Abstract
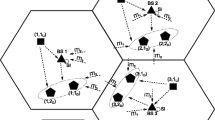
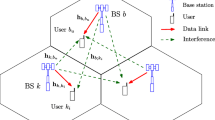
This paper studies the energy efficiency (EE) oriented precoding design in multi-cell massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, with only statistical channel state information (CSI) at the transmitter. During the transmission, as the channel varies dynamically with time and the previously obtained CSI becomes outdated, the base stations must adjust their transmit policies accordingly. To tackle this issue, we propose an online EE maximization algorithm that can achieve a no-regret transmission; i.e., the performance of this online method gradually approaches that of the fixed offline method which has full knowledge of the future CSI. Specifically, we first construct the online EE optimization problem in a distributed way to reduce the information required to be exchanged between cells. Then, we apply the large-dimensional random matrix theory to lower the calculation complexity, and the Charnes-Cooper transform to address the nonconvexity of the problem, respectively. The online gradient ascent method is utilized to perform this no-regret power allocation strategy based on all past CSI. We also assess the robustness of the algorithm to estimation error of statistical CSI under some mild conditions which can usually be satisfied in practice. Numerical results demonstrate the no-regret property and the robustness of the proposed online algorithm for energy efficient multi-cell massive MIMO transmission.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qi Q, Chen X, Lei L, et al. Outage-constrained robust design for sustainable B5G cellular Internet of Things. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun, 2019, 18: 5780–5790
You X, Wang C X, Huang J, et al. Towards 6G wireless communication networks: vision, enabling technologies, and new paradigm shifts. Sci China Inf Sci, 2021, 64: 110301
Ngo H Q, Larsson E G, Marzetta T L. Energy and spectral efficiency of very large multiuser MIMO systems. IEEE Trans Commun, 2013, 61: 1436–1449
Marzetta T L. Fundamentals of Massive MIMO. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2016
Bjornson E, Larsson E G, Marzetta T L. Massive MIMO: ten myths and one critical question. IEEE Commun Mag, 2016, 54: 114–123
Zhang J, Bjornson E, Matthaiou M, et al. Prospective multiple antenna technologies for beyond 5G. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun, 2020, 38: 1637–1660
Interdonato G, Karlsson M, Bjornson E, et al. Local partial zero-forcing precoding for cell-free massive MIMO. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun, 2020, 19: 4758–4774
Zappone A, Jorswieck E. Energy efficiency in wireless networks via fractional programming theory. FNT Commun Inf Theor, 2015, 11: 185–396
You L, Xiong J, Yi X, et al. Energy efficiency optimization for downlink massive MIMO with statistical CSIT. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun, 2020, 19: 2684–2698
You L, Xiong J, Zappone A, et al. Spectral efficiency and energy efficiency tradeoff in massive MIMO downlink transmission with statistical CSIT. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2020, 68: 2645–2659
Gesbert D, Hanly S, Huang H, et al. Multi-cell MIMO cooperative networks: a new look at interference. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun, 2010, 28: 1380–1408
Sun C, Gao X, Ding Z. BDMA in multicell massive MIMO communications: power allocation algorithms. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2017, 65: 2962–2974
He S, Huang Y, Jin S, et al. Coordinated beamforming for energy efficient transmission in multicell multiuser systems. IEEE Trans Commun, 2013, 61: 4961–4971
Ng B L, Evans J S, Hanly S V, et al. Distributed downlink beamforming with cooperative base stations. IEEE Trans Inform Theor, 2008, 54: 5491–5499
You L, Huang Y, Zhang D, et al. Energy efficiency optimization for multi-cell massive MIMO: centralized and distributed power allocation algorithms. IEEE Trans Commun, 2021, 69: 5228–5242
Belmega E V, Mertikopoulos P, Negrel R, et al. Online convex optimization and no-regret learning: algorithms, guarantees and applications. 2020. ArXiv:1804.04529
Hannan J. Approximation to Bayes risk in repeated play. In: Proceedings of Contributions to the Theory of Games. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1957. 97–139
Mertikopoulos P, Belmega E V. Learning to be green: robust energy efficiency maximization in dynamic MIMO-OFDM systems. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun, 2016, 34: 743–757
Marcastel A, Belmega E V, Mertikopoulos P, et al. Online power optimization in feedback-limited, dynamic and unpredictable IoT networks. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2019, 67: 2987–3000
You L, Gao X Q, Xia X G, et al. Pilot reuse for massive MIMO transmission over spatially correlated Rayleigh fading channels. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun, 2015, 14: 3352–3366
Barriac G, Madhow U. Space-time precoding for mean and covariance feedback: application to wideband OFDM. IEEE Trans Commun, 2006, 54: 96–107
Barriac G, Madhow U. Space-time communication for OFDM with implicit channel feedback. IEEE Trans Inform Theor, 2004, 50: 3111–3129
Chen Y, Wang Y, Jiao L. Robust transmission for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided millimeter wave vehicular communications with statistical CSI. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun, 2022, 21: 928–944
