Abstract
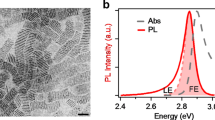
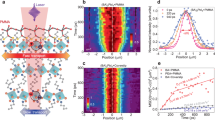
As one of the emerging two-dimensional lead halide materials, lead iodide (PbI2) nanosheets have proven to possess strong application potential in the fields of high-energy radiation detection and highly efficient perovskite solar cells. However, the underlying photophysical properties such as hot-exciton-related carrier dynamics remain unclear for PbI2 nanosheets. Here, we report the exciton dynamics of a single PbI2 nanoflake prepared by an aqueous solution method. Through a three-dimensional (3D) diffusion model, we obtain the exciton annihilation radius and diffusion coefficient of a single PbI2 nanoflake under non-resonant and resonant excitation conditions of band-edge exciton state. As initial exciton densities increase, we find the carrier recombination mechanism for a single PbI2 nanoflake gradually changes from exciton-exciton annihilation to free-carrier recombination. Finally, we reveal the room-temperature circular polarization of a single PbI2 nanoflake is due to free-carrier recombination with a band-edge exciton dissociation time of ~120 fs under the resonant excitation condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plekhanov V G. Lead halides: Electronic properties and applications. Prog Mater Sci, 2004, 49: 787–886
Lin D Y, Guo B C, Dai Z Y, et al. PbI2 single crystal growth and its optical property study. Crystals, 2019, 9: 589
Zhu X H, Wei Z R, Jin Y R, et al. Growth and characterization of a PbI2 single crystal used for gamma ray detectors. Cryst Res Technol, 2007, 42: 456–459
Sun H, Liu Y, Gao X, et al. Bendable 3D-structure X-ray photo-detectors based on pure PbI2 single crystal. Semicond Sci Technol, 2021, 36: 035022
Hassan M, Matuchova M, Zdansky K. Performance of lead iodide nuclear radiation detectors with the introduction of rare earth elements. Open Phys, 2006, 4: 117–123
Fang H H, Yang J, Adjokatse S, et al. Band-edge exciton fine structure and exciton recombination dynamics in single crystals of layered hybrid perovskites. Adv Funct Mater, 2020, 30: 1907979
Kahmann S, Duim H, Fang H H, et al. Photophysics of two-dimensional perovskites: Learning from metal halide substitution. Adv Funct Mater, 2021, 31: 2103778
Wei H, Huang J. Halide lead perovskites for ionizing radiation detection. Nat Commun, 2019, 10: 1066
Li H, He Y, Li W, et al. Perovskite dimensional evolution through cations engineering to tailor the detection limit in hard X-ray response. Small, 2022, 18: 2203884
Zheng W, Zhang Z, Lin R, et al. High-crystalline 2D layered PbI2 with ultrasmooth surface: Liquid-phase synthesis and application of high-speed photon detection. Adv Electron Mater, 2016, 2: 1600291
Tan M, Hu C, Lan Y, et al. 2D lead dihalides for high-performance ultraviolet photodetectors and their detection mechanism investigation. Small, 2017, 13: 1702024
Beckmann P A. A review of polytypism in lead iodide. Cryst Res Technol, 2010, 45: 455–460
Matsui T, Yamamoto T, Nishihara T, et al. Compositional engineering for thermally stable, highly efficient perovskite solar cells exceeding 20% power conversion efficiency with 85°C/85% 1000 h stability. Adv Mater, 2019, 31: 1806823
Yang W S, Noh J H, Jeon N J, et al. High-performance photovoltaic perovskite layers fabricated through intramolecular exchange. Science, 2015, 348: 1234–1237
Jung M, Shin T J, Seo J, et al. Structural features and their functions in surfactant-armoured methylammonium lead iodide perovskites for highly efficient and stable solar cells. Energy Environ Sci, 2018, 11: 2188–2197
Wu C G, Chiang C H, Tseng Z L, et al. High efficiency stable inverted perovskite solar cells without current hysteresis. Energy Environ Sci, 2015, 8: 2725–2733
Roldán-Carmona C, Gratia P, Zimmermann I, et al. High efficiency methylammonium lead triiodide perovskite solar cells: The relevance of non-stoichiometric precursors. Energy Environ Sci, 2015, 8: 3550–3556
