Abstract
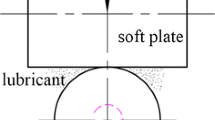
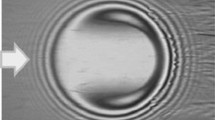
This paper describes a study of point contact elastohydrodynamic (EHD) lubrication behavior at high speeds (up to 20 m s−1). Central film thicknesses were measured by optical interferometry device. The influence of slide-roll ratio and operating temperature on the central film thickness was determined. The influence of thermal effects on the reduction of film thickness was discussed via the analysis of numerical simulation method considering thermal effects. Subsequently, the experimental data was used to amend a set of unified parameters for the thermal corrections for different types of oil at high speeds.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- L :
-
Thermal loading parameter
- E 1,E 2 :
-
Elastic modulus of ball and disc (Pa)
- E′:
-
Reduced modulus (Pa)
- υ 1, υ 2 :
-
Poisson ratio of disc and ball
- R x :
-
Radius of ball (m)
- t :
-
Temperature (K)
- t 0 :
-
Operating temperature (K)
- ρ, ρ 1, ρ 2 :
-
Density of oil, glass disc and steel ball (kg m−3)
- k, k 1, k 2 :
-
Thermal conductivity of oil, glass disc and steel-ball (W m−1 K−1)
- c, c 1, c 2 :
-
Specific heat of oil, glass disc and steel ball (W m−1 K−1)
- η :
-
Dynamic viscosity (Pa s)
- η 0 :
-
Ambient viscosity (Pa s)
- α :
-
Barus viscosity-pressure coefficient (Pa−1)
- S 0 :
-
Roelands viscosity-temperature coefficient (K−1)
- SRR :
-
Slide-roll ratio SRR=2((u 1−u 2)/(u 1−u 2)
- h :
-
Film thickness (nm)
- p :
-
Film pressure (Pa)
- pH :
-
Maximum Herzian pressure (Pa)
- u :
-
Lubricant entrainment speed, u=(u 1 +u 2)/2
- u 1,u 2 :
-
Surface velocities of disc and ball, u 1>u 2 (m s−1)
- w :
-
Load (N)
- x :
-
Coordinate along the entrainment speed (m)
- y :
-
Coordinate perpendicular to the entrainment speed (m)
- z :
-
Coordinate along the film thickness (m)
- H :
-
Dimensionless film thickness, H=hR x /B 2
- P :
-
Dimensionless pressure, P=p/p H
- G :
-
Dimensionless material parameter, G=αE′
- U :
-
Dimensionless velocity parameter, U=η 0 u/E′R x
- W :
-
Dimensionless load parameter, W=w/E′R x 2
- B :
-
Radius of Hertzian contact (m)
- X :
-
Dimensionless coordinate along the entrainment speed, X=x/B
- Y :
-
Dimensionless coordinate perpendicular to the entrainment speed, Y=y/B
References
Cameron A, Gohar R. Theoretical and experimental studies of the oil film in lubricated point contact. P Roy Soc A-Math Phy, 1966, 291: 520–536
Jacobson B O. Rheology and Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication. New York: Elsevier Science, 1991
Johnston G, Wayte R, Spikes H. The measurement and study of very thin lubricant films in concentrated contacts. Tribol Trans, 1991, 34: 187–194
Luo J, Wen S, Huang P. Thin film lubrication. Part I. Study on the transition between EHL and thin film lubrication using a relative optical interference intensity technique. Wear, 1996, 194: 107–115
Hartl M, Krupka I, Poliscuk R, et al. Thin film colorimetric interferometry. Tribol Trans, 2001, 44: 270–276
Hili J, Olver A V, Edwards S, et al. Experimental investigation of elastohydrodynamic (EHD) film thickness behavior at high speeds. Tribol Trans, 2010, 53: 658–666
Gupta P K, Cheng H S, Zhu D, et al. Viscoelastic effects in mil-l-7808-type lubricant, part I: Analytical formulation. Tribol Trans, 1992, 35: 269–274
Crook A W. The lubrication of rollers III. A theoretical discussion of friction and the temperatures in the oil film. P Roy Soc A-Math Phy, 1961, 254: 237–258
Cheng H S. A refined solution to the thermal-elastohydrodynamic lubrication of rolling and sliding cylinders. Tribol Trans, 1965, 8: 397–410
Zhu D, Wen S Z. A full numerical solution for the thermoelastohy-drodynamic problem in elliptical contacts. J Tribol, 1984, 106: 246–254
Kim K H, Sadeghi F. Three-dimensional temperature distribution in ehd lubrication: Part I—circular contact. J Tribol, 1992, 114: 32–41
Qu S, Yang P, Guo F. Theoretical investigation on the dimple occurrence in the thermal EHL of simple sliding steel-glass circular contacts. Tribol Int, 2000, 33: 59–65
Yang P, Qu S, Kaneta M, et al. Formation of steady dimples in point tehl contacts. J Tribol, 2001, 123: 42–49
Yang P, Wen S. A generalized reynolds equation for non-newtonian thermal elastohydrodynamic lubrication. J Tribol, 1990, 112: 631–636
Stachowiak G, Batchelor A W. Engineering Tribology. Burlington: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2011
Ma M. An expedient approach to the non-newtonian thermal EHL in heavily loaded point contacts. Wear, 1997, 206: 100–112
Zhu D, Hu Y. A computer program package for the prediction of EHL and mixed lubrication characteristics, friction, subsurface stresses and flash temperatures based on measured 3D surface roughness. Tribol Trans, 2001, 44: 383–390
Zhu D, Cheng H. An analysis and computational procedure for EHL film thickness, friction and flash temperature in line and point contacts. Tribol Trans, 1989, 32: 364–370
Roelands C J A. Correlational Aspects of the Viscosity-temperature-pressure Relationship of Lubricating Oils. Dissertation for Doctoral Degree. Delft: Technical University of Delft, 1966
Dowson D, Higginson G R, Archard J, et al. Elasto-hydrodynamic Lubrication: The Fundamentals of Roller and Gear Lubrication. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1966
Wen S, Huang P. Principles of Tribology. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2012
Hamrock B J, Dowson D. Isothermal elastohydrodynamic lubrication of point contacts: Part III—fully flooded results. J Lubr Technol, 1977, 99: 264–275
Kaneta M, Shigeta T, Yang P. Film pressure distributions in point contacts predicted by thermal EHL analyses. Tribol Int, 2006, 39: 812–819
Kaneta M, Yang P. Effects of thermal conductivity of contacting surfaces on point EHL contacts. J Tribol, 2003, 125: 731–738
Habchi W, Vergne P, Bair S, et al. Influence of pressure and temperature dependence of thermal properties of a lubricant on the behaviour of circular tehd contacts. Tribol Int, 2010, 43: 1842–1850
Yang P, Liu X. Effects of solid body temperature on the non-newtonian thermal elastohydrodynamic lubrication behaviour in point contacts. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J: J Eng Tribol, 2009, 223: 959–969
Lugt P M, Morales-Espejel G E. A review of elasto-hydrodynamic lubrication theory. Tribol Trans, 2011, 54: 470–496
Yang P, Kaneta M. Effects of the thermal conductivity of contact materials on elastohydrodynamic lubrication characteristics. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C: J Mech Eng Sci, 2010, 224: 2577–2587
Murch L, Wilson W. A thermal elastohydrodynamic inlet zone analysis. J Lubr Technol, 1975, 97: 212–216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, H., Guo, D., Reddyhoff, T. et al. Influence of thermal effects on elastohydrodynamic (EHD) lubrication behavior at high speeds. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 58, 551–558 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5564-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5564-7