Abstract
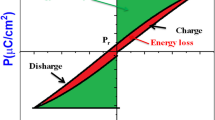
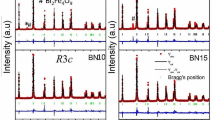
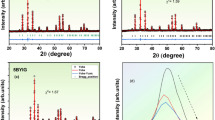
In this work, we have studied a new lead-free ceramic of (1−y)Bi1−x Nd x FeO3-y BiScO3 (0.05≤x≤0.15 and 0.05≤y≤0.15) prepared by a conventional solid-state method, and the influences of Nd and Sc content on their phase structure and electrical properties were investigated in detail. The ceramics with 0.05≤x≤0.10 and 0.05≤y≤0.15 belong to an R3c phase, and the rhombohedral-like and orthorhombic multiphase coexistence is established in the composition range of 0.125≤x≤0.15 and y=0. The electrical properties of the ceramics can be enhanced by modifying x and y values. The highest piezoelectric coefficient (d 33~51 pC/N) is obtained in the ceramics with x=0.075 and y=0.125, which is superior to that of a pure BiFeO3 ceramic. In addition, a lowest dielectric loss (tan δ~0.095%, f=100 kHz) is shown in the ceramics with x=0.15 and y=0 due to the involvement of low defect concentrations, and the improved thermal stability of piezoelectricity at 20–600°C is possessed in the ceramics. We believe that the ceramics can play a meaningful role in the high-temperature lead-free piezoelectric applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fieebig M, Lottermoser T, Frohlich D, et al. Observation of coupled magnetic and electric domains. Nature, 2002, 419: 818–820
Eerenstein W, Mathur N D, Scott J F. Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature, 2009, 442: 759–765
Fiebig M. Revival of the magnetoelectric effect. J Phys D, 2005, 38: R123
Tabares-Munoz C, Rivera J P, Monnier A, et al. Measurement of the quadratic magnetoelectric effect on single crystalline BiFeO3. Jpn J Appl Phys, 1985, 24: 1051–1053
Sahu J R, Rao C N R. Beneficial modification of the properties of multiferroic BiFeO3 by cation substitution. Solid State Sci, 2007, 9: 950–954
Khomchenko V A, Kiselev D A, SeleZneva E K, et al. Weak ferromagnetism in diamagnetically-doped Bi1–x AxFeO3 (A=Ca, Sr, Pn, Ba) multiferroics. Mater Lett, 2008, 62, 1927–1929
Uniyal P, Yadav K L. Study of dielectric, magnetic and ferroelectric properties in Bi1-x GdxFeO3. Mater Lett, 2008, 62: 2858–2861
Moreau J M, Michel C, Gerson R, et al. Ferroelectric BiFeO3 X-ray and neutron study. J Phys Chem Solid, 1971, 32: 1315–1320
Catalan G, Sott J F. Physics and applications of bismuth ferrite. Adv Mater, 2004, 21: 2463–2485
Wang J, Neaton J B, Zheng H, et al. Epitaxial BiFeO3 multiferroic thin film heterostructures. Science, 2003, 299: 1719–1722
Peng Z H, Chen Q, Wu J G, et al. Dielectric and piezoelectric properties of Sb5+ doped (NaBi)0.38(LiCe)0.05-0.14Bi2Nb2O9 ceramics. J Alloys Compd, 2011, 509: 8483–8486
Takeuchi T, Tani T, Saito Y. Piezoelectric properties of bismuth layer-structured ferroelectric ceramics with a preferred orientation processed by the reactive templated grain growth method. Jpn J Appl Phys, 1999, 38: 5553–5556
Wu J G, Wang J, Xiao D Q, et al. A method to improve electrical properties of BiFeO3 thin films. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2012, 4: 1182–1185
Wu J G, Wang J, Xiao D Q, et al. Migration kinetics of oxygen vacancies in mn-modified BiFeO3 thin films. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2011, 3: 2504–1511
Zheng T, Wu J G. Enhanced piezoelectric activity in high-temperature Bi1–x–ySmxLayFeO3 lead-free ceramics. J Mater Chem C, 2015, 3: 3684–3693
Yu B F, Li M Y, Wang J, et al. Enhanced electrical properties in multiferroic BiFeO3 ceramics co-doped by La3+ and V5+. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2008, 41: 185401
Wang T H, Tu C S, Chen H Y, et al. Magnetoelectric coupling and phase transition in BiFeO3 and (Bi-FeO3)0.95(BaTiO3)0.05 ceramics. J Appl Phys, 2011, 1089: 044101
Zeches R J, Rossell M D, Zhang J X, et al. A strain-driven morphotropic phase boundary in BiFeO3. Science, 2009, 326: 977–980
Kumari S, Ortega N, Kumar A, et al. Dielectric anomalies due to grain boundary conduction in chemically substituted BiFeO3. J Appl Phys, 2015, 117: 114102