Barrit D, Sheikh A D, Munir R, et al. Hybrid perovskite solar cells: In situ investigation of solution-processed PbI2 reveals metastable precursors and a pathway to producing porous thin films. J Mater Res, 2017, 32: 1899–1907
Tong G, Son D Y, Ono L K, et al. Removal of residual compositions by powder engineering for high efficiency formamidinium-based perovskite solar cells with operation lifetime over 2000 h. Nano Energy, 2021, 87: 106152
Zhang Z Y, Chen X, Wang H Y, et al. Elucidating the band structure and free charge carrier dynamics of pure and impurities doped CH3NH3PbI3−xClx perovskite thin films. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2015, 17: 30084–30089
Park B, Kedem N, Kulbak M, et al. Understanding how excess lead iodide precursor improves halide perovskite solar cell performance. Nat Commun, 2018, 9: 3301
Zheng W, Zheng B, Jiang Y, et al. Probing and manipulating carrier interlayer diffusion in van der Waals multilayer by constructing type-I heterostructure. Nano Lett, 2019, 19: 7217–7225
Zhang D, Liu Y, He M, et al. Room temperature near unity spin polarization in 2D van der Waals heterostructures. Nat Commun, 2020, 11: 4442
Liu X, Ha S T, Zhang Q, et al. Whispering gallery mode lasing from hexagonal shaped layered lead iodide crystals. ACS Nano, 2015, 9: 687–695
Wang L, Wu C F, Wang H Y, et al. Internal structure-mediated ultrafast energy transfer in self-assembled polymer-blend dots. Nanoscale, 2013, 5: 7265–7270
Sun Y, Zhou Z, Huang Z, et al. Band structure engineering of interfacial semiconductors based on atomically thin lead iodide crystals. Adv Mater, 2019, 31: 1806562
Wang R, Li S, Wang P, et al. PbI2 nanosheets for photodetectors via the facile cooling thermal supersaturation solution method. J Phys Chem C, 2019, 123: 9609–9616
Zhao L Y, Wang H, Wang H Y, et al. Ultrafast modulation of valley dynamics in multiple WS2-Ag gratings strong coupling system. PhotoniX, 2022, 3: 5
Yue Y Y, Wang H Y, Wang L, et al. Direct observation of room-temperature intravalley coherent coupling processes in monolayer MoS2. Laser Photonics Rev, 2021, 16: 2100343
Zheng S W, Wang L, Wang H Y, et al. Observation of quantum-confined exciton states in monolayer WS2 quantum dots by ultrafast spectroscopy. Nanoscale, 2021, 13: 17093–17100
Wang L, Wang Z, Wang H Y, et al. Slow cooling and efficient extraction of C-exciton hot carriers in MoS2 monolayer. Nat Commun, 2017, 8: 13906
Wang L, Li Q, Wang H Y, et al. Ultrafast optical spectroscopy of surface-modified silicon quantum dots: Unraveling the underlying mechanism of the ultrabright and color-tunable photoluminescence. Light Sci Appl, 2015, 4: e245
Qi P, Luo Y, Shi B, et al. Phonon scattering and exciton localization: Molding exciton flux in two dimensional disorder energy landscape. eLight, 2021, 1: 6
Shen C, Wang G. Excitonic effects on layer- and strain-dependent optoelectronic properties of PbI2. Appl Surf Sci, 2019, 470: 143–149
Sim S, Park J, Song J G, et al. Exciton dynamics in atomically thin MoS2: Interexcitonic interaction and broadening kinetics. Phys Rev B, 2013, 88: 075434
Zhao W, Su R, Huang Y, et al. Transient circular dichroism and exciton spin dynamics in all-inorganic halide perovskites. Nat Commun, 2020, 11: 5665
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 62175088, 61927814, 21773087, 21603083 & 21903035) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2016M590259).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, C., Wang, L., Cui, L. et al. Hot-exciton effects on exciton diffusion and circular polarization dynamics in a single PbI2 nanoflake. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 67, 83–90 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-022-2249-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-022-2249-1