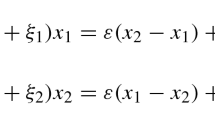Abstract
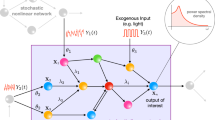
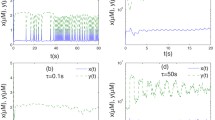
By investigating a stochastic model for intracellular calcium oscillations proposed by Höfer, we have analyzed the transmission behavior of calcium signaling in a one-dimensional two-way coupled hepatocytes system. It is shown that when the first cell is subjected to the external noise, the output signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in the cell exhibits two maxima as a function of external noise intensity, indicating the occurrence of stochastic bi-resonance (SBR). It is more important that when cells are coupled together, the resonant behavior in the 1st cell propagates along the chain with different features through the coupling effect. The cells whose locations are comparatively close to or far from the 1st cell can show SBR, while the cells located in the middle position can display stochastic multi-resonance (SMR). Furthermore, the number of cells that can show SMR increases with coupling strength enhancing. These results indicate that the cells system may make an effective choice in response to external signaling induced by noise, through the mechanism of SMR by adjusting coupling strength.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benzi R, Sutera A, Vulpiani A. The mechanism of stochastic resonance. J Phys A, 1981, 14: L453–L457
Hou Z H, Xin H W. Stochastic resonance in the presence or absence of external signal in the continuous stirred tank reactor system. J Chem Phys, 1999, 111: 721–723
Hu G, Ditzinger T, Ning C Z, et al. Stochastic resonance without external periodic force. Phys Rev Lett, 1993, 71: 807–810
Vilar J M G, Gomila G, Rubi J M. Stochastic resonance in noisy nondynamical systems. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 81: 14–17
Vilar J M G, Rubi J M. Stochastic multiresonance. Phys Rev Lett, 1997, 78: 2882–2885
Liang G Y, Cao L, Wang J, et al. Modulated stochastic multiresonance in a single-mode laser system driven by colored additive and multiplicative noises without external periodic force. Phys A, 2003, 327: 304–312
Krawiecki A, Matyjaśkiewicz S, Kacperski K, et al. Noisefree stochastic multiresonance near chaotic crises. Phys Rev E, 2001, 64: 041104–041107
Matyjaśkiewicz S, Krawiecki A, Hołyst J A, et al. Stochastic multiresonance due to interplay between noise and fractals. Phys Rev E, 2003, 68: 016216–016222
Zhang J Q, Shen C S, Cui Z F. Modulation on the collective response behavior by the system size in two-dimensional coupled cell systems. Sci China Ser G-Phys Mech Astron, 2006, 49: 304–312
Hou Z H, Xin H W. Enhancement of stochastic resonance by noise delay. Phys Lett A, 1999, 263: 360–364
Tsindlekht M I, Felner I, Gitterman M, et al. Stochastic resonance phenomenon in a superconducting surface state of single-crystal Nb. Phys Rev B, 2000, 62: 4073–4078
Volkov E I, Ullner E, Kurths J. Stochastic multiresonance in the coupled relaxation oscillators. Chaos, 2005, 15: 023105–023112
Höfer T. Model of intercellular calcium oscillations in hepatocytes: Synchronization of heterogeneous cells. Biophys J, 1999, 77: 1244–1256
Zhang J Q, Hou Z H, Xin H W. Stochastic bi-resonance induced by external noise for Ca2+ signaling in hepatocytes. Sci China Ser B-Chem, 2005, 48: 286–291
Zhao G, Hou Z H, Xin H W. Frequency-selective response of FitzHugh-Nagumo neuron networks via changing random edges. Chaos, 2006, 16: 043107–043112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Research Fund of Anhui Normal University (Grant No. 2006xzx09), the Educational Commission of Anhui Province of China (Grant No. KJ2007A079), and the Program for Innovative Research Team in Anhui Normal University
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Liu, J. & Chen, H. Selective effects of noise by stochastic multi-resonance in coupled cells system. Sci. China Ser. G-Phys. Mech. As 51, 492–498 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-008-0061-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-008-0061-2