Abstract
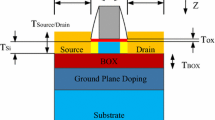
The advancement in the process leads to more concern about the Single Event (SE) sensitivity of the Differential Cascade Voltage Switch Logic (DCVSL) circuits. The simulation results indicate that the Single Event Transient (SET) generated at the DCVSL gate is much larger than that at the ordinary CMOS gate, and their SET variation is different. Based on charge collection, in this paper, the effective collection time theory is proposed to set forth the SET pulse generated at the DCVSL gate. Through 3D TCAD mixed-mode simulation in 65 nm twin-well bulk CMOS process, the effects on SET variation of device parameters such as well contact size and environment parameters such as voltage are investigated.
摘要
创新点
本文基于65nm双阱工艺, 对差分逻辑与普通逻辑单粒子瞬态(SET)响应进行了对照研究。 研究表明受交叉耦合结构的影响, 差分逻辑SET响应与普通逻辑有很大的差异。 为了有效阐释差分逻辑SET随器件因素和环境因素的变化规律, 本文提出了有效收集时间理论。 本文认为晶体管敏感区电荷收集的时间可分为受限收集时间、自由收集时间和残余收集时间; 其中受限收集时间和自由收集时间对SET脉冲宽度其决定性作用。 对于普通逻辑, 粒子入射能量较高时, 受限收集时间支配着SET脉冲宽度; 然而对于差分逻辑, 当脉冲反馈特性较强时, 自由收集时间对SET的贡献接近于受限收集时间。 因而在设计差分逻辑电路时, 有必要适当选择晶体管尺寸, 调节脉冲反馈特性, 从而有效抑制SET。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baze M P, Buchner S P. Attenuation of single event induced pulses in CMOS combinational logic. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 1997, 44: 2217–2223
Cavrois V F, Paillet P, McMorrow D, et al. New insights into single event transient propagation in chains of inverter-sevidence for propagation-induced pulse broadening. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2007, 54: 2338–2346
Bi J S, Liu G, Luo J J, et al. Numerical simulation of single-event-transient effect on ultra-thin-body full-deleted silicon-on-insulator transistor based on 22 nm process node (in Chinese). Acta Phys Sinica, 2013, 62: 208501
Ahlbin J R, Massengill L W, Bhuva B L, et al. Single-event transient pulse quenching in advanced CMOS logic circuits. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2009, 56: 3050–3056
Huang P, Chen S, Chen J, et al. Novel N-hit single event transient technique via open guard transistor in 65 nm bulk CMOS process. Sci China Tech Sci, 2013, 56: 271–279
Huang P, Chen S, Liang Z, et al. Mirror image: newfangled cell-level layout technique for single-event transient mitigation. Chin Sci Bull, 2014, 23: 2850–2858
Huang P, Chen S, Chen J, et al. Single event pulse broadening after narrowing effect in nano CMOS logic circuit. IEEE Trans Dev Mat Rel, 2014, 14: 849–856
Heller L, Griffin W. Cascode voltage switch logic: a differential CMOS logic family. In: Proceeding of IEEE International Solid State Circuits Conference. New York: IEEE, 1984. 16–17
Casey M C, Bhuva B L, Black J D, et al. HBD ssing cascode-voltage switch logic gates for SET tolerant digital designs. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2005, 52: 2510–1515
Hatano H. Single event effects on static and clocked cascade voltage switch logic (CVSL) circuits. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2009, 56: 1987–1991
Amusan O A, Massengill L W, Baze M P, et al. Mitigation techniques for single-event-induced charge sharing in a 90-nm bulk CMOS process. IEEE Trans Dev Mat Rel, 2009, 9: 311–317
Gasiot G, Giot D, Roche P. Multiple cell upsets as the key contribution to the total SER of 65 nm CMOS SRAMs and its dependence on well engineering. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2007, 54: 2468–2473
Selahattim S. Single-event soft errors in CMOS logic. IEEE Potentials, 2012, 31: 15–22
Karnik T, Hazucha P, Patel J. Characterization of soft errors caused by single event upsets in CMOS processes. IEEE Trans Dep Sec Com, 2004, 1: 128–143
Chen J J, Chen S M, He Y B, et al. Novel layout technique for single-event transient mitigation ssing dummy transistor. IEEE Trans Dev Mat Rel, 2013, 13: 177–184
Chen J J, Chen S M, He Y B, et al. Novel layout technique for N-hit single-event transient mitigation via source-extention. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2012, 59: 2859–2866
Buchner S P, Baze M P. Single-event transients in fast electronic circuits. In: Proceedings of IEEE Nuclear and Space Radiation Effects Conference Short Course, Vancouer, 2001. 1–105
Narasimham B, Bhuva B L, Massengill L W, et al. Scaling trends in SET pulse widths in sub-100 nm bulk CMOS processes. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2010, 57: 3336–3341
Gaspard N, Witulski A F, Atkinson N M, et al. Impact of well structure on single-event well potential modulation in bulk CMOS. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2012, 58: 2614–2620
Chen S M, Liang B, Liu B W, et al. Temperature dependence of digital SET pulse width in bulk and SOI technologies. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2008, 55: 2914–2920
Gadlage M J, Ahlbin J R, Ramachandran V, et al. Temperature dependence of digital single-event transients in bulk and fully-depleted SOI technologies. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2009, 56: 3115–3121
Jacoboni C, Canali C, Ottaviani G, et al. A review of some charge transport properties of silicon. Solid-State Electron, 1997, 20: 77
Hazucha P, Karnik T, Maiz J, et al. Neutron soft error rate measurements in a 90-nm CMOS process and scaling trends in SRAM from 0.25-mm to 90-nm generation. In: Proceedings of International Electron Devices Meeting Technical Digest, Washington, 2003. 21.5.1–21.5.4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, P., Chen, S., Chen, J. et al. Simulation study of N-hit SET variation in differential cascade voltage switch logical circuits. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 58, 1–9 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-014-5210-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-014-5210-9
Keywords
- differential cascade voltage switch logic (DCVSL)
- single event transient (SET)
- effective collection time
- pulse feedback feature (PFF)
- across-coupled structure