strong REE events with the maximum daily average flux > 400 cm−2·srt-1·s−1 occur mostly during the transition period from solar maximum to solar minimum. Among these 45 REE events, four strong REE events last a longer time period from 26-to 51-day and correlate closely with high speed solar wind and strong geomagnetic storms. Meanwhile, several strong geomagnetic storms occur continuously before these REE events, and these continuous geomagnetic storms would be an important factor causing these long-lasting strong REE events. The correlation analysis for overall 45 events indicates that the strength of the REE events correlates with the solar wind speed and the strength of the geomagnetic storm, and the correlation for strong REE events is much stronger than that for weak REE events.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tu C Y, et al. Solar-Terrestrial Space Physics (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 1988. 125
Baker D N, Pulkkinen T I, Li X, et al. Coronal mass ejections, magnetic clouds, and relativistic magnetospheric electron events: ISTP. J Geophys Res, 1998, 103: 17279–17291
Baker D N, Pulkkinen T I, Li X, et al. A strong CME-related magnetic cloud interaction with the Earth’s magnetosphere: ISTP observations of rapid relativistic electron acceleration on May 15, 1997. Geophys Res Lett, 1998, 25(15): 2975–2978
Iles R H A, Fazakerley A N, Johnstone A D, et al. The relativistic electron response in the outer radiation belt during magnetic storms. Ann Geophys, 2002, 20: 957–965
Selesnick R S, Blake J B. Radiation belt electron observations following the January 1997 magnetic cloud event. Geopys Res Lett, 1998, 25(14): 2553–2556
Reeves G D. Relativistic electrons and magnetic storms: 1992–1995. Geophys Res Lett, 1998, 25(11): 1817–1820
Czeremuszkin G, Latreche M, Wertheimer M R. Charging/discharge events in coated spacecraft polymers during electron beam irradiation in a scanning electron microscope. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B, 2001, 185: 88–99
Tverskaya L V, Ivanova T A, Pavlov N N, et al. Storm-time formation of a relativistic electron belt and some relevant phenomena in other magnetospheric plasma domains. Advs Space Res, 2005, 36(12): 2392–2400
Zhou G C, Wang X Y, Wang D J, et al. MeV electron-flux enhancement events at the geosynchronous orbit in April–May 1998 (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 2001, 44(3): 293–302
Li L Y, Cao J B, Zhou G C. Relation between the variation of geomagnetospheric relativistic electron flux and storm/substorm (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 2006, 49(1): 9–15
Paulikas G, Blake J. Effects of the solar wind on magnetospheric dynamics: Energetic electrons at the synchronous orbit. In: Olson W, ed. Quantitative Modeling of Magnetospheric Processes. Geophysical Monograph Series. Washington: AGU, 1979. 180–201
Baker D N, Blake J B, Klebesadel R W, et al. Highly relativistic electrons in the Earth’s outer magnetosphere (I): Lifetimes and temporal history 1979–1984. J Geophys Res, 1986, 91: 4265–4276
Baker D N, Kanekal S G, Blake J B, et al. The global efficiency of relativistic electron production in the Earth’s magnetosphere. J Geophys Res, 2001, 106: 19169–19178
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Wang, S. Observation results of relativistic electrons detected by Fengyun-1 satellite and analysis of relativistic electron enhancement (REE) events. Sci. China Ser. G-Phys. Mech. Astron. 51, 1947–1956 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-008-0179-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-008-0179-2