Abstract
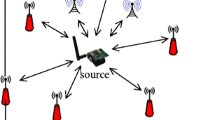
A novel distributed localization method based on the Doppler effect for wireless sensor networks is proposed in this paper, which only relies on radio transceivers without the need of other auxiliary measurement equipments. Based on radio interference, each sensor node can obtain a multi-group of distance variations from itself to a mobile anchor through the measurement of the cumulative phase variations caused by Doppler effect, by which its position can be determined. The proposed method has the following advantages: the sensor node conducts localization in a completely distributed manner without information exchange or centralized processing, and the measurement result equals the actual distance without modulus operation, which is in reality measuring the distance with a ruler of radio wavelength, and will significantly reduce the system complexity and achieve high location accuracy. Analysis and simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz I F, Su W, Sankarasubramaniam Y, et al. Wireless sensor networks: a survey. Comput Netw, 2002, 38: 393–422
Mao G, Fidan B, Anderson B. Wireless sensor network localization techniques. Comput Netw, 2007, 51: 2529–2553
Bahl P, Padmanabhan V N. RADAR: An in-building RF-based user location and tracking sytem. In: Proc of INFOCOM, Israel: IEEE, 2000. 775–784
Priyantha N B, Chakraborty A, Balakrishnan H. The cricket location-support sytem. In: Proc of MobiCom, Boston: ACM, 2000. 32–43
Bulusu N, Heidemann J, Estrin D. GPS-less low cost outdoor localization for very small devices. IEEE Personal Commu, 2000, 7: 28–34
Niculescu D, Nath B. Ad Hoc positioning system (APS). In: Proc of IEEE GLOBECOM, San Antonio: IEEE, 2001. 2926–2931
He T, Huang C, Blum B M, et al. Range-free localization schemes for large scale sensor networks. In: Proc of MobiCom, San Diego: ACM, 2003. 81–95
Maroti M, Kusy B, Balogh G, et al. Radio interferometric geolocation. In: Proc of ACM SenSys, San Diego: ACM, 2005. 1–12
Smith J O, Abel J S. Closed-form least squares source location estimation from range-difference measurements. IEEE Trans ASSP, 1987, 35: 1661–1669
Chan Y T, Ho K C. A simple and efficient estimator for hyperbolic location. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 1994, 42: 1905–1915
Kusy B, Sallai J. Analytical solution for radio-interferometric localization of mobile sensors. Technical Report, ISIS-06-710, 2006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Yin, Q., Han, W. et al. Radio interferometric localization of WSNs based on Doppler effect. Sci. China Ser. F-Inf. Sci. 53, 158–167 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-010-0004-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-010-0004-1