Yu X, Guo J, Li X, et al. Deep learning based user scheduling for massive MIMO downlink system. Sci China Inf Sci, 2021, 64: 182304
Weichselberger W, Herdin M, Ozcelik H, et al. A stochastic MIMO channel model with joint correlation of both link ends. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun, 2006, 5: 90–100
Wen C K, Jin S, Wong K K. On the sum-rate of multiuser MIMO uplink channels with jointly-correlated Rician fading. IEEE Trans Commun, 2011, 59: 2883–2895
Wu Y, Wen C K, Xiao C, et al. Linear precoding for the MIMO multiple access channel with finite alphabet inputs and statistical CSI. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun, 2015, 14: 983–997
Gao X Q, Jiang B, Li X, et al. Statistical eigenmode transmission over jointly correlated MIMO channels. IEEE Trans Inform Theor, 2009, 55: 3735–3750
Adhikary A, Nam J, Ahn J Y, et al. Joint spatial division and multiplexing-the large-scale array regime. IEEE Trans Inform Theor, 2013, 59: 6441–6463
Hassibi B, Hochwald B M. How much training is needed in multiple-antenna wireless links? IEEE Trans Inform Theor, 2003, 49: 951–963
Lu A A, Gao X, Zhong W, et al. Robust transmission for massive MIMO downlink with imperfect CSI. IEEE Trans Commun, 2019, 67: 5362–5376
Wu W, Gao X, Wu Y, et al. Beam domain secure transmission for massive MIMO communications. IEEE Trans Veh Technol, 2018, 67: 7113–7127
Sun C, Gao X, Jin S, et al. Beam division multiple access transmission for massive MIMO communications. IEEE Trans Commun, 2015, 63: 2170–2184
Ng D W K, Lo E S, Schober R. Energy-efficient resource allocation in OFDMA systems with large numbers of base station antennas. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun, 2012, 11: 3292–3304
You L, Wang W, Gao X. Energy-efficient multicast precoding for massive MIMO transmission with statistical CSI. Energies, 2018, 11: 3175
Maghsudi S, Stanczak S. Joint channel selection and power control in infrastructureless wireless networks: a multiplayer multiarmed bandit framework. IEEE Trans Veh Technol, 2015, 64: 4565–4578
Shalev-Shwartz S. Online learning and online convex optimization. FNT Machine Learn, 2011, 4: 107–194
Cesa-Bianchi N, Lugosi G. Prediction, Learning, and Games. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006
Hazan E. A survey: the convex optimization approach to regret minimization. In: Proceedings of Optimization for Machine Learning, Cambridge: MIT Press, 2012. 287–304
Lu A A, Gao X, Xiao C. Free deterministic equivalents for the analysis of MIMO multiple access channel. IEEE Trans Inform Theor, 2016, 62: 4604–4629
Couillet R, Debbah M. Random Matrix Methods for Wireless Communications. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2011
Shen K, Yu W. Fractional programming for communication systems-part I: power control and beamforming. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2018, 66: 2616–2630
Boyd S, Vandenberghe L. Convex Optimization. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2004
Charnes A, Cooper W W. Programming with linear fractional functionals. Naval Res Logist, 1962, 9: 181–186
Maculan N, de Paula J G G. A linear-time median-finding algorithm for projecting a vector on the simplex of Rn. Operations Res Lett, 1989, 8: 219–222
Kwon J, Mertikopoulos P. A continuous-time approach to online optimization. 2014. ArXiv:1401.6956
Davie A M, Stothers A J. Improved bound for complexity of matrix multiplication. Proc R Soc Edinburgh-Sect Math, 2013, 143: 351–369
Mertikopoulos P, Moustakas A L. Learning in an uncertain world: MIMO covariance matrix optimization with imperfect feedback. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2016, 64: 5–18
Stojanovic M, Proakis J G, Catipovic J A. Analysis of the impact of channel estimation errors on the performance of a decision-feedback equalizer in fading multipath channels. IEEE Trans Commun, 1995, 43: 877–886
Pascual-Iserte A, Palomar D P, Perez-Neira A I, et al. A robust maximin approach for MIMO communications with imperfect channel state information based on convex optimization. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2006, 54: 346–360
Zhang L, Liang Y-C, Xin Y, et al. Robust cognitive beamforming with partial channel state information. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun, 2009, 8: 4143–4153
Kyösti P, Meinilä J, Hentila L, et al. IST-4-027756 WINNER II D1.1.2 V1.2 WINNER II Channel Models. 2008. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234055761_WINNER_II_channel_models
Dietrich F A, Utschick W. Pilot-assisted channel estimation based on second-order statistics. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2005, 53: 1178–1193
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFB1801103), Jiangsu Province Basic Research Project (Grant No. BK20192002), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61801114), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant 2242021R41148), and Young Elite Scientist Sponsorship Program by China Institute of Communications.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, L., Huang, Y., Zhong, W. et al. Robust online energy efficiency optimization for distributed multi-cell massive MIMO networks. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 66, 132302 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-021-3437-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-021-3437-8