Abstract
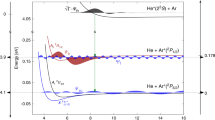
The principle and technique details of recoil ion momentum imaging are discussed and summarized. The recoil ion momentum spectroscopy built at the Institute of Modern Physics (Lanzhou) is presented. The first results obtained at the setup are analyzed. For 30 keV He2+ on He collision, it is found that the capture of single electron occurs dominantly into the first excited states, and the related scattering angle results show that the ground state capture occurs at large impact parameters, while the capture into excited states occurs at small impact parameters. The results manifest the collision dynamics for the sub-femto-second process can be studied through the techniques uniquely. Finally, the future possibilities of applications of the recoil ion momentum spectroscopy in other fields are outlined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rescigno T N, Baertschy M, Isaacs W A, et al. Collisional breakup in a quantum system of three charged particles. Science, 1999, 286: 2474–2479
McCurdy C W, Rescigno T N. Practical calculations of quantum breakup cross sections. Phys Rev A, 2000, 62: 32712
Schmidt-Böcking H, Mergel V, Dörner R, et al. Polarization, and ionization in atomic system. In: American Institute of Physics Conference Proceedings of Correlations. New York: American Institute of Physics, 2002. 604: 120
McGuire J H, Godunov A L, Tolmanov S G, et al. Time correlation in two-electron transitions produced in fast collisions of atoms with matter and light. Phys Rev A, 2001, 63: 052706
Barat M, Roncin P J. Multiple electron capture by highly charged ions at keV energies. Phys B: At Mol Opt Phys, 1992, 25: 2205–2243
Ullrich J, Dörner R, Schmidt-Böcking H, et al. Multielectron processes. In: Berényi D, Hock G, eds. Lecture Notes in Physics. Debrecen: Springer, 1990. 376: 287–296
Schmidt-Böcking H, Dörner R, Ullrich J, et al. Multiple ionization in ion-atom collisions investigated by recoil ion momentum spectroscopy. In: Berényi D, Hock G, eds. Lecture Notes in Physics. Debrecen: Springer, 1990. 376: 268–281
Ullrich J, Moshammer R, Dörner R, et al. Recoil-ion momentum spectroscopy: Reaction-microscopes. Rep Prog Phys, 2003, 66: 1463–1545
Jagutzki O, Mergel V, Ullmann-Pfleger K, et al. Proceeding of international symposium on optical science engineering and instrumentation. Proc SPIE, 1998, 3438: 322
Dörner R, Vergel V, Spielberger L, et al. Kinematically complete experiments using cold target recoil ion momentum spectroscopy. Nucl Instr Meth B, 1997, 124: 225–231
Moshammer R, Perumal A, Schulz M, et al. Three-body Coulomb problem probed by mapping the Bethe surface in ionizing ion-atom collisions. Phys Rev Lett, 2001, 87: 223201
Fischer D, Feuerstein B, Dubois R D, et al. State resolved measurement of single electron capture in slow Ne7+ and Ne8+-Helium collisions. J Phys B, 2002, 35, 1369–1377
Moshammer R, Fainstein P D, Schulz M, et al. Initial state dependence of low energy electron emission in fast ion atom collisions. Phys Rev Lett, 1999, 83: 4721–4724
Spielberger L, Jagutzki O, Dörner R, et al. Separation of photoabsorption and Compton scattering contributions to He single and double ionization. Phys Rev Lett, 1995, 74: 4615–4618
Knapp A, Kheifets A, Bray I, et al. Mechanisms of photo double ionization of helium by 530 eV photons. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 89: 033004
Ma X W, Liu H P, Chen X M, et al. Transfer ionization cross-section measured in collisions of highly charged argon ions with neon target. Sci China Ser G-Phys Mech Astron, 2003, 46: 552–560
Zhang S F, Ma X W, Liu H P, et al. Properties and applications of cold supersonic gas jet. Sci China Ser G-Phys Mech Astron, 2006, 49(6): 709–715
Zhu X L, Ma X W, Sha S, et al. Two-dimention delay-line microchannel plate imaging detector. Nucl Electr Det Tech, 2004, 24: 253–256
Feng W T, Ma X W, Liu H P, et al. Test and analysis of uniform magnetic fields for imaging of electrons produced in ion-atom collisions. Acta Phys Sin (in Chinese), 2007, 56: 3637–3641
Fritsch W. Theoretical study of electron processes in slow He2+-He collisions. J Phys B-At Mol Opt Phys, 1994, 27: 3461–3474
Zhu X L, Ma X W, Li B, et al. State-selective electron capture for keV He2+ ions on helium collisions studied by recoil momentum spectroscopy. Chin Phys Lett, 2006, 23: 587–590
Li B, Ma X W, Zhu X L, et al. Average energy loss measured in single and double electron capture collisions of He2+ on Ar at low velocities. Chin Phys Lett, 2006, 23: 1452–1456
Anton J, Fricke B, Ma X, et al. The many-particle scattering system He++ on He: Experiment and a complete unified description. Phys Lett A, 2007, 369: 85–89
Schmidt-Böcking H, Mergel V, Schmidt L, et al. Dynamics of ionization processes studied with the COLTRIMS method—New insight into e-e correlation. Rad Phys Chem, 2003, 68: 41–50
Dörner R, Mergel V, Jagutzki O, et al. Cold target recoil ion momentum spectroscopy: A ‘momentum microscope’ to view atomic collision dynamics. Phys Rep, 2000, 330: 95–192
Dürr M, Dorn A, Ullrich J, et al. (e, 3e) on helium at low impact energy: The strongly correlated three-electron continuum. Phys Rev Lett, 2007, 98: 193201
Cao S P, Ma X W, Dorn A, et al. Correlation of emitted electrons in near threshold double ionization of helium by electron impact. Acta Phys Sin (in Chinese), 2007, 56: 6386–6392
Cao S P, Ma X W, Dorn A, et al. Analysis of recoil ion momentum in near threshold double ionization of helium by electron impact. Nucl Phys Rev (in Chinese), 2007, 24: 208–213
Koonp S, Turkstra J W, Morgenstern R, et al. Multi-electron processes in slow He2+-Na collisions measured with MOTRIMS. Nucl Instr Meth B, 2003, 205: 560–567
Ergler Th, Rudenko A, Feuerstein B, et al. Spatio-temporal imaging of ultrafast molecular motion: Collapse and revival of the D2 + nuclear wave packet. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 97: 193001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 10434100)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Zhu, X., Liu, H. et al. Investigation of ion-atom collision dynamics through imaging techniques. Sci. China Ser. G-Phys. Mech. Astron. 51, 755–764 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-008-0096-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-008-0096-4