Abstract
The broad learning system (BLS) based on the minimum mean square error (MMSE) criterion can achieve outstanding performance without spending too much time in various machine learning tasks. However, when data are polluted by non-Gaussian noise, the stability of BLS may be destroyed because the MMSE criterion is sensitive to outliers. Different from the MMSE criterion, the minimum error entropy (MEE) criterion utilizes the kernel function to capture high-dimensional information and decrease the negative influence of outliers, which will make BLS more discriminative and robust. Nevertheless, the computational complexity of MEE is high due to a double summation of the data size. To solve these issues, this paper proposes a new robust BLS variant based on the quantized minimum error entropy (QMEE) criterion, in which a quantization operation is used to reduce the computational complexity of MEE. The proposed model BLS-QMEE is optimized by the fixed-point iterative method, and a sufficient condition for its convergence is provided. Compared with the standard BLS and other existing robust variants of BLS, BLS-QMEE performs more satisfactorily without consuming too much time. The desirable performance of BLS-QMEE is verified by various experiments on function approximation, several public datasets, and a practical application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deng L, Yu D. Deep learning: methods and applications. Found Trends Signal, 2014, 7: 197–387
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature, 2015, 521: 436–444
Leung H, Haykin S. The complex backpropagation algorithm. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 1991, 39: 2101–2104
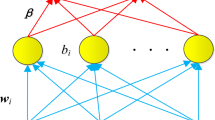
Chen C L P, Liu Z. Broad learning system: an effective and efficient incremental learning system without the need for deep architecture. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2017, 29: 10–24
Chen C L P, Liu Z, Feng S. Universal approximation capability of broad learning system and its structural variations. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2018, 30: 1191–1204
Hoerl A E, Kennard R W. Ridge regression: biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems. Technometrics, 1970, 12: 55–67
Gong X, Zhang T, Chen C L P, et al. Research review for broad learning system: algorithms, theory, and applications. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2022, 52: 8922–8950
Jin J, Li Y, Yang T, et al. Discriminative group-sparsity constrained broad learning system for visual recognition. Inf Sci, 2021, 576: 800–818
Sheng B, Li P, Zhang Y, et al. GreenSea: visual soccer analysis using broad learning system. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2020, 51: 1463–1477
Jin J W, Liu Z L, Chen C L P. Discriminative graph regularized broad learning system for image recognition. Sci China Inf Sci, 2018, 61: 112209
Wang Y, Jia P, Cui H, et al. A novel regression prediction method for electronic nose based on broad learning system. IEEE Sens J, 2021, 21: 19374–19381
Zhang D, Li T S, Chen C L P, et al. Target tracking algorithm based on a broad learning system. Sci China Inf Sci, 2022, 65: 154201
Yu W, Zhao C. Broad convolutional neural network based industrial process fault diagnosis with incremental learning capability. IEEE Trans Ind Electron, 2019, 67: 5081–5091
Lin J, Liu Z, Chen C L P, et al. Three-domain fuzzy wavelet broad learning system for tremor estimation. Knowledge-Based Syst, 2020, 192: 105295
Liu Z, Chen C L P, Feng S, et al. Stacked broad learning system: from incremental flatted structure to deep model. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst, 2020, 51: 209–222
Ye H, Li H, Chen C L P. Adaptive deep cascade broad learning system and its application in image denoising. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2020, 51: 4450–4463
Guo D N, Wu Y H, Shitz S S, et al. Estimation in Gaussian noise: properties of the minimum mean-square error. IEEE Trans Inform Theor, 2011, 57: 2371–2385
Hampel F R, Ronchetti E M, Rousseeuw P J, et al. Robust Statistics: The Approach Based on Influence Functions. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2011
Jin J W, Chen C L P. Regularized robust broad learning system for uncertain data modeling. Neurocomputing, 2018, 322: 58–69
Zheng Y, Chen B, Wang S, et al. Broad learning system based on maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2020, 32: 3083–3097
He R, Zheng W-S, Hu B-G. Maximum correntropy criterion for robust face recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2010, 33: 1561–1576
Chen B, Dang L, Gu Y, et al. Minimum error entropy Kalman filter. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst, 2019, 51: 5819–5829
Principe J C. Information Theoretic Learning: Renyi’s Entropy and Kernel Perspectives. Berlin: Springer, 2010
de Sá J P M, Silva L M A, Santos J M F, et al. Minimum Error Entropy Classification. Berlin: Springer, 2013
Jiang J, He Y L, Dai D X, et al. A new kernel density estimator based on the minimum entropy of data set. Inf Sci, 2019, 491: 223–231
Peng S, Ser W, Chen B, et al. Robust constrained adaptive filtering under minimum error entropy criterion. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II, 2018, 65: 1119–1123
Wang Y, Tang Y Y, Li L. Minimum error entropy based sparse representation for robust subspace clustering. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2015, 63: 4010–4021
Lu L, Zhao H, Chen C. A new normalized subband adaptive filter under minimum error entropy criterion. Signal Image Video Process, 2016, 10: 1097–1103
Wang G, Chen B, Yang X, et al. Numerically stable minimum error entropy Kalman filter. Signal Process, 2021, 181: 107914
Chen B, Xing L, Zheng N, et al. Quantized minimum error entropy criterion. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2018, 30: 1370–1380
Silverman B W. Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis. New York: Routledge, 2018
Parzen E. On estimation of a probability density function and mode. Ann Math Statist, 1962, 33: 1065–1076
Chen B, Xing L, Xu B, et al. Insights into the robustness of minimum error entropy estimation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2016, 29: 731–737
Agarwal R P, Meehan M, O’regan D. Fixed Point Theory and Applications. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001
Heravi A R, Hodtani G A. A new robust fixed-point algorithm and its convergence analysis. J Fixed Point Theor Appl, 2017, 19: 3191–3215
Xie Y, Li Y, Gu Y, et al. Fixed-point minimum error entropy with fiducial points. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2020, 68: 3824–3833
Blake C. UCI repository of machine learning databases. 1998. http://www.ics.uci.edu/mlearn/MLRepository.html
Shi X. Effect of water-cement ratio on setting time of cement paste (in Chinese). Sichuan Cem, 2018, 7: 8
Baseri H, Rabiee S M, Moztarzadeh F, et al. Mechanical strength and setting times estimation of hydroxyapatite cement by using neural network. Mater Des (1980-2015), 2010, 31: 2585–2591
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2019YFB1703600), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 62006079, 61751202, U1813203, U1801262), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2020TQ0105), Science and Technology Major Project of Guangzhou (Grant No. 202007030006), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2021A1515011998), Program for Guangdong Introducing Innovative and Enterpreneurial Teams (Grant No. 2019ZT08X214), and Science and Technology Project of Guangzhou (Grant No. 202102020634).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Liu, Z. & Chen, C.L.P. Broad learning system based on the quantized minimum error entropy criterion. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 65, 222203 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-022-3560-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-022-3560-8