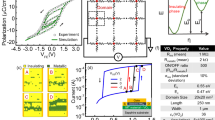
Abstract
Driven by the explosive development of data-centric computation applications, it is becoming urgent to develop in-memory computing devices that are beyond the von Neumann architecture with an arrangement of separated logic and memory components. The transistor-type solid-state non-volatile memories, such as ferroelectric field-effect transistors (FeFETs), have long been regarded as a competitive candidate for future in-memory computing architectures. However, the density scaling towards high-density arrays would require advanced FeFETs with reduced footprints, which remains a great challenge so far. Here, a vertical-transport (VT) FeFET that flips the charge transport channel perpendicular to the substrate plane is proposed, in which a ferroelectric gate and a van der Waals (vdW) heterojunction channel are vertically integrated, effectively reducing the device footprints. The proposed VT-FeFET shows not only the robust binary non-volatile memory states but also several key synaptic functionalities at the device level. An artificial neural network with supervised learning was simulated based on the device conductance switching properties, showing excellent classification accuracy for the MNIST handwritten digits. These findings suggest that the proposed VT-FeFET could offer a new solution for future non-volatile memories as well as more advanced neuromorphic systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castellanos-Gomez A, Duan X, Fei Z, et al. Van der Waals heterostructures. Nat Rev Methods Primers, 2022, 2: 58
Novoselov K S, Mishchenko A, Carvalho A, et al. 2D materials and van der Waals heterostructures. Science, 2016, 353: aac9439
Lee J H, Shin D H, Yang H, et al. Semiconductor-less vertical transistor with Ion/Ioff of 106. Nat Commun, 2021, 12: 1000
Luo Z D, Yang M M, Liu Y, et al. Emerging opportunities for 2D semiconductor/ferroelectric transistor-structure devices. Adv Mater, 2021, 33: e2005620
Sangwan V K, Hersam M C. Neuromorphic nanoelectronic materials. Nat Nanotechnol, 2020, 15: 517–528
Ahn J, Ko K, Kyhm J, et al. Near-infrared self-powered linearly polarized photodetection and digital incoherent holography using WSe2/ReSe2 van der Waals heterostructure. ACS Nano, 2021, 15: 17917–17925
Wang Z, Gutiérrez-Lezama I, Ubrig N, et al. Very large tunneling magnetoresistance in layered magnetic semiconductor CrI3. Nat Commun, 2018, 9: 2516
Liu L, Kong L, Li Q, et al. Transferred van der Waals metal electrodes for sub-1-nm MoS2 vertical transistors. Nat Electron, 2021, 4: 342–347
Ma L, Tao Q, Chen Y, et al. Realizing on/off ratios over 104 for sub-2 nm vertical transistors. Nano Lett, 2023, 23: 8303–8309
Cheng R, Wang F, Yin L, et al. High-performance, multifunctional devices based on asymmetric van der Waals heterostructures. Nat Electron, 2018, 1: 356–361
Huang M, Li S, Zhang Z, et al. Multifunctional high-performance van der Waals heterostructures. Nat Nanotech, 2017, 12: 1148–1154
Yu W J, Li Z, Zhou H, et al. Vertically stacked multi-heterostructures of layered materials for logic transistors and complementary inverters. Nat Mater, 2013, 12: 246–252
Britnell L, Gorbachev R V, Jalil R, et al. Field-effect tunneling transistor based on vertical graphene heterostructures. Science, 2012, 335: 947–950
Yang Q, Luo Z D, Duan H, et al. Steep-slope vertical-transport transistors built from sub-5 nm thin van der Waals heterostructures. Nat Commun, 2024, 15: 1138
Yakimets D, Eneman G, Schuddinck P, et al. Vertical GAAFETs for the ultimate CMOS scaling. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2015, 62: 1433–1439
Jagannathan H, Anderson B, Sohn C-W, et al. Vertical-transport nanosheet technology for CMOS scaling beyond lateraltransport devices. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, 2021
Ye S, Yamabe K, Endoh T. Ultimate vertical gate-all-around metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor and its three-dimensional integrated circuits. Mater Sci Semicond Process, 2021, 134: 106046
Georgiou T, Jalil R, Belle B D, et al. Vertical field-effect transistor based on graphene-WS2 heterostructures for flexible and transparent electronics. Nat Nanotech, 2013, 8: 100–103
Cao W, Bu H, Vinet M, et al. The future transistors. Nature, 2023, 620: 501–515
Lanza M, Sebastian A, Lu W D, et al. Memristive technologies for data storage, computation, encryption, and radio-frequency communication. Science, 2022, 376: 9979
Mehonic A, Kenyon A J. Brain-inspired computing needs a master plan. Nature, 2022, 604: 255–260
Luo Z D, Zhang S, Liu Y, et al. Dual-ferroelectric-coupling-engineered two-dimensional transistors for multifunctional inmemory computing. ACS Nano, 2022, 16: 3362–3372
Khan A I, Keshavarzi A, Datta S. The future of ferroelectric field-effect transistor technology. Nat Electron, 2020, 3: 588–597
Yang T H, Liang B W, Hu H C, et al. Ferroelectric transistors based on shear-transformation-mediated rhombohedral-stacked molybdenum disulfide. Nat Electron, 2024, 7: 29–38
Si M, Saha A K, Gao S, et al. A ferroelectric semiconductor field-effect transistor. Nat Electron, 2019, 2: 580–586
Zhao Z, Rakheja S, Zhu W. Nonvolatile reconfigurable 2D Schottky barrier transistors. Nano Lett, 2021, 21: 9318–9324
Luo Z D, Xia X, Yang M M, et al. Artificial optoelectronic synapses based on ferroelectric field-effect enabled 2D transition metal dichalcogenide memristive transistors. ACS Nano, 2020, 14: 746–754
Zhang J, Gao F, Hu P A. A vertical transistor with a sub-1-nm channel. Nat Electron, 2021, 4: 325
Zhou C, Chai Y. Ferroelectric-gated two-dimensional-material-based electron devices. Adv Elect Mater, 2017, 3: 1600400
Chanthbouala A, Garcia V, Cherifi R O, et al. A ferroelectric memristor. Nat Mater, 2012, 11: 860–864
Lecun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE, 1998, 86: 2278–2324
Ning H, Yu Z, Zhang Q, et al. An in-memory computing architecture based on a duplex two-dimensional material structure for in situ machine learning. Nat Nanotechnol, 2023, 18: 493–500
Fuller E J, Gabaly F E, Leonard F, et al. Li-ion synaptic transistor for low power analog computing. Adv Mater, 2017, 29: 1604310
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2023YFB4402303), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 62090033, 62025402, 62274128, 92264202, 62293522, 92364204), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. LDT23F04023F04, LDT23F04024F04, LR21F010003), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. QTZX23079), and Key Research and Development Program of Ningbo City (Grant No. 2023Z071). Zheng-Dong LUO would like to thank Dr. C. Zhao with Analytic&Testing Center of NPU for the assistance of device fabrication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supporting information Supplementary Notes 1–7. The supporting information is available online at info.scichina.com and link.springer.com. The supporting materials are published as submitted, without typesetting or editing. The responsibility for scientific accuracy and content remains entirely with the authors.
Supplementary File
11432_2024_4004_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Solid-state nonvolatile memories based on vdW heterostructure-based vertical-transport ferroelectric field-effect transistors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q., Luo, ZD., Xiao, F. et al. Solid-state non-volatile memories based on vdW heterostructure-based vertical-transport ferroelectric field-effect transistors. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 67, 160405 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-024-4004-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-024-4004-9