Pandit P, Satapathy S, Gupta P K, et al. Effect of coalesce doping of Nd and La on structure, dielectric, and magnetic properties of BiFeO3. J Appl Phys, 2009, 106: 114105
Wu J G, Qian S, Wang J, et al. A giant polarization value of Zn and Mn co-modified bismuth ferrite thin films. Appl Phys Lett, 2013, 102: 052904
Wu J G, Xiao D Q, Zhu J G. Effect of (Bi, La)(Fe, Zn)O3 thickness on the microstructure and multiferroic properties of BiFeO3 thin films. J Appl Phys, 2012, 112: 094109
Zhao T, Scholl A, Zavaliche F, et al. Electrical control of antiferromagnetic domains in multiferroic BiFeO3 films at room temperature. Nat Mater, 2008, 7: 478–482
Qi H Y, Qi Y J, Xiao M. Leakage mechanisms in rare-earth (La, Nd) doped Bi4Ti3O12 ferroelectric ceramics. J Mater Sci Mater Electron, 2014, 25: 1325–1330
Sati P C, Kumar M, Chhoker S, et al. Influence of Eu substitution on structural, magnetic, optical and dielectric properties of BiFeO3 multiferroic ceramics. Ceram Int, 2015, 41: 2389–2398
Sharma P, Varshney D, Satapathy S, et al. Effect of Pr substitution on structural and electrical properties of BiFeO3 ceramics. Mater Chem Phys, 2014, 143: 629–236
Godara P, Agarwal A, Ahlawat N, et al. Crystal structure refinement, dielectric nd magnetic properties of Sm modified BiFeO3 multiferroic. J Mol Struct, 2015, 1097: 207–213
Wang C A, Pang H Z, Zhang A H, et al. Enhanced ferroelectric polarization and magnetization in BiFe1–x ScxO3 ceramics. Mater Res Bull, 2015, 70: 595–599
Chaudhari Y, Mahajan C M, Singh A, et al. Multiferroic properties of nanocrystalline BiFe1–x NixO3 (x=0.0–0.15) perovskite ceramics. J Magn Magn Mater, 2015, 395: 329–335
Pattanayak S, Choudhary R N P. Systhesis, electrical and magnetic characteristics of Nd-modified BiFeO3. Ceram Int, 2015, 41: 9403–9410
Rao T D, Asthana S, Niranjan M K. Observation of coexistence of ferroelectric and antiferroelectric phases in Sc substitution BiFeO3. J Alloys Compd, 2015, 642: 192–199
Hernandez N, Gonzalez-Gonzalez V A, Dzul-Bautista B I, et al. Nd and Sc co-doped BiFeO3 nanopowders displaying enhanced ferromagnetism at room temperature. J. Alloys Compd, 2015, 638: 282–288
Lv J, Wu J G. Enhanced electrical properties of quenched (1–x)Bi1y SmyFeO3–x BiScO3 lead-free ceramics. J Phys Chem C, 2015, 119: 21105–21115
Singh K, Jang H M, Ryu S, et al. Polarized raman scattering of multiferroic BiFeO3 epitaxial films with rhombohedral R3c symmetry. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 88: 042907
Hermet P, Goffinet M, Kreisel J, et al. Raman and infrared spectra of multiferroic bismuth ferrite from first principles. Phys Rev B Condens Matter Mater Phys, 2007, 75: 220102
Coondoo I, Panwar N, Bdikin I, et al. Structural, morphological and piezoresponse studies of Pr and Sc co-substituted BiFeO3 ceramics. J Phys D Appl Phys, 2012, 45: 055302
Verma V. Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of rare-earth and transition element co-doped bismuth ferrites. J Alloys Compd, 2015, 641: 205–209
Valant M, Axelsson A K, Alford N. Peculiarities of a solidstate synthesis of multiferroic polycrystalline BiFeO3. Chem Mater, 2007, 19: 5431–5436
Sun C, Wang Y P, Yang Y, et al. Multiferroic properties of Bi1–x DyxFeO3 (x=0–0.2) ceramics at various temperatures. Mater Lett, 2012, 72: 160–163
Ke S, Lin P, Zeng X, et al. Tuning of dielectric and ferroelectric properties in single phase BiFeO3 ceramics with controlled Fe2+/Fe3+ ratio. Ceram Int, 2014, 40: 5263–5268
Wu J G, Xiao D Q, Zhu J G. Effect of La and Co-doping on microstructure and electrical properties of BiFeO3 thin films. Chin Sci Bull, 2014, 59: 5205–5211
Hussain A, Xu X J, Yuan G L, et al. The development of BiFeO3-based ceramics. Chin Sci Bull, 2014, 56: 5161–5169
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, H., Wu, J. Composition dependence of phase structure and electrical properties of (1−y)Bi1−x Nd x FeO3−y BiScO3 ceramics. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 59, 1029–1035 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-016-6051-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-016-6051-0